本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.special.y0_zeros 的用法。
用法:
scipy.special.y0_zeros(nt, complex=False)#計算貝塞爾函數 Y0(z) 的 nt 個零點,以及每個零點處的導數。
每個零 z0 處的導數由 Y0’(z0) = -Y1(z0) 給出。
- nt: int
要返回的零數
- complex: 布爾值,默認為 False
設置為 False 僅返回實數零;設置為 True 僅返回具有負實部和正虛部的複數零。請注意,後者的複共軛也是函數的零,但此例程不返回。
- z0n: ndarray
Y0(z)的第n個零的位置
- y0pz0n: ndarray
第 n 個零的導數 Y0’(z0) 值
參數 ::
返回 ::
參考:
[1]張善傑和金建明。 “特殊函數的計算”,John Wiley and Sons,1996 年,第 5 章。https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/f77_src/special_functions/special_functions.html
例子:
計算 的前 4 個實根和根處的導數:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.special import y0_zeros >>> zeros, grads = y0_zeros(4) >>> with np.printoptions(precision=5): ... print(f"Roots: {zeros}") ... print(f"Gradients: {grads}") Roots: [ 0.89358+0.j 3.95768+0.j 7.08605+0.j 10.22235+0.j] Gradients: [-0.87942+0.j 0.40254+0.j -0.3001 +0.j 0.2497 +0.j]繪製 的實部和前四個計算根。
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.special import y0 >>> xmin = 0 >>> xmax = 11 >>> x = np.linspace(xmin, xmax, 500) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots() >>> ax.hlines(0, xmin, xmax, color='k') >>> ax.plot(x, y0(x), label=r'$Y_0$') >>> zeros, grads = y0_zeros(4) >>> ax.scatter(zeros.real, np.zeros((4, )), s=30, c='r', ... label=r'$Y_0$_zeros', zorder=5) >>> ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 0.6) >>> ax.set_xlim(xmin, xmax) >>> plt.legend(ncol=2) >>> plt.show()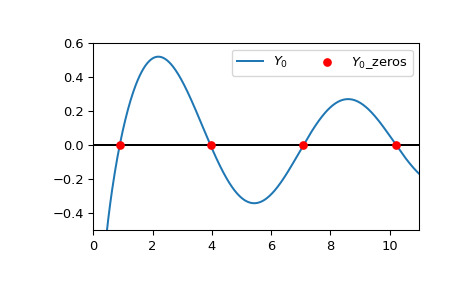
通過設置
complex=True計算 的前 4 個複數根和根處的導數:>>> y0_zeros(4, True) (array([ -2.40301663+0.53988231j, -5.5198767 +0.54718001j, -8.6536724 +0.54841207j, -11.79151203+0.54881912j]), array([ 0.10074769-0.88196771j, -0.02924642+0.5871695j , 0.01490806-0.46945875j, -0.00937368+0.40230454j]))
相關用法
- Python SciPy special.y0用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.y1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ynp_zeros用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.yve用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.yvp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.y1_zeros用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.yn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.y1p_zeros用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.yv用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.yn_zeros用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.exp1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.expn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ncfdtri用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.gamma用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ellip_harm_2用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.i1e用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.smirnovi用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ker用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.k0e用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.j1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.logsumexp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.expit用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.polygamma用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.nbdtrik用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.nbdtrin用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.special.y0_zeros。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
