表示 x 、 ymin 和 ymax 定义的垂直间隔的各种方式。每个案例绘制一个图形对象。
用法
geom_crossbar(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
...,
fatten = 2.5,
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
geom_errorbar(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
geom_linerange(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
geom_pointrange(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
...,
fatten = 4,
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)参数
- mapping
-
由
aes()创建的一组美学映射。如果指定且inherit.aes = TRUE(默认),它将与绘图顶层的默认映射组合。如果没有绘图映射,则必须提供mapping。 - data
-
该层要显示的数据。有以下三种选择:
如果默认为
NULL,则数据继承自ggplot()调用中指定的绘图数据。data.frame或其他对象将覆盖绘图数据。所有对象都将被强化以生成 DataFrame 。请参阅fortify()将为其创建变量。将使用单个参数(绘图数据)调用
function。返回值必须是data.frame,并将用作图层数据。可以从formula创建function(例如~ head(.x, 10))。 - stat
-
用于该层数据的统计变换,可以作为
ggprotoGeom子类,也可以作为命名去掉stat_前缀的统计数据的字符串(例如"count"而不是"stat_count") - position
-
位置调整,可以是命名调整的字符串(例如
"jitter"使用position_jitter),也可以是调用位置调整函数的结果。如果需要更改调整设置,请使用后者。 - ...
-
其他参数传递给
layer()。这些通常是美学,用于将美学设置为固定值,例如colour = "red"或size = 3。它们也可能是配对的 geom/stat 的参数。 - fatten
-
用于增加
geom_crossbar()中的中间条和geom_pointrange()中的中点的大小的乘法因子。 - na.rm
-
如果
FALSE,则默认缺失值将被删除并带有警告。如果TRUE,缺失值将被静默删除。 - orientation
-
层的方向。默认值 (
NA) 自动根据美学映射确定方向。万一失败,可以通过将orientation设置为"x"或"y"来显式给出。有关更多详细信息,请参阅方向部分。 - show.legend
-
合乎逻辑的。该层是否应该包含在图例中?
NA(默认值)包括是否映射了任何美学。FALSE从不包含,而TRUE始终包含。它也可以是一个命名的逻辑向量,以精细地选择要显示的美学。 - inherit.aes
-
如果
FALSE,则覆盖默认美学,而不是与它们组合。这对于定义数据和美观的辅助函数最有用,并且不应继承默认绘图规范的行为,例如borders()。
方向
该几何体以不同的方式对待每个轴,因此可以有两个方向。通常,方向很容易从给定映射和使用的位置比例类型的组合中推断出来。因此,ggplot2 默认情况下会尝试猜测图层应具有哪个方向。在极少数情况下,方向不明确,猜测可能会失败。在这种情况下,可以直接使用 orientation 参数指定方向,该参数可以是 "x" 或 "y" 。该值给出了几何图形应沿着的轴,"x" 是您期望的几何图形的默认方向。
美学
geom_linerange() 理解以下美学(所需的美学以粗体显示):
-
x或者y -
ymin或者xmin -
ymax或者xmax -
alpha -
colour -
group -
linetype -
linewidth
请注意,geom_pointrange() 也可以理解size 的点大小。
在 vignette("ggplot2-specs") 中了解有关设置这些美学的更多信息。
也可以看看
stat_summary() 用于这些家伙的使用示例,geom_smooth() 用于连续模拟,geom_errorbarh() 用于水平误差条。
例子
# Create a simple example dataset
df <- data.frame(
trt = factor(c(1, 1, 2, 2)),
resp = c(1, 5, 3, 4),
group = factor(c(1, 2, 1, 2)),
upper = c(1.1, 5.3, 3.3, 4.2),
lower = c(0.8, 4.6, 2.4, 3.6)
)
p <- ggplot(df, aes(trt, resp, colour = group))
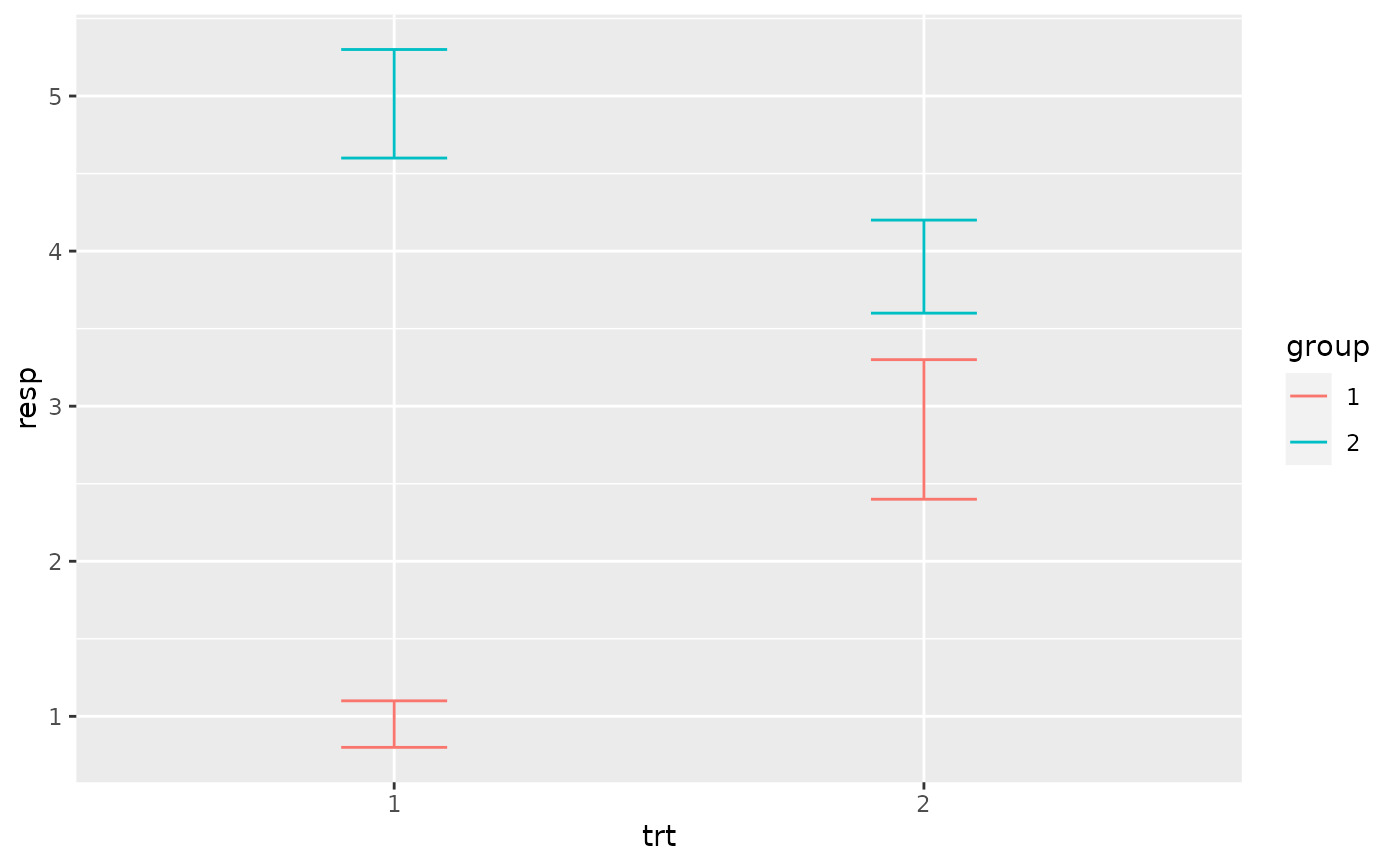
p + geom_linerange(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper))
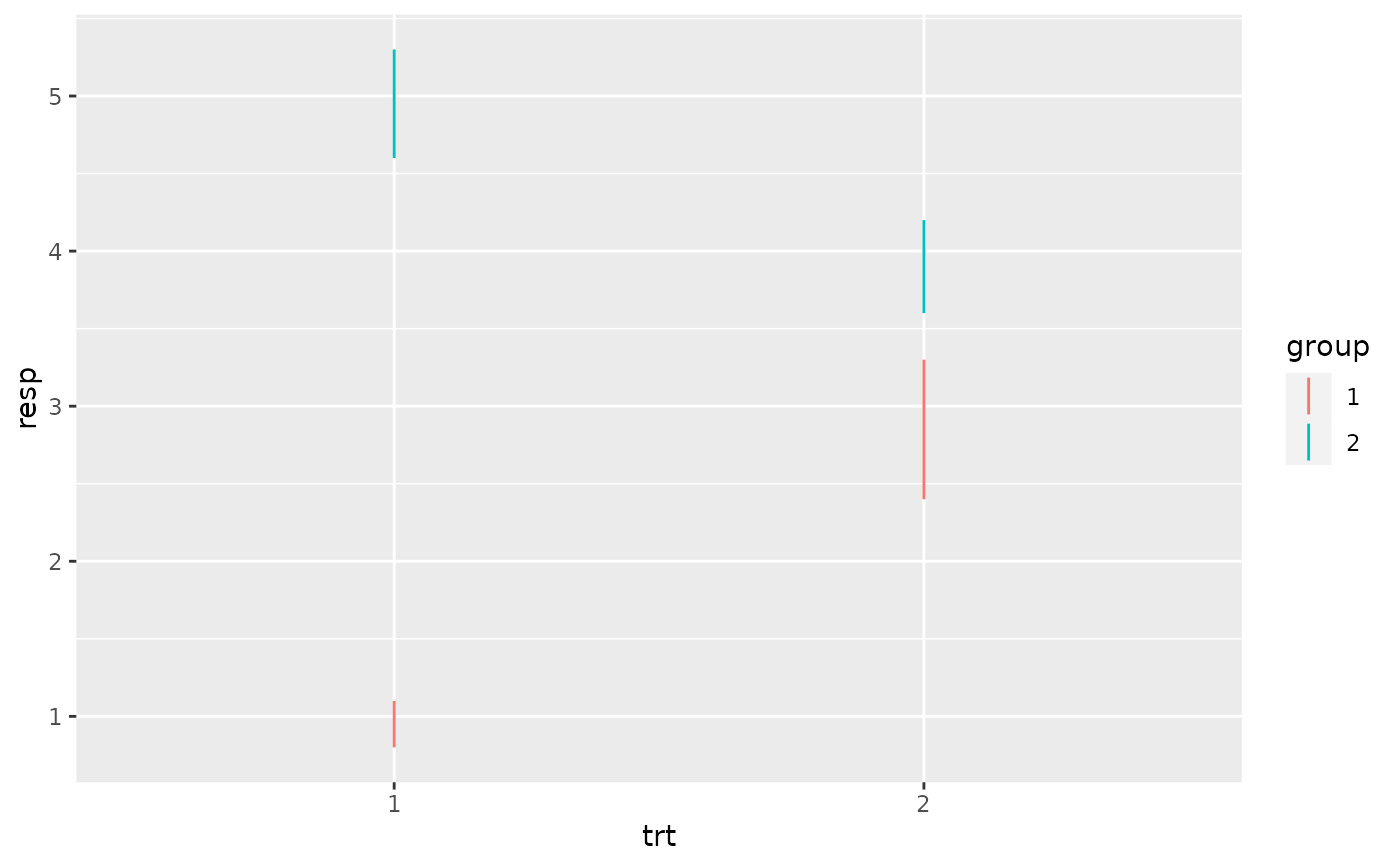 p + geom_pointrange(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper))
p + geom_pointrange(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper))
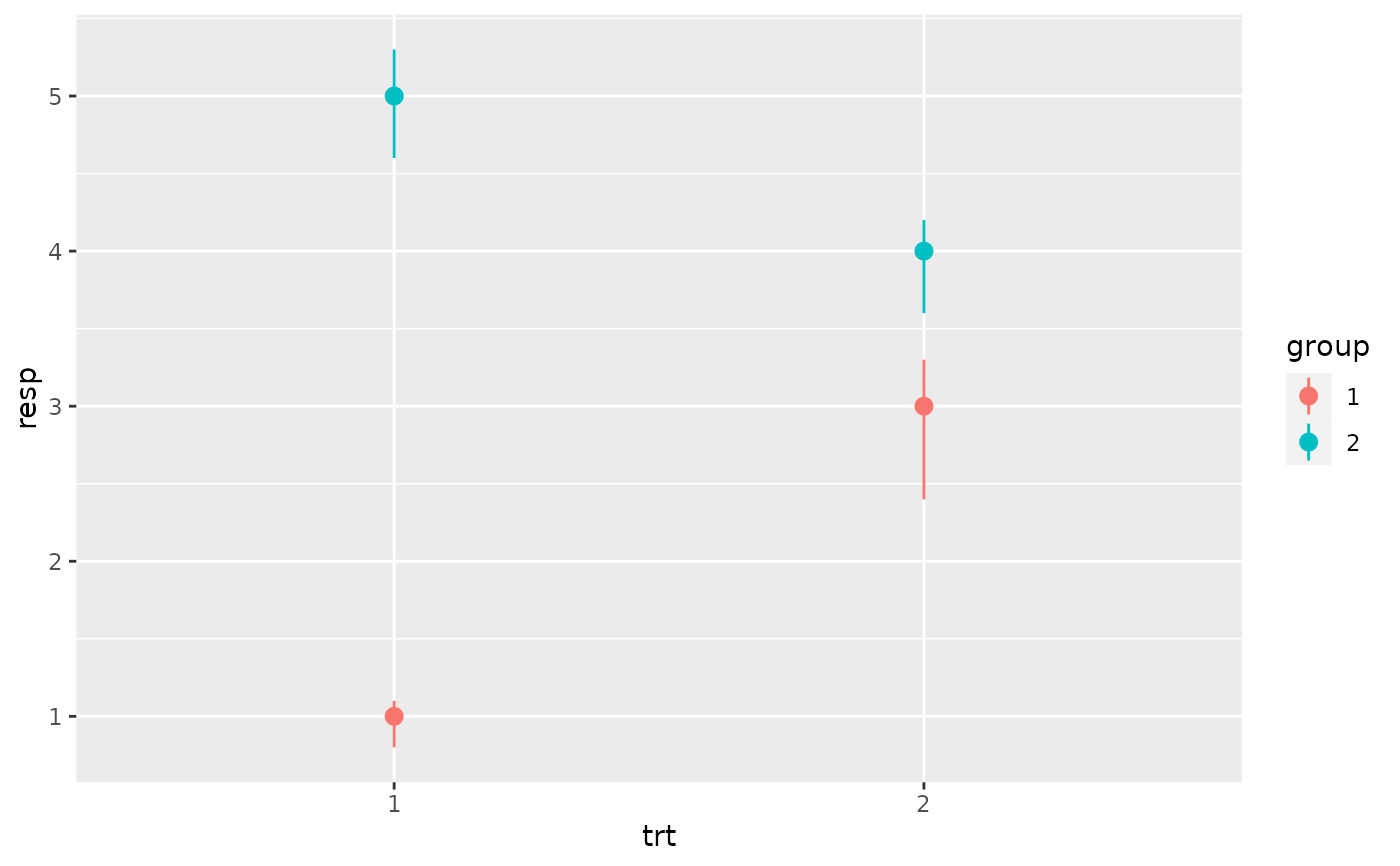 p + geom_crossbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
p + geom_crossbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
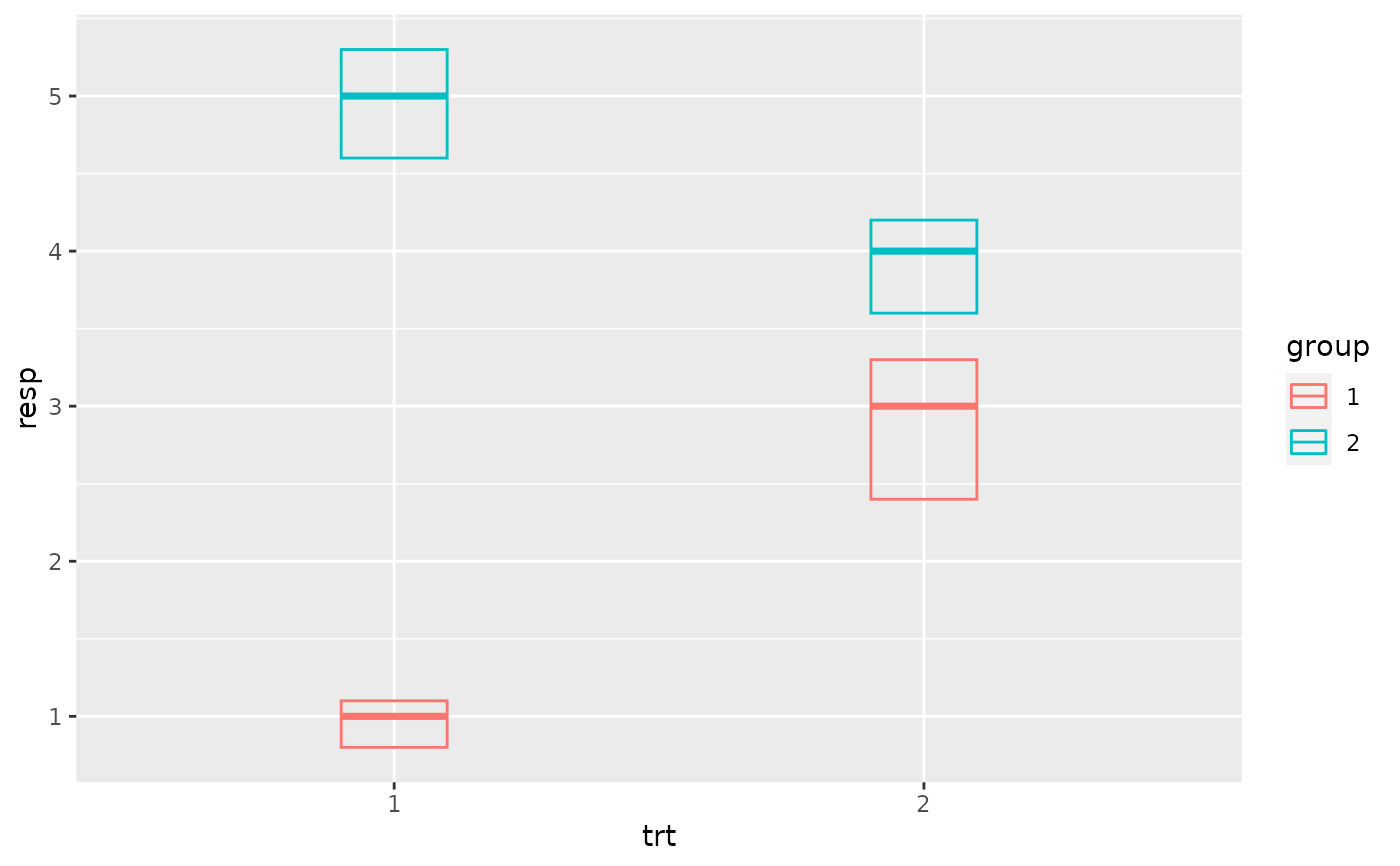 p + geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
p + geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
 # Flip the orientation by changing mapping
ggplot(df, aes(resp, trt, colour = group)) +
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = lower, xmax = upper))
# Flip the orientation by changing mapping
ggplot(df, aes(resp, trt, colour = group)) +
geom_linerange(aes(xmin = lower, xmax = upper))
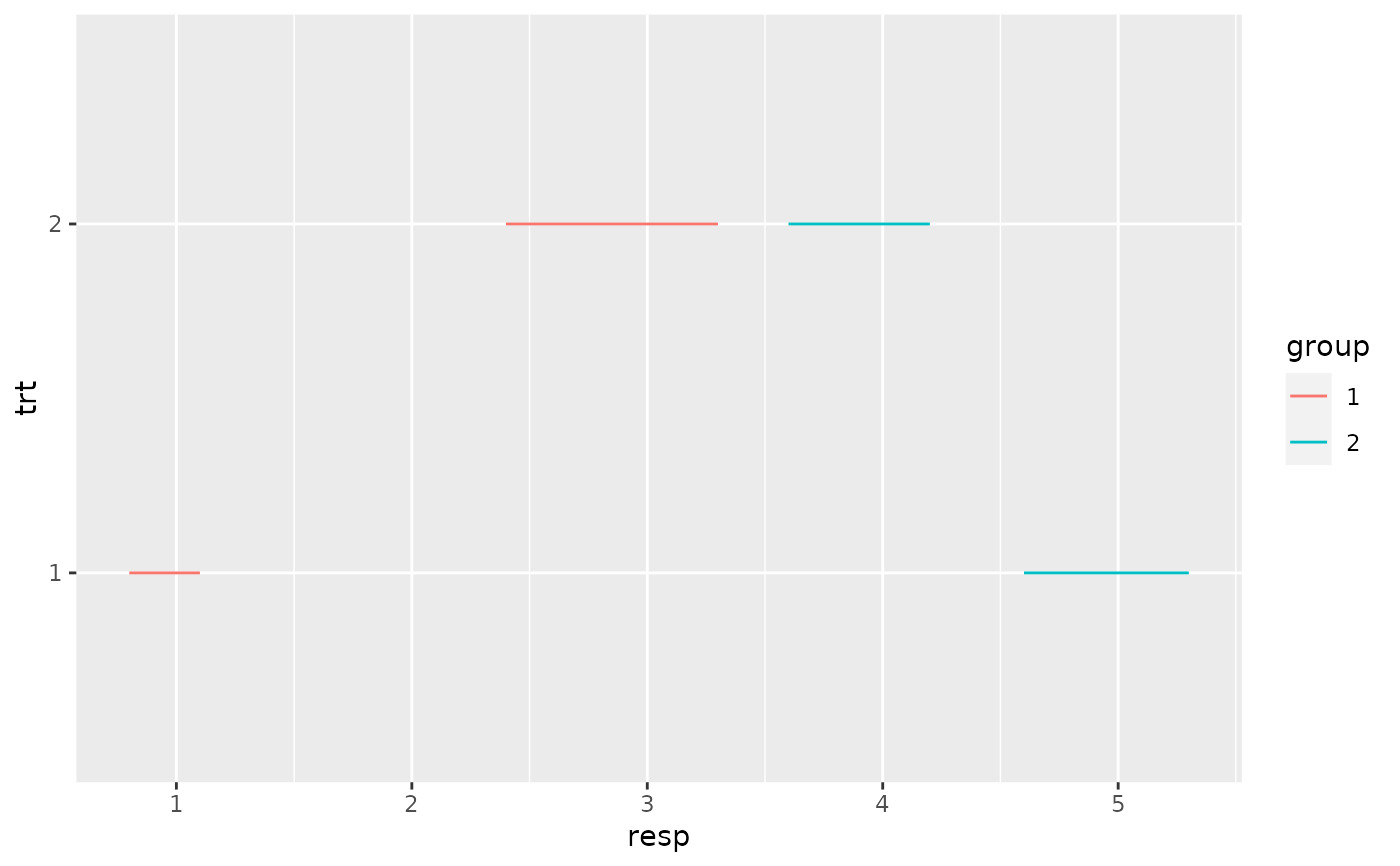 # Draw lines connecting group means
p +
geom_line(aes(group = group)) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
# Draw lines connecting group means
p +
geom_line(aes(group = group)) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), width = 0.2)
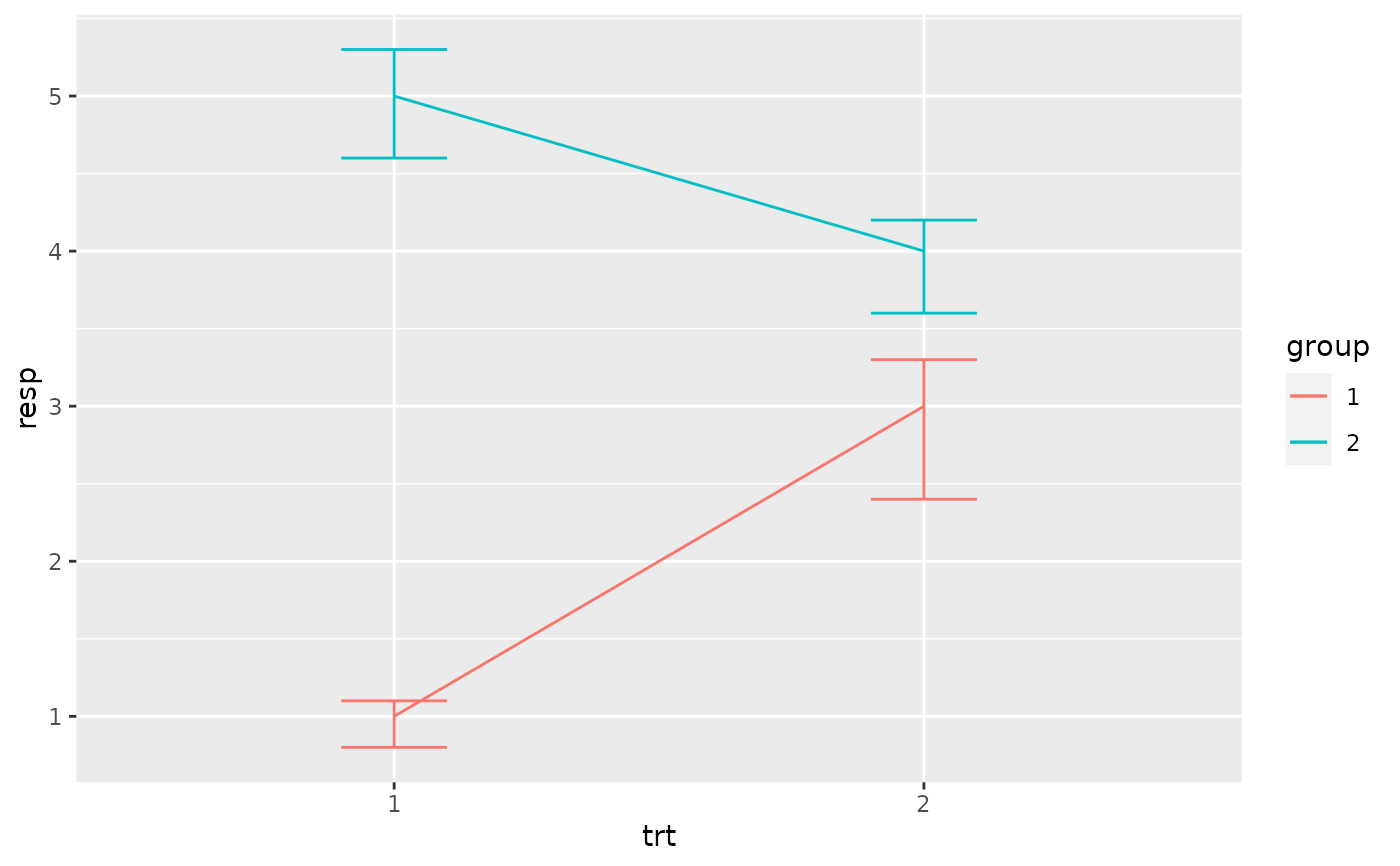 # If you want to dodge bars and errorbars, you need to manually
# specify the dodge width
p <- ggplot(df, aes(trt, resp, fill = group))
p +
geom_col(position = "dodge") +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), position = "dodge", width = 0.25)
# If you want to dodge bars and errorbars, you need to manually
# specify the dodge width
p <- ggplot(df, aes(trt, resp, fill = group))
p +
geom_col(position = "dodge") +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), position = "dodge", width = 0.25)
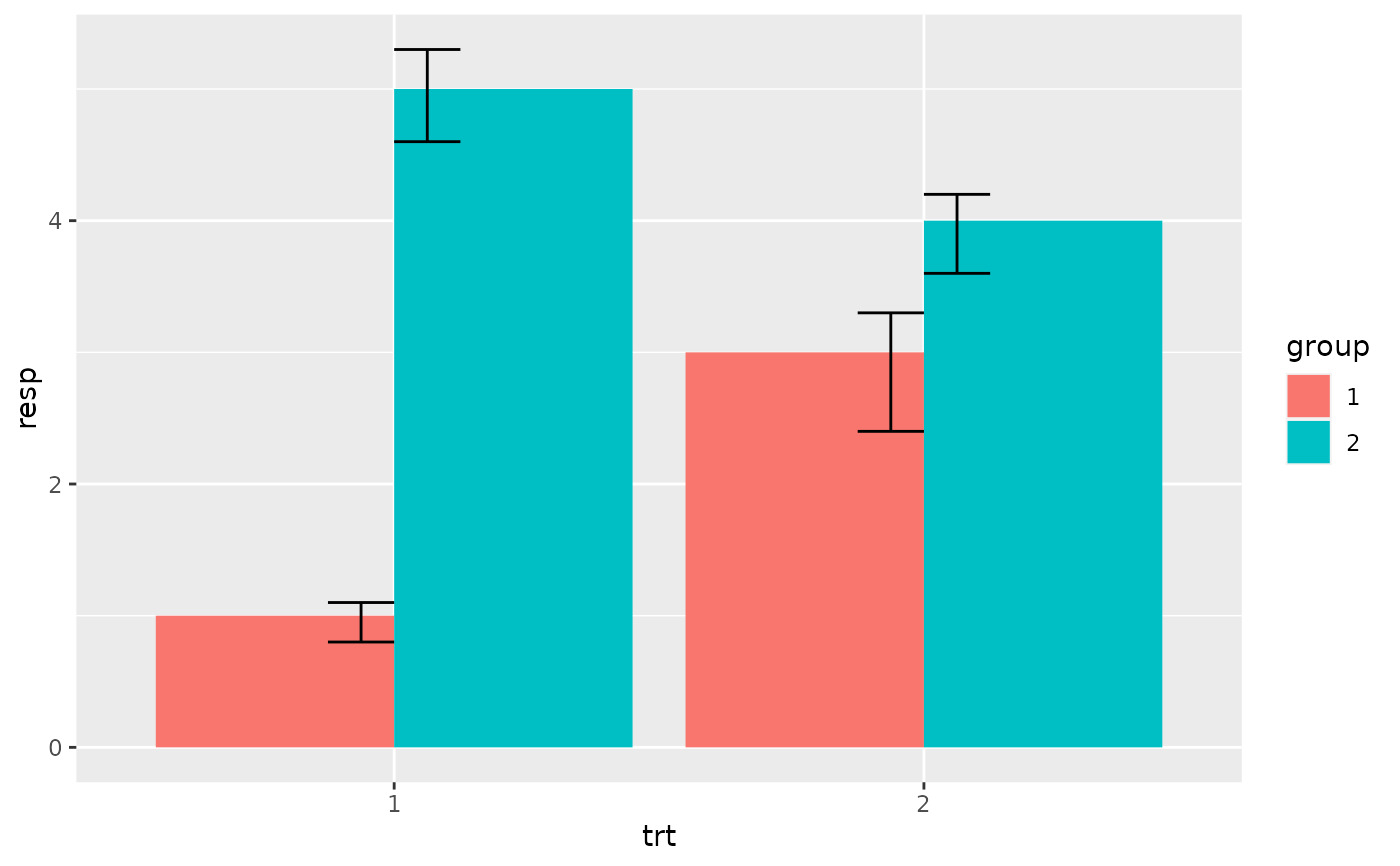 # Because the bars and errorbars have different widths
# we need to specify how wide the objects we are dodging are
dodge <- position_dodge(width=0.9)
p +
geom_col(position = dodge) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), position = dodge, width = 0.25)
# Because the bars and errorbars have different widths
# we need to specify how wide the objects we are dodging are
dodge <- position_dodge(width=0.9)
p +
geom_col(position = dodge) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper), position = dodge, width = 0.25)
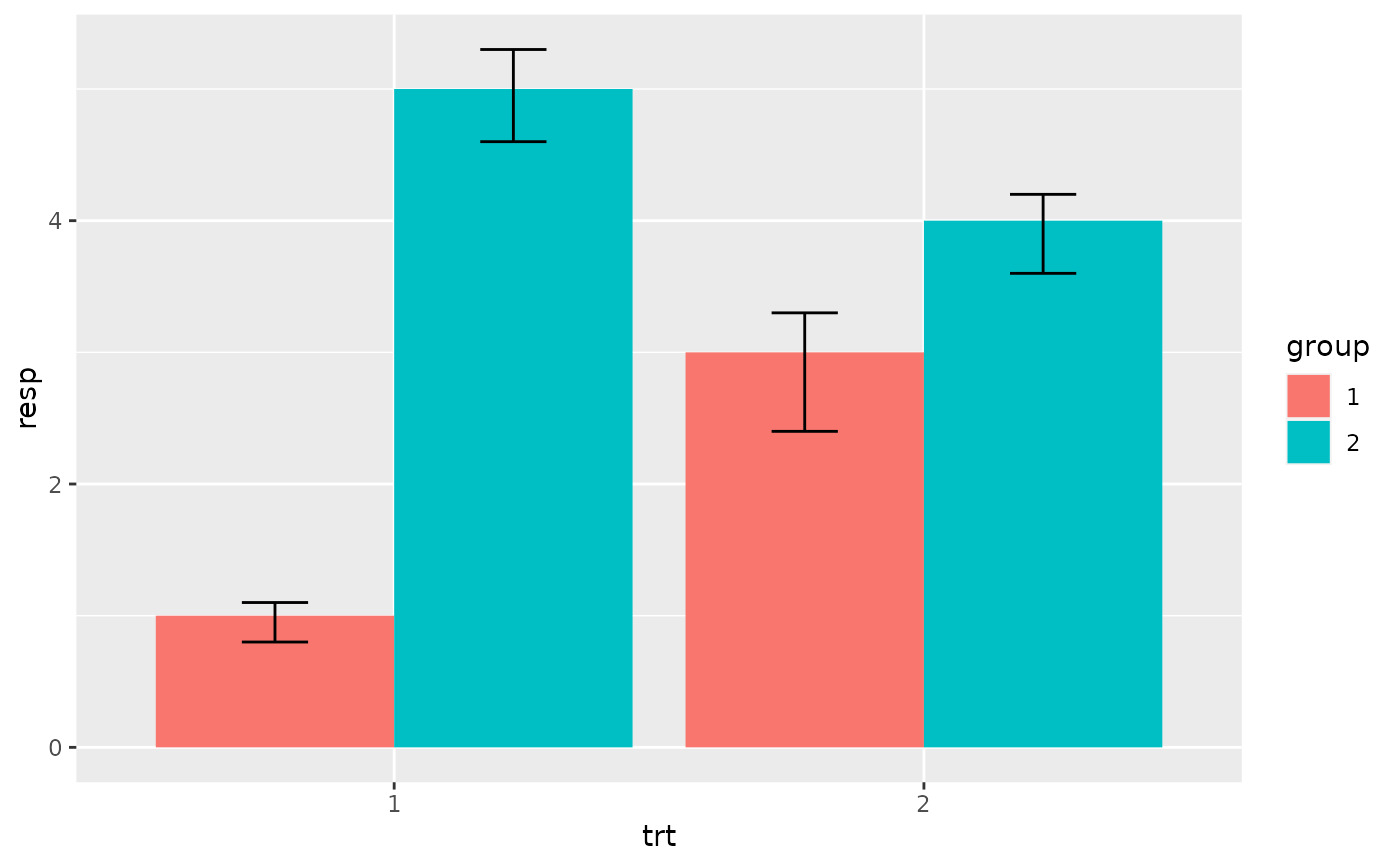 # When using geom_errorbar() with position_dodge2(), extra padding will be
# needed between the error bars to keep them aligned with the bars.
p +
geom_col(position = "dodge2") +
geom_errorbar(
aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper),
position = position_dodge2(width = 0.5, padding = 0.5)
)
# When using geom_errorbar() with position_dodge2(), extra padding will be
# needed between the error bars to keep them aligned with the bars.
p +
geom_col(position = "dodge2") +
geom_errorbar(
aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper),
position = position_dodge2(width = 0.5, padding = 0.5)
)
相关用法
- R ggplot2 geom_qq 分位数-分位数图
- R ggplot2 geom_spoke 由位置、方向和距离参数化的线段
- R ggplot2 geom_quantile 分位数回归
- R ggplot2 geom_text 文本
- R ggplot2 geom_ribbon 函数区和面积图
- R ggplot2 geom_boxplot 盒须图(Tukey 风格)
- R ggplot2 geom_hex 二维箱计数的六边形热图
- R ggplot2 geom_bar 条形图
- R ggplot2 geom_bin_2d 二维 bin 计数热图
- R ggplot2 geom_jitter 抖动点
- R ggplot2 geom_point 积分
- R ggplot2 geom_blank 什么也不画
- R ggplot2 geom_path 连接观察结果
- R ggplot2 geom_violin 小提琴情节
- R ggplot2 geom_dotplot 点图
- R ggplot2 geom_errorbarh 水平误差线
- R ggplot2 geom_function 将函数绘制为连续曲线
- R ggplot2 geom_polygon 多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_histogram 直方图和频数多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_tile 矩形
- R ggplot2 geom_segment 线段和曲线
- R ggplot2 geom_density_2d 二维密度估计的等值线
- R ggplot2 geom_map 参考Map中的多边形
- R ggplot2 geom_density 平滑密度估计
- R ggplot2 geom_abline 参考线:水平、垂直和对角线
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Hadley Wickham等大神的英文原创作品 Vertical intervals: lines, crossbars & errorbars。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
