本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.stats.truncnorm 的用法。
用法:
scipy.stats.truncnorm = <scipy.stats._continuous_distns.truncnorm_gen object>#截斷的正態連續隨機變量。
作為
rv_continuous類的實例,truncnorm對象從它繼承了一組通用方法(完整列表見下文),並用特定於此特定發行版的詳細信息來完成它們。注意:
該分布是以
loc(默認 0),帶標準差scale(默認 1),並截斷於a和b標準偏差從loc。對於任意loc和scale,a和b是不是平移和縮放分布被截斷的橫坐標。注意
如果
a_trunc和b_trunc是我們希望截斷分布的橫坐標(而不是loc的標準差數),那麽我們可以計算分布參數a和b如下:a, b = (a_trunc - loc) / scale, (b_trunc - loc) / scale這是一個常見的混淆點。如需更多說明,請參閱下麵的示例。
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.stats import truncnorm >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)計算前四個時刻:
>>> a, b = 0.1, 2 >>> mean, var, skew, kurt = truncnorm.stats(a, b, moments='mvsk')顯示概率密度函數(
pdf):>>> x = np.linspace(truncnorm.ppf(0.01, a, b), ... truncnorm.ppf(0.99, a, b), 100) >>> ax.plot(x, truncnorm.pdf(x, a, b), ... 'r-', lw=5, alpha=0.6, label='truncnorm pdf')或者,可以調用分布對象(作為函數)來固定形狀、位置和比例參數。這將返回一個 “frozen” RV 對象,其中包含固定的給定參數。
凍結分布並顯示凍結的
pdf:>>> rv = truncnorm(a, b) >>> ax.plot(x, rv.pdf(x), 'k-', lw=2, label='frozen pdf')檢查
cdf和ppf的準確性:>>> vals = truncnorm.ppf([0.001, 0.5, 0.999], a, b) >>> np.allclose([0.001, 0.5, 0.999], truncnorm.cdf(vals, a, b)) True生成隨機數:
>>> r = truncnorm.rvs(a, b, size=1000)並比較直方圖:
>>> ax.hist(r, density=True, bins='auto', histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.2) >>> ax.set_xlim([x[0], x[-1]]) >>> ax.legend(loc='best', frameon=False) >>> plt.show()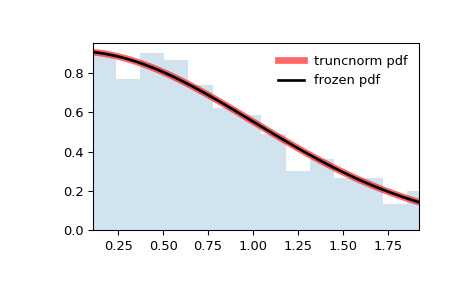
在上麵的示例中,
loc=0和scale=1,因此繪圖在左側的a和右側的b處被截斷。但是,假設我們要使用loc = 1和scale=0.5生成相同的直方圖。>>> loc, scale = 1, 0.5 >>> rv = truncnorm(a, b, loc=loc, scale=scale) >>> x = np.linspace(truncnorm.ppf(0.01, a, b), ... truncnorm.ppf(0.99, a, b), 100) >>> r = rv.rvs(size=1000)>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1) >>> ax.plot(x, rv.pdf(x), 'k-', lw=2, label='frozen pdf') >>> ax.hist(r, density=True, bins='auto', histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.2) >>> ax.set_xlim(a, b) >>> ax.legend(loc='best', frameon=False) >>> plt.show()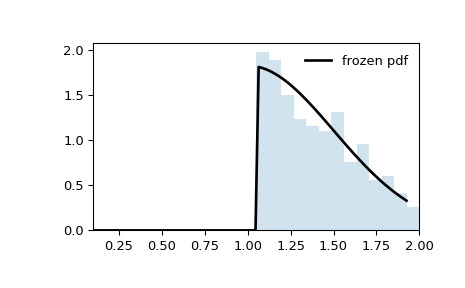
請注意,分布不再在橫坐標處被截斷
a和b。那是因為標準正態分布首先被截斷a和b,然後所得分布按比例縮放scale並移動了loc。如果我們希望將平移和縮放的分布截斷為a和b,我們需要在將這些值作為分布參數傳遞之前對其進行轉換。>>> a_transformed, b_transformed = (a - loc) / scale, (b - loc) / scale >>> rv = truncnorm(a_transformed, b_transformed, loc=loc, scale=scale) >>> x = np.linspace(truncnorm.ppf(0.01, a, b), ... truncnorm.ppf(0.99, a, b), 100) >>> r = rv.rvs(size=10000)>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1) >>> ax.plot(x, rv.pdf(x), 'k-', lw=2, label='frozen pdf') >>> ax.hist(r, density=True, bins='auto', histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.2) >>> ax.set_xlim(a-0.1, b+0.1) >>> ax.legend(loc='best', frameon=False) >>> plt.show()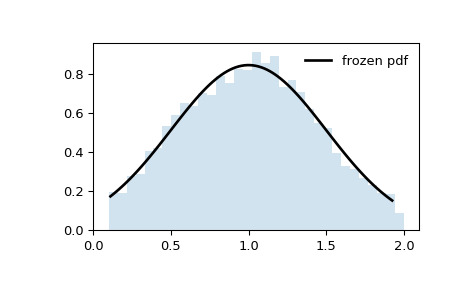
相關用法
- Python SciPy stats.truncpareto用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncweibull_min用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.truncexpon用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.triang用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.trim_mean用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.trim1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.trimboth用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.trapezoid用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.theilslopes用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.t用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_rel用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tvar用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tsem用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_ind_from_stats用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_1samp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.ttest_ind用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmean用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmin用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tmax用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tukeylambda用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tstd用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tiecorrect用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.tukey_hsd用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.iqr用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.stats.truncnorm。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
