当箭头从原点出现时,罗盘图显示方向或速度矢量。 X、Y 和 Z 在笛卡尔坐标中并绘制在圆形网格上。
用法
compass(X,Y) // It shows the compass plot having n arrows, where n is the number of components in X or Y. The area of the base of each arrow is the origin.
compass(Z) // It displays a compass plot having n arrows, where n is the number of elements in Z.
compass(...,LineSpec) // It draws a compass plot using the line type, marker symbol, and color specified by LineSpec.
h = compass(...)// It returns handles to line objects.示例
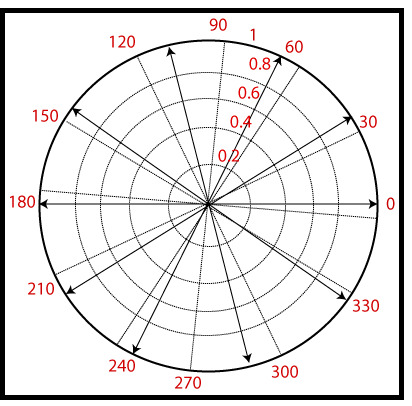
z=cosθ+isinθ,-π≤θ≤π
th=-pi:pi/5:pi;
zx=cos(th);
zy=sin(th);
z=zx+i*zy;
compass(z)输出:
相关用法
- MATLAB comet()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB contour()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB contour3()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB cylinder()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB meshz()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB loglog()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB ribbon()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB Stairs()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB pcolor()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB Bar()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB barh()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB area()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB stem3()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB waterfall()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB quiver()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB slice()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB Semilogy()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB plotyy()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB fill3()用法及代码示例
- MATLAB fill()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 MATLAB compass()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
