本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.stats.siegelslopes 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.siegelslopes(y, x=None, method='hierarchical')#計算一組點 (x, y) 的 Siegel 估計量。
siegelslopes實現了一種使用重複中值(參見 [1])來擬合點 (x, y) 的直線的穩健線性回歸方法。該方法對於漸近崩潰點為 50% 的異常值具有魯棒性。- y: array_like
因變量。
- x: 數組 或 None,可選
自變量。如果沒有,請改用
arange(len(y))。- method: {‘hierarchical’, ‘separate’}
如果‘hierarchical’,使用估計的斜率
slope(默認選項)估計截距。如果‘separate’,估計與估計斜率無關的截距。有關詳細信息,請參閱注釋。
- result:
SiegelslopesResult實例 返回值是一個具有以下屬性的對象:
- 坡 浮點數
回歸線斜率的估計。
- 截距 浮點數
估計回歸線的截距。
- result:
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
和
n = len(y), 計算m_j作為從該點開始的斜率的中位數(x[j], y[j])對所有其他n-1點。slope那麽是所有斜率的中位數m_j.給出了兩種估計截距的方法[1]可以通過參數選擇method.分層方法使用估計的斜率slope並計算intercept作為中位數y - slope*x.另一種方法分別估計截距如下:對於每個點(x[j], y[j]),計算所有的截距n-1穿過其餘點並取中位數i_j.intercept是中位數i_j.實現計算n乘以大小向量的中位數n對於大型向量,這可能會很慢。有更有效的算法(見[2]) 這裏沒有實現。
為了與舊版本的 SciPy 兼容,返回值的行為類似於長度為 2 的
namedtuple,其中包含字段slope和intercept,因此可以繼續編寫:slope, intercept = siegelslopes(y, x)參考:
[1] (1,2)A. Siegel,“使用重複中位數的穩健回歸”,Biometrika,卷。 69,第 242-244 頁,1982 年。
[2]A. Stein 和 M. Werman,“尋找重複中值回歸線”,第三屆年度 ACM-SIAM 離散算法研討會論文集,第 409-413 頁,1992 年。
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import stats >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt>>> x = np.linspace(-5, 5, num=150) >>> y = x + np.random.normal(size=x.size) >>> y[11:15] += 10 # add outliers >>> y[-5:] -= 7計算斜率和截距。為了進行比較,還可以使用
linregress計算最小二乘擬合:>>> res = stats.siegelslopes(y, x) >>> lsq_res = stats.linregress(x, y)繪製結果。西格爾回歸線以紅色顯示。綠線顯示用於比較的最小二乘擬合。
>>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111) >>> ax.plot(x, y, 'b.') >>> ax.plot(x, res[1] + res[0] * x, 'r-') >>> ax.plot(x, lsq_res[1] + lsq_res[0] * x, 'g-') >>> plt.show()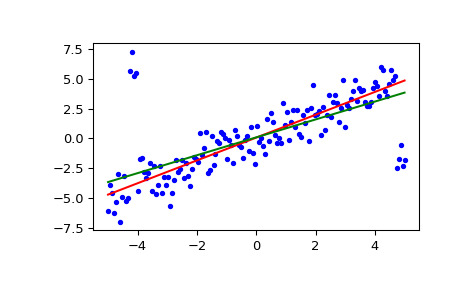
相關用法
- Python SciPy stats.sigmaclip用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.skewnorm用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.semicircular用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.skellam用法及代碼示例
- Python scipy.stats.somersd用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.sem用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.skewcauchy用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.scoreatpercentile用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.skew用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.spearmanr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.shapiro用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.studentized_range用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.skewtest用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.special_ortho_group用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.sobol_indices用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.iqr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.genpareto用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.cosine用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.norminvgauss用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.directional_stats用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.invwishart用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bartlett用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.levy_stable用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.page_trend_test用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.stats.siegelslopes。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
