小提琴圖是連續分布的緊湊顯示。它是 geom_boxplot() 和 geom_density() 的混合:小提琴圖是鏡像密度圖,顯示方式與箱線圖相同。
用法
geom_violin(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "ydensity",
position = "dodge",
...,
draw_quantiles = NULL,
trim = TRUE,
scale = "area",
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_ydensity(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "violin",
position = "dodge",
...,
bw = "nrd0",
adjust = 1,
kernel = "gaussian",
trim = TRUE,
scale = "area",
na.rm = FALSE,
orientation = NA,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)參數
- mapping
-
由
aes()創建的一組美學映射。如果指定且inherit.aes = TRUE(默認),它將與繪圖頂層的默認映射組合。如果沒有繪圖映射,則必須提供mapping。 - data
-
該層要顯示的數據。有以下三種選擇:
如果默認為
NULL,則數據繼承自ggplot()調用中指定的繪圖數據。data.frame或其他對象將覆蓋繪圖數據。所有對象都將被強化以生成 DataFrame 。請參閱fortify()將為其創建變量。將使用單個參數(繪圖數據)調用
function。返回值必須是data.frame,並將用作圖層數據。可以從formula創建function(例如~ head(.x, 10))。 - position
-
位置調整,可以是命名調整的字符串(例如
"jitter"使用position_jitter),也可以是調用位置調整函數的結果。如果需要更改調整設置,請使用後者。 - ...
-
其他參數傳遞給
layer()。這些通常是美學,用於將美學設置為固定值,例如colour = "red"或size = 3。它們也可能是配對的 geom/stat 的參數。 - draw_quantiles
-
如果
not(NULL)(默認),則在密度估計的給定分位數處繪製水平線。 - trim
-
如果
TRUE(默認),將小提琴的尾部修剪到數據範圍。如果FALSE,不要修剪尾巴。 - scale
-
如果"area"(默認),則所有小提琴都具有相同的麵積(修剪尾部之前)。如果"count",麵積將根據觀測值的數量按比例縮放。如果"width",所有小提琴都具有相同的最大寬度。
- na.rm
-
如果
FALSE,則默認缺失值將被刪除並帶有警告。如果TRUE,缺失值將被靜默刪除。 - orientation
-
層的方向。默認值 (
NA) 自動根據美學映射確定方向。萬一失敗,可以通過將orientation設置為"x"或"y"來顯式給出。有關更多詳細信息,請參閱方向部分。 - show.legend
-
合乎邏輯的。該層是否應該包含在圖例中?
NA(默認值)包括是否映射了任何美學。FALSE從不包含,而TRUE始終包含。它也可以是一個命名的邏輯向量,以精細地選擇要顯示的美學。 - inherit.aes
-
如果
FALSE,則覆蓋默認美學,而不是與它們組合。這對於定義數據和美觀的輔助函數最有用,並且不應繼承默認繪圖規範的行為,例如borders()。 - geom, stat
-
用於覆蓋
geom_violin()和stat_ydensity()之間的默認連接。 - bw
-
要使用的平滑帶寬。如果是數字,則為平滑內核的標準差。如果是字符,則選擇帶寬的規則,如
stats::bw.nrd()中列出。 - adjust
-
多重帶寬調整。這使得在仍然使用帶寬估計器的同時調整帶寬成為可能。例如
adjust = 1/2表示使用默認帶寬的一半。 - kernel
-
核心。請參閱
density()中的可用內核列表。
方向
該幾何體以不同的方式對待每個軸,因此可以有兩個方向。通常,方向很容易從給定映射和使用的位置比例類型的組合中推斷出來。因此,ggplot2 默認情況下會嘗試猜測圖層應具有哪個方向。在極少數情況下,方向不明確,猜測可能會失敗。在這種情況下,可以直接使用 orientation 參數指定方向,該參數可以是 "x" 或 "y" 。該值給出了幾何圖形應沿著的軸,"x" 是您期望的幾何圖形的默認方向。
美學
geom_violin() 理解以下美學(所需的美學以粗體顯示):
-
x -
y -
alpha -
colour -
fill -
group -
linetype -
linewidth -
weight
在 vignette("ggplot2-specs") 中了解有關設置這些美學的更多信息。
計算變量
這些是由層的 'stat' 部分計算的,可以使用 delayed evaluation 訪問。
-
after_stat(density)
密度估計。 -
after_stat(scaled)
密度估計,縮放至最大值 1。 -
after_stat(count)
密度 * 點數 - 對於小提琴圖可能沒用。 -
after_stat(violinwidth)
根據麵積、計數或恒定最大寬度縮放小提琴圖的密度。 -
after_stat(n)
點數。 -
after_stat(width)
小提琴邊界框的寬度。
也可以看看
geom_violin() 為示例,stat_density() 為沿 x 軸的數據示例。
例子
p <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(factor(cyl), mpg))
p + geom_violin()
 # Orientation follows the discrete axis
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, factor(cyl))) +
geom_violin()
# Orientation follows the discrete axis
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, factor(cyl))) +
geom_violin()
 # \donttest{
p + geom_violin() + geom_jitter(height = 0, width = 0.1)
# \donttest{
p + geom_violin() + geom_jitter(height = 0, width = 0.1)
 # Scale maximum width proportional to sample size:
p + geom_violin(scale = "count")
# Scale maximum width proportional to sample size:
p + geom_violin(scale = "count")
 # Scale maximum width to 1 for all violins:
p + geom_violin(scale = "width")
# Scale maximum width to 1 for all violins:
p + geom_violin(scale = "width")
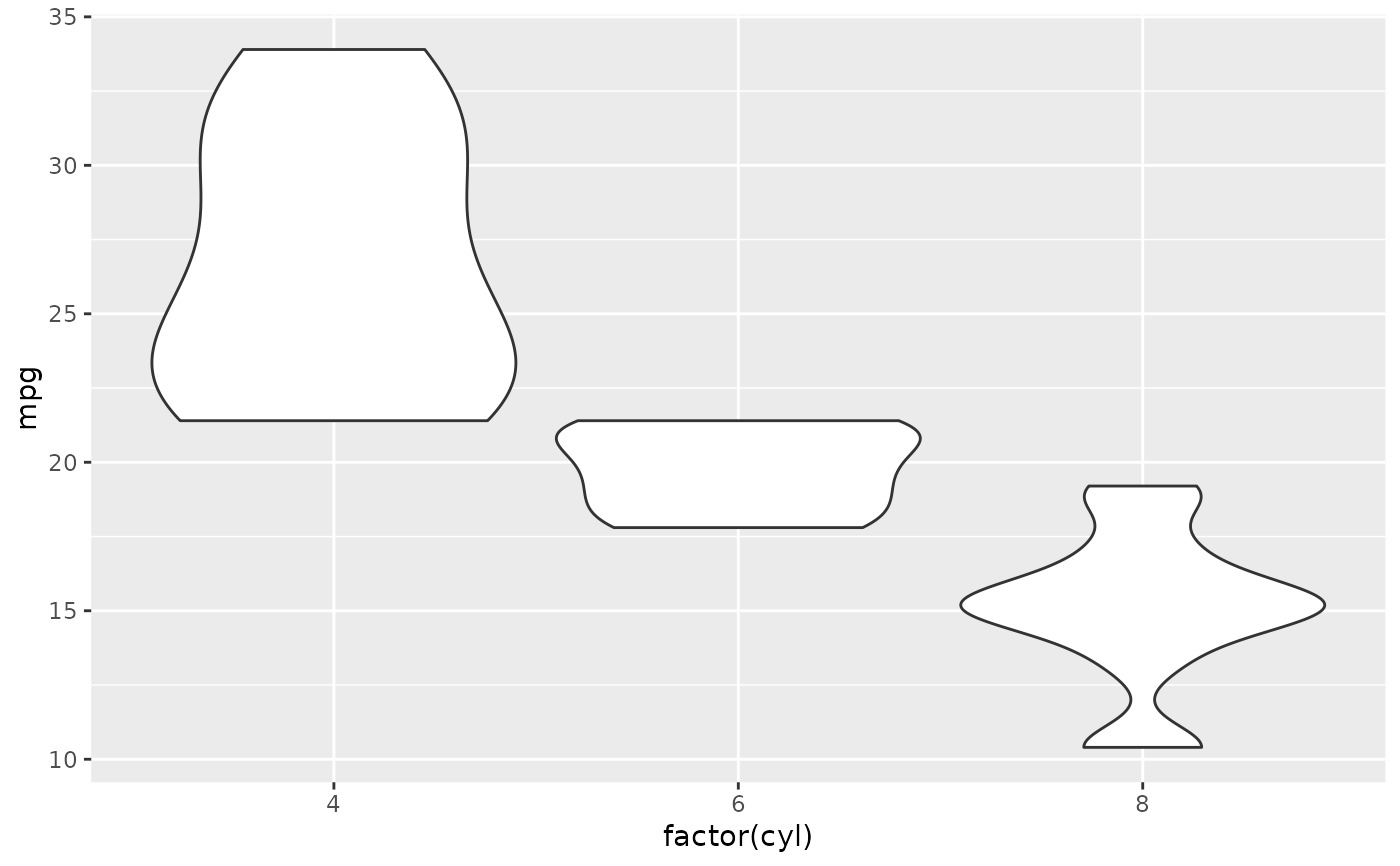 # Default is to trim violins to the range of the data. To disable:
p + geom_violin(trim = FALSE)
# Default is to trim violins to the range of the data. To disable:
p + geom_violin(trim = FALSE)
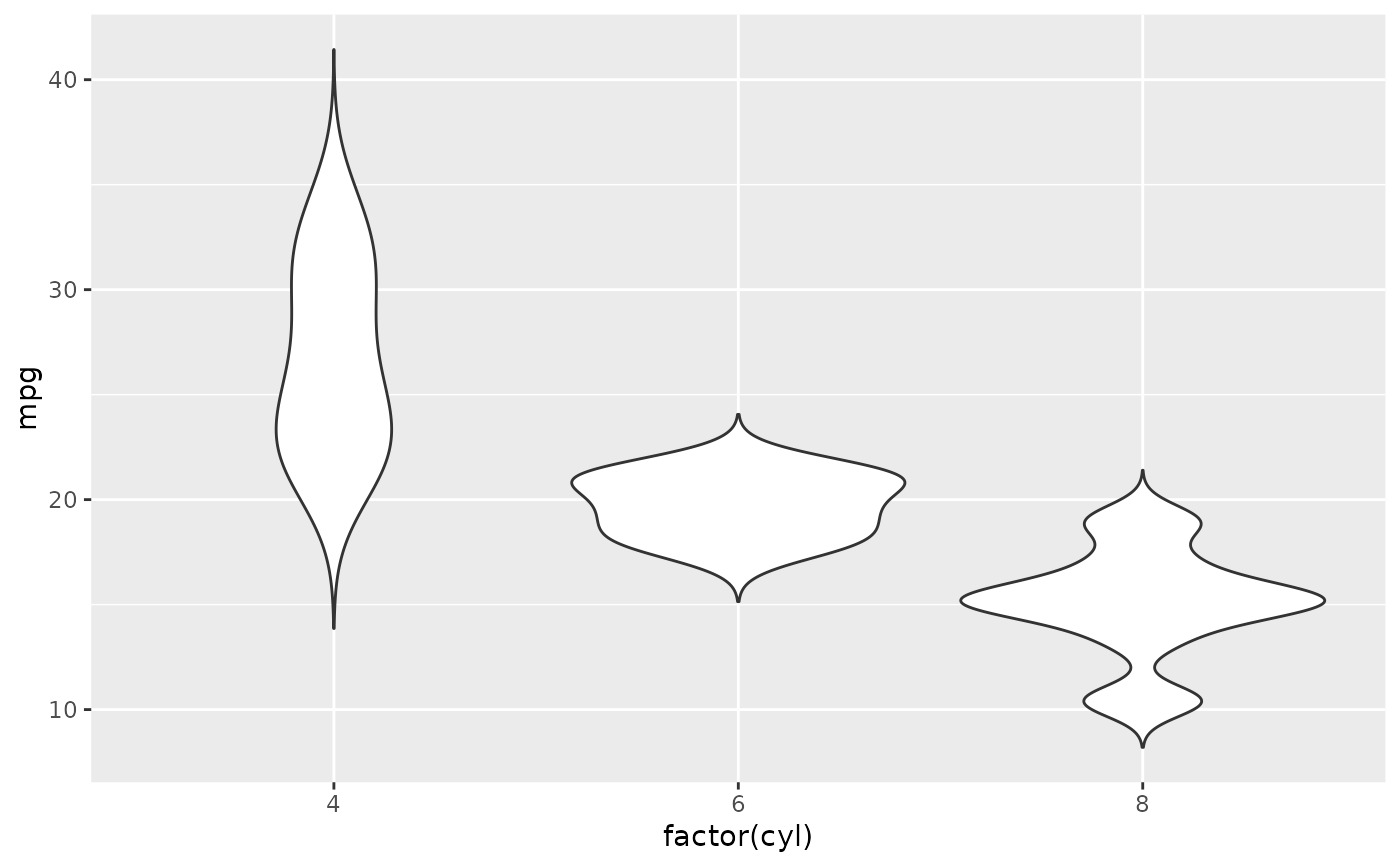 # Use a smaller bandwidth for closer density fit (default is 1).
p + geom_violin(adjust = .5)
# Use a smaller bandwidth for closer density fit (default is 1).
p + geom_violin(adjust = .5)
 # Add aesthetic mappings
# Note that violins are automatically dodged when any aesthetic is
# a factor
p + geom_violin(aes(fill = cyl))
# Add aesthetic mappings
# Note that violins are automatically dodged when any aesthetic is
# a factor
p + geom_violin(aes(fill = cyl))
 p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(cyl)))
p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(cyl)))
 p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(vs)))
#> Warning: Groups with fewer than two data points have been dropped.
p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(vs)))
#> Warning: Groups with fewer than two data points have been dropped.
 p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(am)))
p + geom_violin(aes(fill = factor(am)))
 # Set aesthetics to fixed value
p + geom_violin(fill = "grey80", colour = "#3366FF")
# Set aesthetics to fixed value
p + geom_violin(fill = "grey80", colour = "#3366FF")
 # Show quartiles
p + geom_violin(draw_quantiles = c(0.25, 0.5, 0.75))
# Show quartiles
p + geom_violin(draw_quantiles = c(0.25, 0.5, 0.75))
 # Scales vs. coordinate transforms -------
if (require("ggplot2movies")) {
# Scale transformations occur before the density statistics are computed.
# Coordinate transformations occur afterwards. Observe the effect on the
# number of outliers.
m <- ggplot(movies, aes(y = votes, x = rating, group = cut_width(rating, 0.5)))
m + geom_violin()
m +
geom_violin() +
scale_y_log10()
m +
geom_violin() +
coord_trans(y = "log10")
m +
geom_violin() +
scale_y_log10() + coord_trans(y = "log10")
# Violin plots with continuous x:
# Use the group aesthetic to group observations in violins
ggplot(movies, aes(year, budget)) +
geom_violin()
ggplot(movies, aes(year, budget)) +
geom_violin(aes(group = cut_width(year, 10)), scale = "width")
}
#> Warning: Removed 53573 rows containing non-finite values (`stat_ydensity()`).
#> Warning: Groups with fewer than two data points have been dropped.
# Scales vs. coordinate transforms -------
if (require("ggplot2movies")) {
# Scale transformations occur before the density statistics are computed.
# Coordinate transformations occur afterwards. Observe the effect on the
# number of outliers.
m <- ggplot(movies, aes(y = votes, x = rating, group = cut_width(rating, 0.5)))
m + geom_violin()
m +
geom_violin() +
scale_y_log10()
m +
geom_violin() +
coord_trans(y = "log10")
m +
geom_violin() +
scale_y_log10() + coord_trans(y = "log10")
# Violin plots with continuous x:
# Use the group aesthetic to group observations in violins
ggplot(movies, aes(year, budget)) +
geom_violin()
ggplot(movies, aes(year, budget)) +
geom_violin(aes(group = cut_width(year, 10)), scale = "width")
}
#> Warning: Removed 53573 rows containing non-finite values (`stat_ydensity()`).
#> Warning: Groups with fewer than two data points have been dropped.
 # }
# }
相關用法
- R ggplot2 geom_qq 分位數-分位數圖
- R ggplot2 geom_spoke 由位置、方向和距離參數化的線段
- R ggplot2 geom_quantile 分位數回歸
- R ggplot2 geom_text 文本
- R ggplot2 geom_ribbon 函數區和麵積圖
- R ggplot2 geom_boxplot 盒須圖(Tukey 風格)
- R ggplot2 geom_hex 二維箱計數的六邊形熱圖
- R ggplot2 geom_bar 條形圖
- R ggplot2 geom_bin_2d 二維 bin 計數熱圖
- R ggplot2 geom_jitter 抖動點
- R ggplot2 geom_point 積分
- R ggplot2 geom_linerange 垂直間隔:線、橫線和誤差線
- R ggplot2 geom_blank 什麽也不畫
- R ggplot2 geom_path 連接觀察結果
- R ggplot2 geom_dotplot 點圖
- R ggplot2 geom_errorbarh 水平誤差線
- R ggplot2 geom_function 將函數繪製為連續曲線
- R ggplot2 geom_polygon 多邊形
- R ggplot2 geom_histogram 直方圖和頻數多邊形
- R ggplot2 geom_tile 矩形
- R ggplot2 geom_segment 線段和曲線
- R ggplot2 geom_density_2d 二維密度估計的等值線
- R ggplot2 geom_map 參考Map中的多邊形
- R ggplot2 geom_density 平滑密度估計
- R ggplot2 geom_abline 參考線:水平、垂直和對角線
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Hadley Wickham等大神的英文原創作品 Violin plot。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
