本文简要介绍 python 语言中 scipy.stats.bayes_mvs 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.bayes_mvs(data, alpha=0.9)#均值、var 和 std 的贝叶斯置信区间。
- data: array_like
输入数据,如果是多维的,则通过
bayes_mvs展平为一维。需要 2 个或更多数据点。- alpha: 浮点数,可选
返回的置信区间包含真实参数的概率。
- mean_cntr, var_cntr, std_cntr: 元组
这三个结果分别是均值、方差和标准差。每个结果都是以下形式的元组:
(center, (lower, upper))和中央给定数据的值的条件 pdf 的平均值,以及(小写大写)以中位数为中心的置信区间,包含对概率的估计
alpha.
参数 ::
返回 ::
注意:
每个均值、方差和标准差估计元组表示(中心,(下,上)),中心是给定数据值的条件 pdf 的平均值,(下,上)是以中位数为中心的置信区间,包含对概率
alpha的估计。将数据转换为一维数据并假设所有数据具有相同的均值和方差。对方差和标准使用 Jeffrey 的先验。
相当于
tuple((x.mean(), x.interval(alpha)) for x in mvsdist(dat))参考:
T.E. Oliphant,“从数据中估计均值、方差和标准差的贝叶斯观点”,https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/facpub/278,2006 年。
例子:
首先是一个演示输出的基本示例:
>>> from scipy import stats >>> data = [6, 9, 12, 7, 8, 8, 13] >>> mean, var, std = stats.bayes_mvs(data) >>> mean Mean(statistic=9.0, minmax=(7.103650222612533, 10.896349777387467)) >>> var Variance(statistic=10.0, minmax=(3.176724206..., 24.45910382...)) >>> std Std_dev(statistic=2.9724954732045084, minmax=(1.7823367265645143, 4.945614605014631))现在我们生成一些正态分布的随机数据,并获得这些估计的 95% 置信区间的均值和标准差估计值:
>>> n_samples = 100000 >>> data = stats.norm.rvs(size=n_samples) >>> res_mean, res_var, res_std = stats.bayes_mvs(data, alpha=0.95)>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111) >>> ax.hist(data, bins=100, density=True, label='Histogram of data') >>> ax.vlines(res_mean.statistic, 0, 0.5, colors='r', label='Estimated mean') >>> ax.axvspan(res_mean.minmax[0],res_mean.minmax[1], facecolor='r', ... alpha=0.2, label=r'Estimated mean (95% limits)') >>> ax.vlines(res_std.statistic, 0, 0.5, colors='g', label='Estimated scale') >>> ax.axvspan(res_std.minmax[0],res_std.minmax[1], facecolor='g', alpha=0.2, ... label=r'Estimated scale (95% limits)')>>> ax.legend(fontsize=10) >>> ax.set_xlim([-4, 4]) >>> ax.set_ylim([0, 0.5]) >>> plt.show()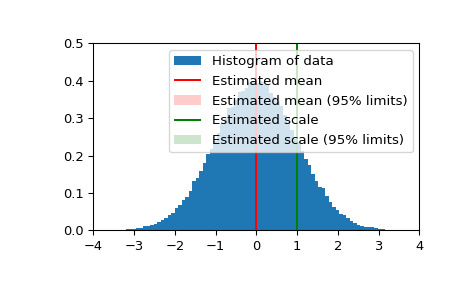
相关用法
- Python SciPy stats.bartlett用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.barnard_exact用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boltzmann用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.brunnermunzel用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.betaprime用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.betabinom用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_normplot用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic_2d用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_normmax用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr12用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boschloo_exact用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.bootstrap用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.burr用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.bws_test用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.beta用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.bradford用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binomtest用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binned_statistic_dd用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.boxcox_llf用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.binom_test用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.bernoulli用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自scipy.org大神的英文原创作品 scipy.stats.bayes_mvs。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
