帮助眼睛在存在过度绘制的情况下看到模式。 geom_smooth() 和 stat_smooth() 实际上是别名:它们都使用相同的参数。如果要使用非标准几何图形显示结果,请使用stat_smooth()。
用法
geom_smooth(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "smooth",
position = "identity",
...,
method = NULL,
formula = NULL,
se = TRUE,
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_smooth(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "smooth",
position = "identity",
...,
method = NULL,
formula = NULL,
se = TRUE,
n = 80,
span = 0.75,
fullrange = FALSE,
level = 0.95,
method.args = list(),
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)参数
- mapping
-
由
aes()创建的一组美学映射。如果指定且inherit.aes = TRUE(默认),它将与绘图顶层的默认映射组合。如果没有绘图映射,则必须提供mapping。 - data
-
该层要显示的数据。有以下三种选择:
如果默认为
NULL,则数据继承自ggplot()调用中指定的绘图数据。data.frame或其他对象将覆盖绘图数据。所有对象都将被强化以生成 DataFrame 。请参阅fortify()将为其创建变量。将使用单个参数(绘图数据)调用
function。返回值必须是data.frame,并将用作图层数据。可以从formula创建function(例如~ head(.x, 10))。 - position
-
位置调整,可以是命名调整的字符串(例如
"jitter"使用position_jitter),也可以是调用位置调整函数的结果。如果需要更改调整设置,请使用后者。 - ...
-
其他参数传递给
layer()。这些通常是美学,用于将美学设置为固定值,例如colour = "red"或size = 3。它们也可能是配对的 geom/stat 的参数。 - method
-
要使用的平滑方法(函数)接受
NULL或字符向量,例如"lm"、"glm"、"gam"、"loess"或函数,例如MASS::rlm或mgcv::gam、stats::lm或stats::loess。为了向后兼容,"auto"也被接受。它相当于NULL。对于
method = NULL,平滑方法是根据最大组的大小(跨所有面板)选择的。stats::loess()用于少于 1,000 个观测值;否则mgcv::gam()与formula = y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")和method = "REML"一起使用。有趣的是,loess提供了更好的外观,但在内存中是 \(O(N^{2})\),因此不适用于较大的数据集。如果您的观测值少于 1,000 个,但想要使用与
method = NULL相同的gam()模型,则设置method = "gam", formula = y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")。 - formula
-
用于平滑函数的公式,例如
y ~ x、y ~ poly(x, 2)、y ~ log(x)。默认情况下NULL,在这种情况下,当观测值少于 1,000 个时,method = NULL意味着formula = y ~ x,否则formula = y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")。 - se
-
显示平滑周围的置信区间? (默认为
TRUE,参见level进行控制。) - na.rm
-
如果
FALSE,则默认缺失值将被删除并带有警告。如果TRUE,缺失值将被静默删除。 - orientation
-
层的方向。默认值 (
NA) 自动根据美学映射确定方向。万一失败,可以通过将orientation设置为"x"或"y"来显式给出。有关更多详细信息,请参阅方向部分。 - show.legend
-
合乎逻辑的。该层是否应该包含在图例中?
NA(默认值)包括是否映射了任何美学。FALSE从不包含,而TRUE始终包含。它也可以是一个命名的逻辑向量,以精细地选择要显示的美学。 - inherit.aes
-
如果
FALSE,则覆盖默认美学,而不是与它们组合。这对于定义数据和美观的辅助函数最有用,并且不应继承默认绘图规范的行为,例如borders()。 - geom, stat
-
用于覆盖
geom_smooth()和stat_smooth()之间的默认连接。 - n
-
评估更平滑的点数。
- span
-
控制默认 loess 平滑器的平滑量。较小的数字产生较弯曲的线条,较大的数字产生较平滑的线条。仅与黄土一起使用,即当
method = "loess"或method = NULL(默认)且观测值少于 1,000 个时。 - fullrange
-
如果
TRUE,平滑线将扩展到绘图范围,可能超出数据范围。这不会将该行扩展到expansion创建的任何附加填充中。 - level
-
要使用的置信区间水平(默认为 0.95)。
- method.args
-
传递给
method定义的建模函数的附加参数列表。
细节
计算由(当前未记录的)predictdf() 泛型及其方法执行。对于大多数方法,标准误差界限是使用 predict() 方法计算的 - 例外是 loess() ,它使用基于 t 的近似,以及 glm() ,其中正常置信区间是在链接尺度上构造的,然后back-transformed 到响应量表。
方向
该几何体以不同的方式对待每个轴,因此可以有两个方向。通常,方向很容易从给定映射和使用的位置比例类型的组合中推断出来。因此,ggplot2 默认情况下会尝试猜测图层应具有哪个方向。在极少数情况下,方向不明确,猜测可能会失败。在这种情况下,可以直接使用 orientation 参数指定方向,该参数可以是 "x" 或 "y" 。该值给出了几何图形应沿着的轴,"x" 是您期望的几何图形的默认方向。
美学
geom_smooth() 理解以下美学(所需的美学以粗体显示):
-
x -
y -
alpha -
colour -
fill -
group -
linetype -
linewidth -
weight -
ymax -
ymin
在 vignette("ggplot2-specs") 中了解有关设置这些美学的更多信息。
计算变量
这些是由层的 'stat' 部分计算的,可以使用 delayed evaluation 访问。 stat_smooth() 提供以下变量,其中一些取决于方向:
-
after_stat(y)或者after_stat(x)
预测值。 -
after_stat(ymin)或者after_stat(xmin)
均值附近逐点置信区间较低。 -
after_stat(ymax)或者after_stat(xmax)
均值周围逐点置信区间的上限。 -
after_stat(se)
标准误差。
例子
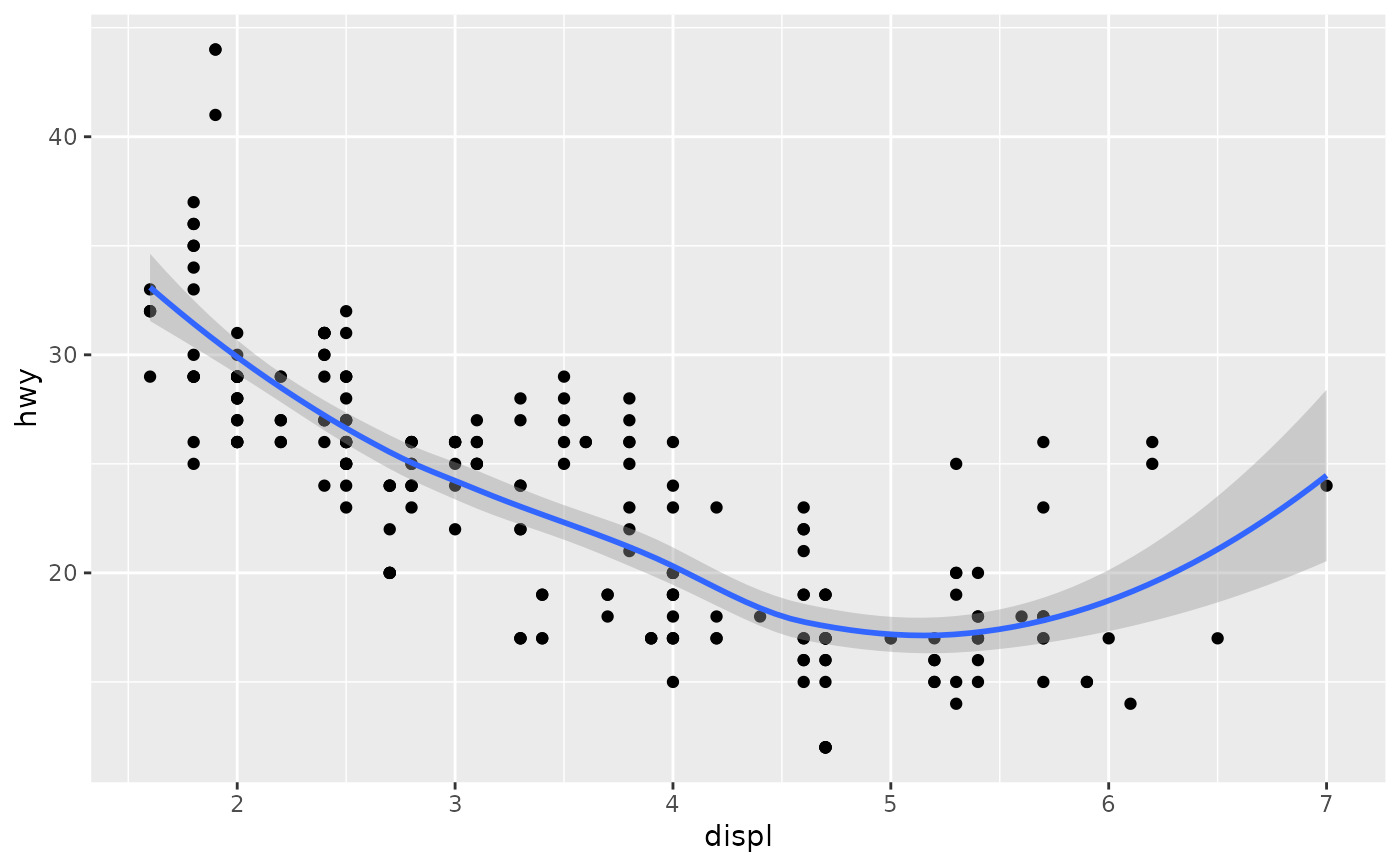
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
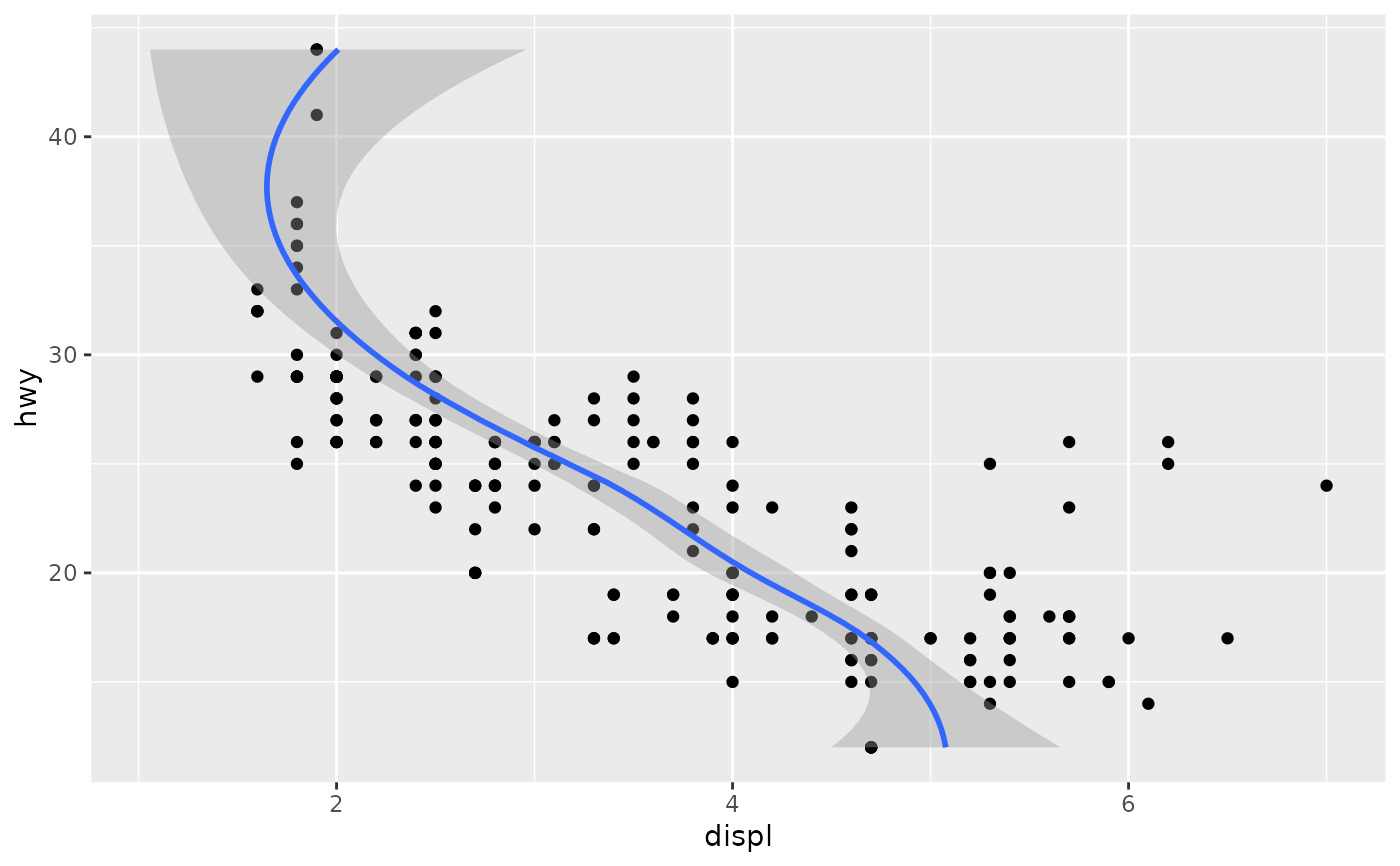
 # If you need the fitting to be done along the y-axis set the orientation
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(orientation = "y")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
# If you need the fitting to be done along the y-axis set the orientation
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(orientation = "y")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
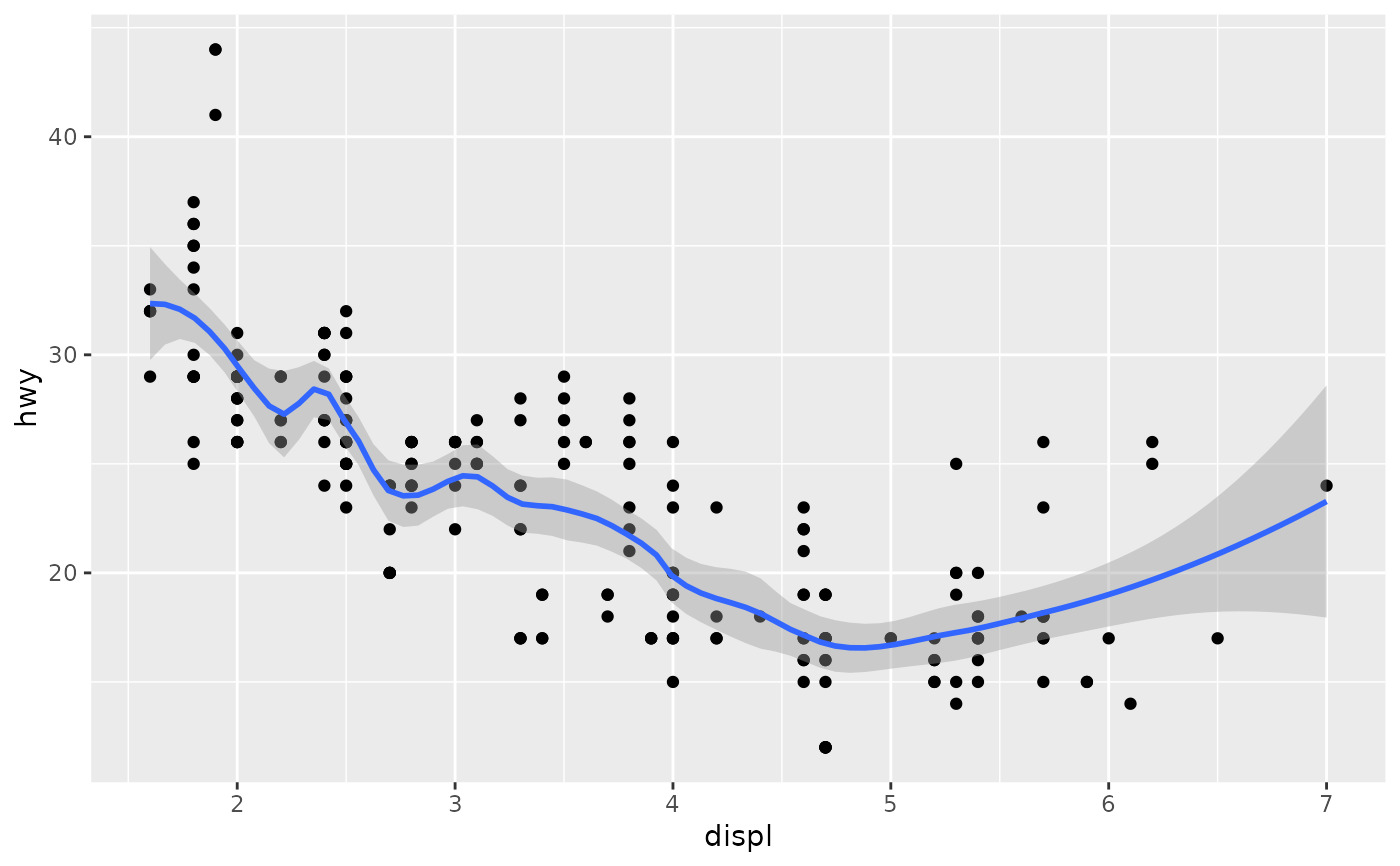
 # Use span to control the "wiggliness" of the default loess smoother.
# The span is the fraction of points used to fit each local regression:
# small numbers make a wigglier curve, larger numbers make a smoother curve.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(span = 0.3)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
# Use span to control the "wiggliness" of the default loess smoother.
# The span is the fraction of points used to fit each local regression:
# small numbers make a wigglier curve, larger numbers make a smoother curve.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(span = 0.3)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
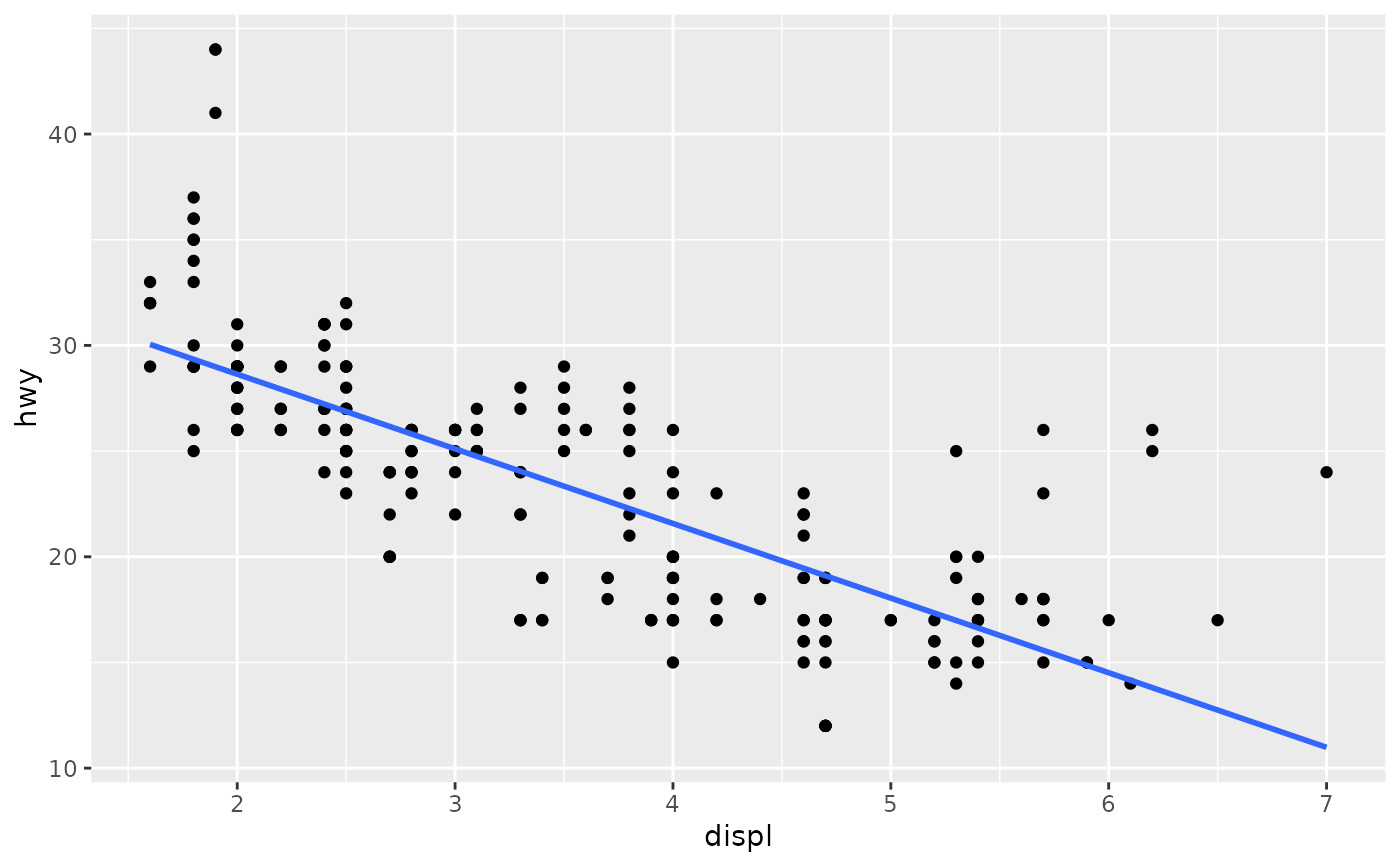
 # Instead of a loess smooth, you can use any other modelling function:
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = lm, se = FALSE)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
# Instead of a loess smooth, you can use any other modelling function:
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = lm, se = FALSE)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
 ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = lm, formula = y ~ splines::bs(x, 3), se = FALSE)
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = lm, formula = y ~ splines::bs(x, 3), se = FALSE)
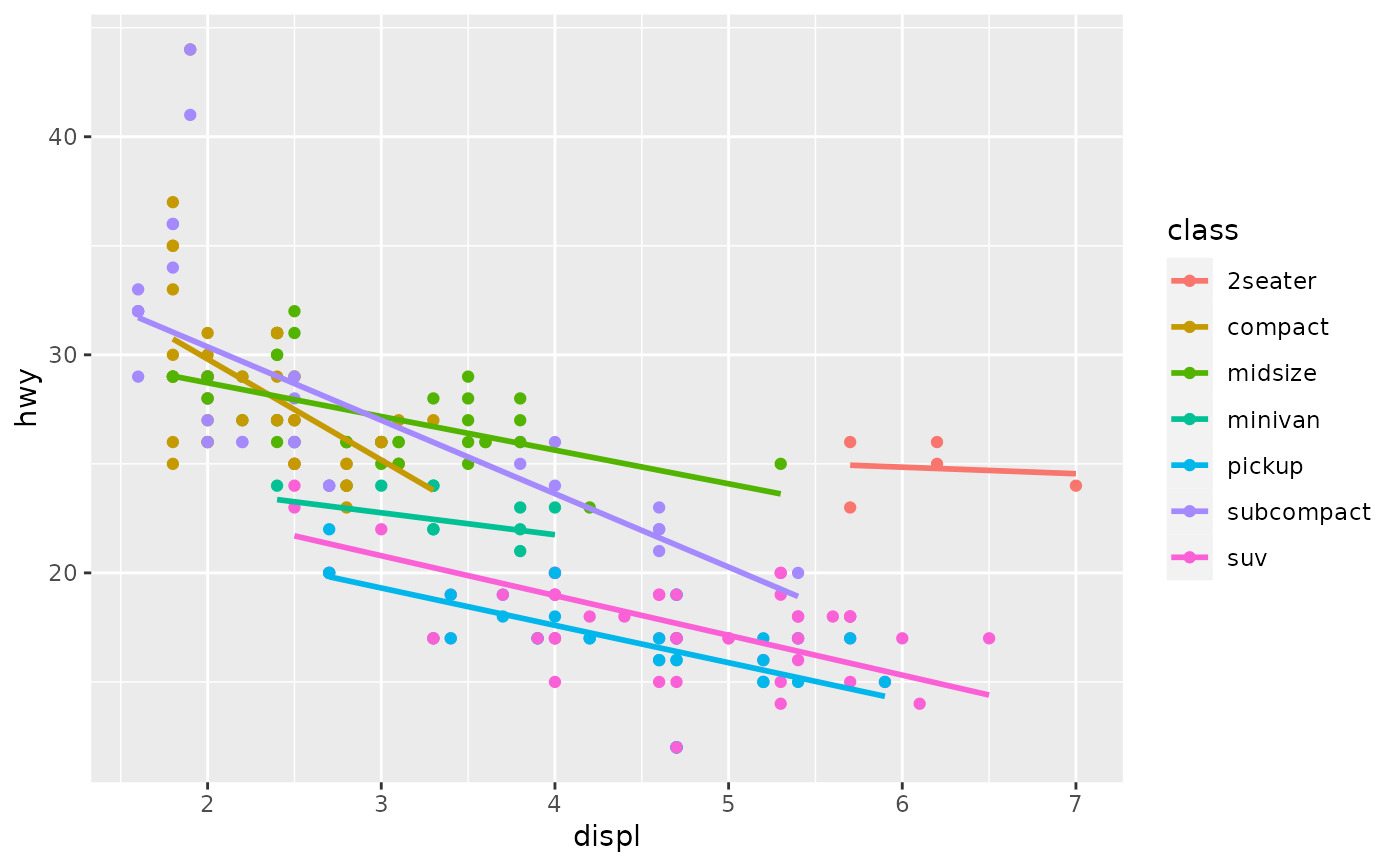
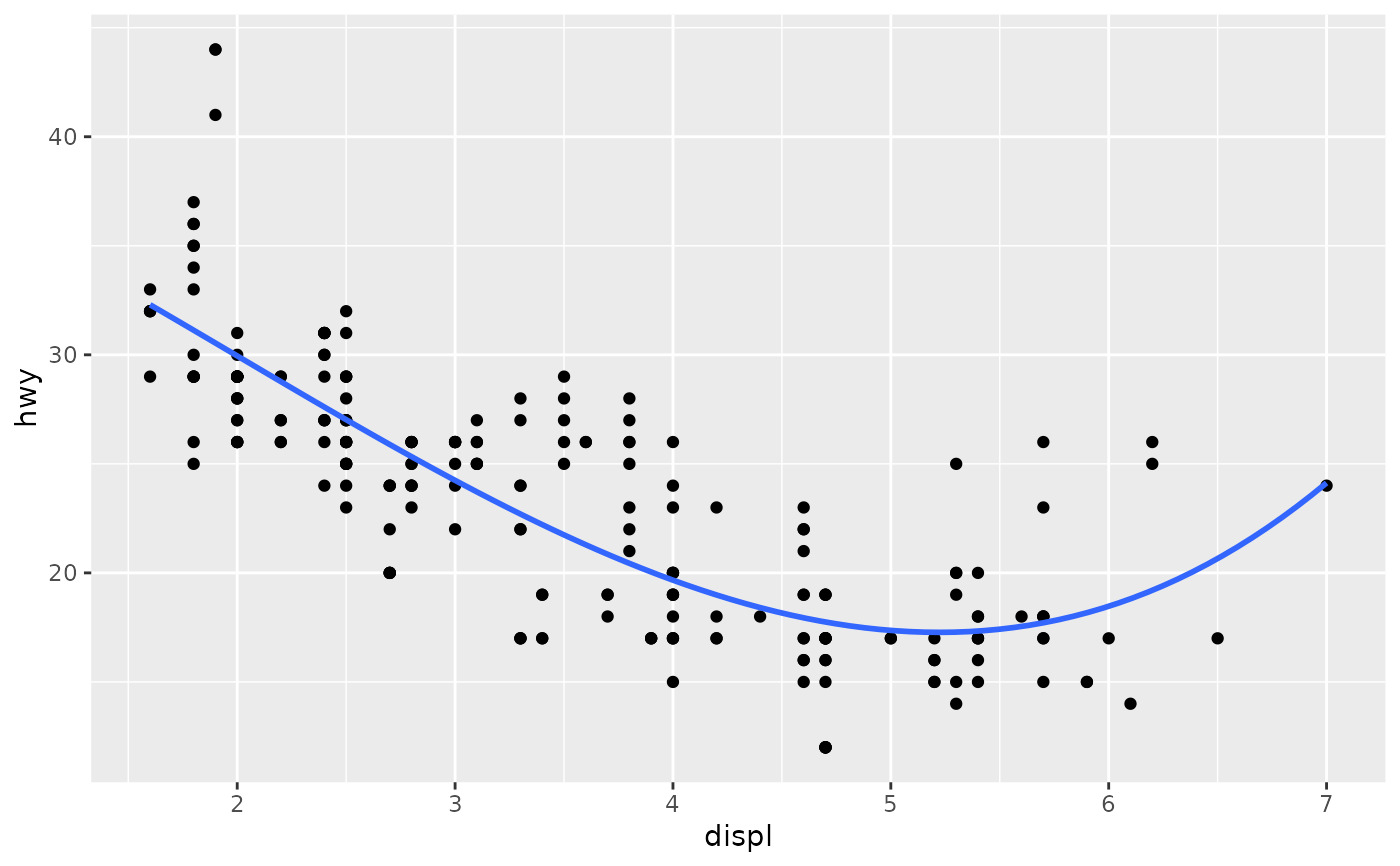 # Smooths are automatically fit to each group (defined by categorical
# aesthetics or the group aesthetic) and for each facet.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy, colour = class)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE, method = lm)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
# Smooths are automatically fit to each group (defined by categorical
# aesthetics or the group aesthetic) and for each facet.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy, colour = class)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE, method = lm)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
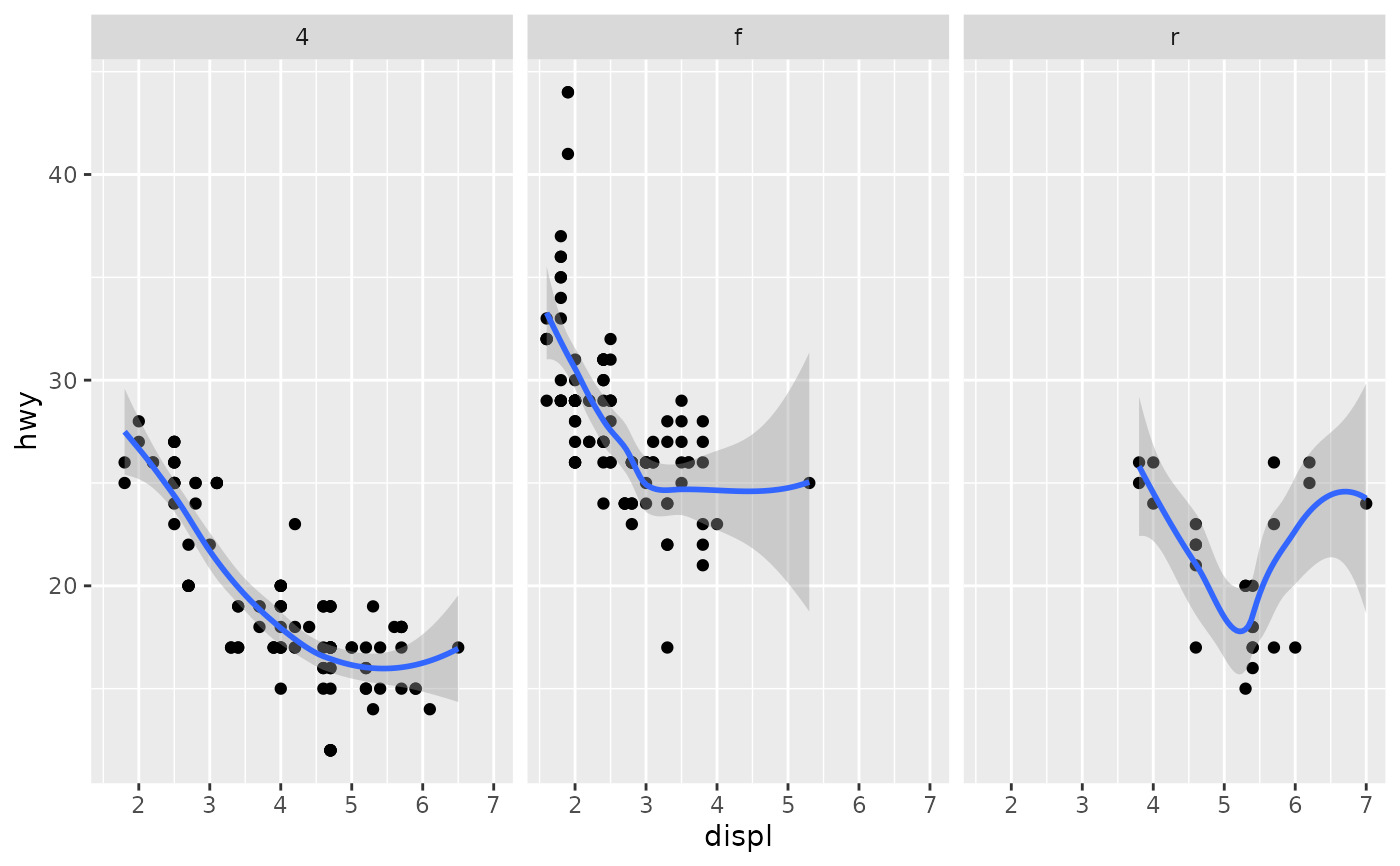
 ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(span = 0.8) +
facet_wrap(~drv)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(span = 0.8) +
facet_wrap(~drv)
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
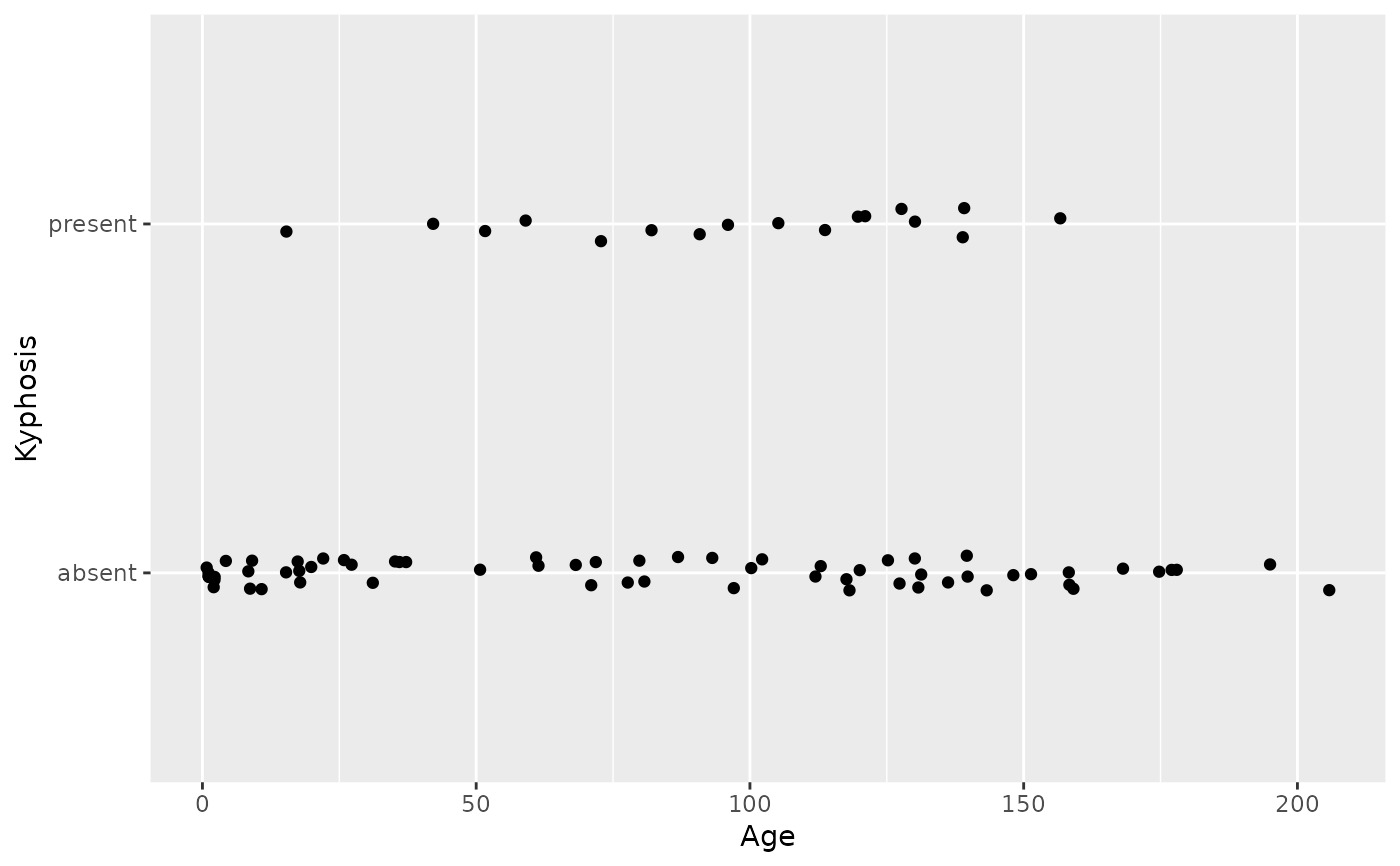
 # \donttest{
binomial_smooth <- function(...) {
geom_smooth(method = "glm", method.args = list(family = "binomial"), ...)
}
# To fit a logistic regression, you need to coerce the values to
# a numeric vector lying between 0 and 1.
ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, Kyphosis)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
#> Warning: Computation failed in `stat_smooth()`
#> Caused by error:
#> ! y values must be 0 <= y <= 1
# \donttest{
binomial_smooth <- function(...) {
geom_smooth(method = "glm", method.args = list(family = "binomial"), ...)
}
# To fit a logistic regression, you need to coerce the values to
# a numeric vector lying between 0 and 1.
ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, Kyphosis)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
#> Warning: Computation failed in `stat_smooth()`
#> Caused by error:
#> ! y values must be 0 <= y <= 1
 ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, as.numeric(Kyphosis) - 1)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, as.numeric(Kyphosis) - 1)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth()
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
 ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, as.numeric(Kyphosis) - 1)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth(formula = y ~ splines::ns(x, 2))
ggplot(rpart::kyphosis, aes(Age, as.numeric(Kyphosis) - 1)) +
geom_jitter(height = 0.05) +
binomial_smooth(formula = y ~ splines::ns(x, 2))
 # But in this case, it's probably better to fit the model yourself
# so you can exercise more control and see whether or not it's a good model.
# }
# But in this case, it's probably better to fit the model yourself
# so you can exercise more control and see whether or not it's a good model.
# }
相关用法
- R ggplot2 geom_spoke 由位置、方向和距离参数化的线段
- R ggplot2 geom_segment 线段和曲线
- R ggplot2 geom_qq 分位数-分位数图
- R ggplot2 geom_quantile 分位数回归
- R ggplot2 geom_text 文本
- R ggplot2 geom_ribbon 函数区和面积图
- R ggplot2 geom_boxplot 盒须图(Tukey 风格)
- R ggplot2 geom_hex 二维箱计数的六边形热图
- R ggplot2 geom_bar 条形图
- R ggplot2 geom_bin_2d 二维 bin 计数热图
- R ggplot2 geom_jitter 抖动点
- R ggplot2 geom_point 积分
- R ggplot2 geom_linerange 垂直间隔:线、横线和误差线
- R ggplot2 geom_blank 什么也不画
- R ggplot2 geom_path 连接观察结果
- R ggplot2 geom_violin 小提琴情节
- R ggplot2 geom_dotplot 点图
- R ggplot2 geom_errorbarh 水平误差线
- R ggplot2 geom_function 将函数绘制为连续曲线
- R ggplot2 geom_polygon 多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_histogram 直方图和频数多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_tile 矩形
- R ggplot2 geom_density_2d 二维密度估计的等值线
- R ggplot2 geom_map 参考Map中的多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_density 平滑密度估计
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Hadley Wickham等大神的英文原创作品 Smoothed conditional means。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
