本文简要介绍 python 语言中 scipy.spatial.HalfspaceIntersection 的用法。
用法:
class scipy.spatial.HalfspaceIntersection(halfspaces, interior_point, incremental=False, qhull_options=None)#N 维的半空间交点。
- halfspaces: 浮点数的ndarray,形状(nineq,ndim+1)
Ax + b <= 0 形式的堆叠不等式,格式为 [A;乙]
- interior_point: 浮点数的ndarray,形状(ndim,)
清楚地指向由半空间定义的区域内。也称为可行点,可以通过线性规划得到。
- incremental: 布尔型,可选
允许增量添加新的半空间。这会占用一些额外的资源。
- qhull_options: str,可选
传递给 Qhull 的其他选项。有关详细信息,请参阅 Qhull 手册。 (默认值:“Qx” 用于 ndim > 4,否则为“”)选项 “H” 始终启用。
- QhullError
当 Qhull 遇到错误条件时引发,例如在未启用解决选项时出现几何退化。
- ValueError
如果将不兼容的数组作为输入给出,则引发。
参数 ::
抛出 ::
注意:
使用 Qhull library 计算交点。这再现了 Qhull 的“qhalf” 函数。
参考:
[1]S. Boyd、L. Vandenberghe,凸优化,可在 http://stanford.edu/~boyd/cvxbook/ 获得
例子:
形成一些多边形的平面的半空间相交
>>> from scipy.spatial import HalfspaceIntersection >>> import numpy as np >>> halfspaces = np.array([[-1, 0., 0.], ... [0., -1., 0.], ... [2., 1., -4.], ... [-0.5, 1., -2.]]) >>> feasible_point = np.array([0.5, 0.5]) >>> hs = HalfspaceIntersection(halfspaces, feasible_point)将半空间绘制为填充区域和交点:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect='equal') >>> xlim, ylim = (-1, 3), (-1, 3) >>> ax.set_xlim(xlim) >>> ax.set_ylim(ylim) >>> x = np.linspace(-1, 3, 100) >>> symbols = ['-', '+', 'x', '*'] >>> signs = [0, 0, -1, -1] >>> fmt = {"color": None, "edgecolor": "b", "alpha": 0.5} >>> for h, sym, sign in zip(halfspaces, symbols, signs): ... hlist = h.tolist() ... fmt["hatch"] = sym ... if h[1]== 0: ... ax.axvline(-h[2]/h[0], label='{}x+{}y+{}=0'.format(*hlist)) ... xi = np.linspace(xlim[sign], -h[2]/h[0], 100) ... ax.fill_between(xi, ylim[0], ylim[1], **fmt) ... else: ... ax.plot(x, (-h[2]-h[0]*x)/h[1], label='{}x+{}y+{}=0'.format(*hlist)) ... ax.fill_between(x, (-h[2]-h[0]*x)/h[1], ylim[sign], **fmt) >>> x, y = zip(*hs.intersections) >>> ax.plot(x, y, 'o', markersize=8)默认情况下,qhull 不提供计算内点的方法。这可以很容易地使用线性规划来计算。考虑 形式的半空间,求解线性程序:
是 A 的行,即每个平面的法线。
将产生一个在凸多面体内部最远的点 x。准确地说,它是多面体中半径为 y 的最大超球面的中心。该点称为多面体的切比雪夫中心(参见 [1] 4.3.1,pp148-149)。 Qhull 输出的方程总是被归一化的。
>>> from scipy.optimize import linprog >>> from matplotlib.patches import Circle >>> norm_vector = np.reshape(np.linalg.norm(halfspaces[:, :-1], axis=1), ... (halfspaces.shape[0], 1)) >>> c = np.zeros((halfspaces.shape[1],)) >>> c[-1] = -1 >>> A = np.hstack((halfspaces[:, :-1], norm_vector)) >>> b = - halfspaces[:, -1:] >>> res = linprog(c, A_ub=A, b_ub=b, bounds=(None, None)) >>> x = res.x[:-1] >>> y = res.x[-1] >>> circle = Circle(x, radius=y, alpha=0.3) >>> ax.add_patch(circle) >>> plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.6, 1.0)) >>> plt.show()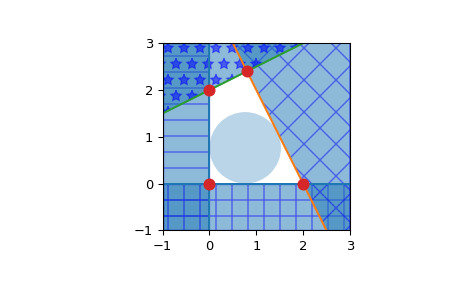
- halfspaces: ndarray of double, shape (nineq, ndim+1)
输入半空格。
- interior_point :ndarray of floats, shape (ndim,):
输入内点。
- intersections: ndarray of double, shape (ninter, ndim)
所有半空间的交点。
- dual_points: ndarray of double, shape (nineq, ndim)
输入半空间的对偶点。
- dual_facets: 整数列表列表
形成双凸包的(不一定是单纯的)面的点的索引。
- dual_vertices: 整数的ndarray,形状(nvertices,)
形成双凸包顶点的半空间索引。对于二维凸包,顶点按逆时针顺序排列。对于其他维度,它们按输入顺序排列。
- dual_equations: ndarray of double, shape (nfacet, ndim+1)
[normal, offset] 形成双面的超平面方程(更多信息请参见Qhull documentation)。
- dual_area: 浮点数
双凸包面积
- dual_volume: 浮点数
双凸包的体积
属性 ::
相关用法
- Python SciPy spatial.tsearch用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.Voronoi用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.procrustes用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.SphericalVoronoi用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.minkowski_distance用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.voronoi_plot_2d用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.minkowski_distance_p用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.geometric_slerp用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.distance_matrix用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.ConvexHull用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.convex_hull_plot_2d用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.Delaunay用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy spatial.delaunay_plot_2d用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.save_npz用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.issparse用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.coo_matrix用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix_csc用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix_csr用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.tril用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.coo_array用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.dia_array用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.bmat用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.hstack用法及代码示例
- Python SciPy sparse.rand用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自scipy.org大神的英文原创作品 scipy.spatial.HalfspaceIntersection。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
