本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.stats.binned_statistic_dd 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.binned_statistic_dd(sample, values, statistic='mean', bins=10, range=None, expand_binnumbers=False, binned_statistic_result=None)#計算一組數據的多維分箱統計量。
這是 histogramdd 函數的概括。直方圖將空間劃分為多個 bin,並返回每個 bin 中的點數。此函數允許計算每個 bin 內的值的總和、平均值、中位數或其他統計量。
- sample: array_like
直方圖的數據作為長度為 D 的 N 個數組的序列或作為 (N,D) 數組傳遞。
- values: (N,) 數組 或 (N,) 數組 列表
將根據其計算統計數據的數據。這必須與樣本的形狀相同,或者是一個序列列表——每個序列的形狀都與樣本相同。如果 values 是這樣一個列表,則將獨立計算每個值的統計信息。
- statistic: 字符串或可調用,可選
要計算的統計數據(默認為‘mean’)。可用的統計數據如下:
‘mean’ : compute the mean of values for points within each bin. Empty bins will be represented by NaN.
‘median’ : compute the median of values for points within each bin. Empty bins will be represented by NaN.
‘count’ : compute the count of points within each bin. This is identical to an unweighted histogram. values array is not referenced.
‘sum’ : compute the sum of values for points within each bin. This is identical to a weighted histogram.
‘std’ : compute the standard deviation within each bin. This is implicitly calculated with ddof=0. If the number of values within a given bin is 0 or 1, the computed standard deviation value will be 0 for the bin.
‘min’ : compute the minimum of values for points within each bin. Empty bins will be represented by NaN.
‘max’ : compute the maximum of values for point within each bin. Empty bins will be represented by NaN.
function : a user-defined function which takes a 1D array of values, and outputs a single numerical statistic. This function will be called on the values in each bin. Empty bins will be represented by function([]), or NaN if this returns an error.
- bins: 序列或正整數,可選
bin 規範必須采用以下形式之一:
A sequence of arrays describing the bin edges along each dimension.
The number of bins for each dimension (nx, ny, … = bins).
The number of bins for all dimensions (nx = ny = … = bins).
- range: 順序,可選
如果邊沒有在 bin 中明確給出,則使用一係列較低和較高的 bin 邊。默認為每個維度的最小值和最大值。
- expand_binnumbers: 布爾型,可選
‘False’(默認):返回的二進製數是線性化 bin 索引的形狀 (N,) 數組。 ‘True’:返回的二進製數將 ‘unraveled’ 轉換為形狀 (D,N) ndarray,其中每一行給出相應維度中的 bin 編號。見二進製數返回值,以及例子部分scipy.stats.binned_statistic_2d.
- binned_statistic_result: binnedStatisticddResult
先前調用函數的結果,以便重新使用具有新值和/或不同統計信息的 bin 邊和 bin 編號。要重複使用 bin 編號,expand_binnumbers 必須已設置為 False(默認值)
- statistic: ndarray,形狀(nx1,nx2,nx3,…)
每個二維 bin 中所選統計數據的值。
- bin_edges: ndarrays 列表
說明每個維度的 (nxi + 1) 個 bin 邊的 D 數組列表。
- binnumber: (N,) 整數數組或 (D,N) 整數數組
這會為樣本的每個元素分配一個整數,該整數表示該觀測值所在的 bin。表示取決於expand_binnumbers 參數。有關詳細信息,請參閱注釋。
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
Binedges:除了最後一個 (righthand-most) bin,所有的 bin 在每個維度上都是半開的。換句話說,如果箱子是
[1, 2, 3, 4],那麽第一個 bin 是[1, 2)(包括1個,但不包括2個)和第二個[2, 3).然而,最後一個箱子是[3, 4], 哪一個包括 4.binnumber:這個返回的參數為 sample 的每個元素分配一個整數,表示它所屬的 bin。表示取決於expand_binnumbers 參數。如果“False”(默認):返回的 binnumber 是一個線性化索引的形狀 (N,) 數組,將樣本的每個元素映射到其對應的 bin(使用行優先排序)。如果“真”:返回的 binnumber 是一個形狀 (D,N) ndarray,其中每一行分別表示每個維度的 bin 位置。在每個維度中,i 的 bin 數表示對應的值在 (bin_edges[D][i-1], bin_edges[D][i]) 之間,對於每個維度“D”。
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import stats >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D以一個 600 (x, y) 坐標的數組為例。
binned_statistic_dd可以處理更高維度的數組D.但是一個維度的情節D+1是必須的。>>> mu = np.array([0., 1.]) >>> sigma = np.array([[1., -0.5],[-0.5, 1.5]]) >>> multinormal = stats.multivariate_normal(mu, sigma) >>> data = multinormal.rvs(size=600, random_state=235412) >>> data.shape (600, 2)創建 bin 並計算每個 bin 中有多少數組:
>>> N = 60 >>> x = np.linspace(-3, 3, N) >>> y = np.linspace(-3, 4, N) >>> ret = stats.binned_statistic_dd(data, np.arange(600), bins=[x, y], ... statistic='count') >>> bincounts = ret.statistic設置條形的音量和位置:
>>> dx = x[1] - x[0] >>> dy = y[1] - y[0] >>> x, y = np.meshgrid(x[:-1]+dx/2, y[:-1]+dy/2) >>> z = 0>>> bincounts = bincounts.ravel() >>> x = x.ravel() >>> y = y.ravel()>>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') >>> with np.errstate(divide='ignore'): # silence random axes3d warning ... ax.bar3d(x, y, z, dx, dy, bincounts)使用新值重用 bin 編號和 bin 邊:
>>> ret2 = stats.binned_statistic_dd(data, -np.arange(600), ... binned_statistic_result=ret, ... statistic='mean')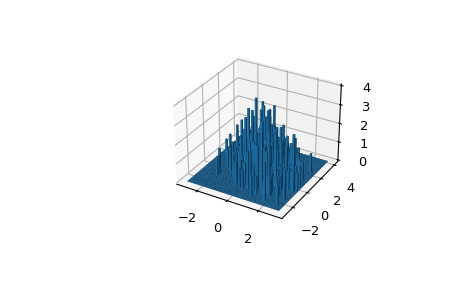
相關用法
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic_2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binomtest用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom_test用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bartlett用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boltzmann用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.brunnermunzel用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.betaprime用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.betabinom用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_normplot用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bayes_mvs用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_normmax用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr12用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boschloo_exact用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bootstrap用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bws_test用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.beta用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bradford用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_llf用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bernoulli用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.barnard_exact用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.stats.binned_statistic_dd。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
