本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.stats.boxcox_normmax 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.boxcox_normmax(x, brack=None, method='pearsonr', optimizer=None)#計算輸入數據的最佳Box-Cox 變換參數。
- x: array_like
輸入數組。所有條目必須是正數、有限實數。
- brack: 2 元組,可選,默認 (-2.0, 2.0)
默認 optimize.brent 解算器的下坡括號搜索的起始間隔。請注意,這在大多數情況下並不重要;最終結果允許在這個括號之外。如果優化器通過,brack 必須為 None。
- method: str,可選
確定最優變換參數的方法(
boxcoxlmbda參數)。選項是:- ‘pearsonr’(默認)
最大化 Pearson 相關係數
y = boxcox(x)和預期值y如果x將是normally-distributed。- ‘mle’
最大化對數似然
boxcox_llf。這是boxcox中使用的方法。- ‘all’
使用所有可用的優化方法,並返回所有結果。有助於比較不同的方法。
- optimizer: 可調用的,可選的
優化器是一個接受一個參數的可調用對象:
- 樂趣 可調用的
要最小化的目標函數。 fun 接受一個參數,即 Box-Cox 變換參數 lmbda,並返回所提供參數處的函數值(例如負對數似然)。優化器的工作是找到使樂趣最小化的 lmbda 值。
並返回一個對象,例如
scipy.optimize.OptimizeResult,它持有的最優值lmbda在一個屬性中x.有關詳細信息,請參閱下麵的示例或
scipy.optimize.minimize_scalar的文檔。
- maxlog: 浮點數或 ndarray
找到的最佳變換參數。
method='all'的數組而不是標量。
參數 ::
返回 ::
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import stats >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt我們可以通過各種方式生成一些數據並確定最佳
lmbda:>>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> x = stats.loggamma.rvs(5, size=30, random_state=rng) + 5 >>> y, lmax_mle = stats.boxcox(x) >>> lmax_pearsonr = stats.boxcox_normmax(x)>>> lmax_mle 2.217563431465757 >>> lmax_pearsonr 2.238318660200961 >>> stats.boxcox_normmax(x, method='all') array([2.23831866, 2.21756343])>>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111) >>> prob = stats.boxcox_normplot(x, -10, 10, plot=ax) >>> ax.axvline(lmax_mle, color='r') >>> ax.axvline(lmax_pearsonr, color='g', ls='--')>>> plt.show()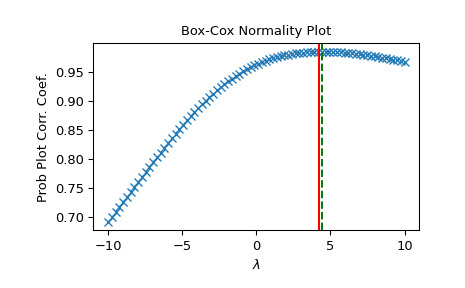
或者,我們可以定義自己的優化器函數。假設我們隻對值感興趣lmbda在區間 [6, 7] 上,我們要使用scipy.optimize.minimize_scalar和
method='bounded',並且我們希望在優化對數似然函數時使用更嚴格的容差。為此,我們定義一個接受位置參數的函數樂趣和用途scipy.optimize.minimize_scalar盡量減少樂趣受限於提供的界限和公差:>>> from scipy import optimize >>> options = {'xatol': 1e-12} # absolute tolerance on `x` >>> def optimizer(fun): ... return optimize.minimize_scalar(fun, bounds=(6, 7), ... method="bounded", options=options) >>> stats.boxcox_normmax(x, optimizer=optimizer) 6.000...
相關用法
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_normplot用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_llf用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boltzmann用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.boschloo_exact用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bootstrap用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bartlett用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.brunnermunzel用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.betaprime用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.betabinom用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic_2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bayes_mvs用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr12用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bws_test用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.beta用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bradford用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binomtest用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic_dd用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom_test用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.bernoulli用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.barnard_exact用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.stats.boxcox_normmax。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
