本文简要介绍 python 语言中 scipy.stats.theilslopes 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.theilslopes(y, x=None, alpha=0.95, method='separate')#计算一组点 (x, y) 的 Theil-Sen 估计量。
theilslopes实现了稳健线性回归的方法。它将斜率计算为配对值之间所有斜率的中值。- y: array_like
因变量。
- x: 数组 或 None,可选
自变量。如果没有,请改用
arange(len(y))。- alpha: 浮点数,可选
置信度介于 0 和 1 之间。默认为 95% 置信度。请注意,
alpha在 0.5 附近是对称的,即 0.1 和 0.9 都被解释为“找到 90% 置信区间”。- method: {‘joint’, ‘separate’},可选
用于计算截距估计值的方法。支持以下方法,
‘joint’: Uses np.median(y - slope * x) as intercept.
- ‘separate’: Uses np.median(y) - slope * np.median(x)
as intercept.
默认值为‘separate’。
- result:
TheilslopesResult实例 返回值是一个具有以下属性的对象:
- 坡 浮点数
泰尔坡。
- 截距 浮点数
Theil线的拦截。
- low_slope 浮点数
斜率置信区间的下限。
- high_slope 浮点数
斜率置信区间的上限。
- result:
参数 ::
返回 ::
注意:
theilslopes的实现遵循 [1]。截距在[1]中没有定义,这里定义为median(y) - slope*median(x),在[3]中给出。截距的其他定义存在于文献中,例如[4]中的median(y - slope*x)。计算截距的方法可以由参数method确定。没有给出截距的置信区间,因为[1]中没有解决这个问题。为了与旧版本的 SciPy 兼容,返回值的行为类似于长度为 4 的
namedtuple,其中包含字段slope、intercept、low_slope和high_slope,因此可以继续编写:slope, intercept, low_slope, high_slope = theilslopes(y, x)参考:
[1] (1,2,3)PK Sen,“基于 Kendall tau 的回归系数估计”,J. Am。统计。协会,卷。 63,第 1379-1389 页,1968 年。
[2]H. Theil,“线性和多项式回归分析 I、II 和 III 的rank-invariant 方法”,Nederl。阿卡德。韦滕施,PROC。 53:第 386-392 页、第 521-525 页、第 1397-1412、1950 页。
[3]W.L. Conover,“Practical nonparametric statistics”,第 2 版,John Wiley and Sons,纽约,第 493 页。
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import stats >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt>>> x = np.linspace(-5, 5, num=150) >>> y = x + np.random.normal(size=x.size) >>> y[11:15] += 10 # add outliers >>> y[-5:] -= 7计算斜率、截距和 90% 置信区间。为了进行比较,还可以使用
linregress计算最小二乘拟合:>>> res = stats.theilslopes(y, x, 0.90, method='separate') >>> lsq_res = stats.linregress(x, y)绘制结果。 Theil-Sen 回归线以红色显示,红色虚线表示斜率的置信区间(请注意,红色虚线不是回归的置信区间,因为不包括截距的置信区间)。绿线显示用于比较的最小二乘拟合。
>>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111) >>> ax.plot(x, y, 'b.') >>> ax.plot(x, res[1] + res[0] * x, 'r-') >>> ax.plot(x, res[1] + res[2] * x, 'r--') >>> ax.plot(x, res[1] + res[3] * x, 'r--') >>> ax.plot(x, lsq_res[1] + lsq_res[0] * x, 'g-') >>> plt.show()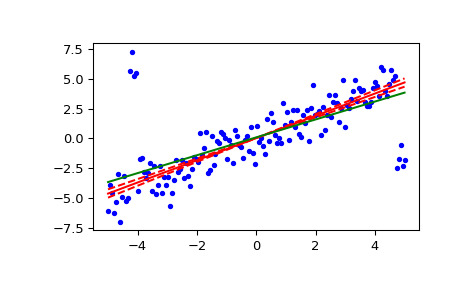
相关用法
- Python SciPy stats.triang用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.t用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_rel用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tvar用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.trim_mean用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tsem用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_ind_from_stats用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncpareto用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_1samp用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_ind用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmean用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncweibull_min用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.trim1用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmin用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.trimboth用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmax用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncexpon用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncnorm用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tukeylambda用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.trapezoid用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tstd用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tiecorrect用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.tukey_hsd用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.iqr用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自scipy.org大神的英文原创作品 scipy.stats.theilslopes。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
