本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.special.stdtr 的用法。
用法:
scipy.special.stdtr(df, t, out=None) = <ufunc 'stdtr'>#學生 t 分布 累積分布函數
返回積分:
- df: array_like
自由度
- t: array_like
積分的上限
- out: ndarray,可選
函數結果的可選輸出數組
- 標量或 ndarray
學生 t CDF 在 t 時的值
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
學生 t 分布也可作為
scipy.stats.t獲得。與scipy.stats.t的cdf方法相比,直接調用stdtr可以提高性能(請參見下麵的最後一個示例)。例子:
計算
t=1處df=3的函數。>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.special import stdtr >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> stdtr(3, 1) 0.8044988905221148繪製三個不同自由度的函數。
>>> x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots() >>> parameters = [(1, "solid"), (3, "dashed"), (10, "dotted")] >>> for (df, linestyle) in parameters: ... ax.plot(x, stdtr(df, x), ls=linestyle, label=f"$df={df}$") >>> ax.legend() >>> ax.set_title("Student t distribution cumulative distribution function") >>> plt.show()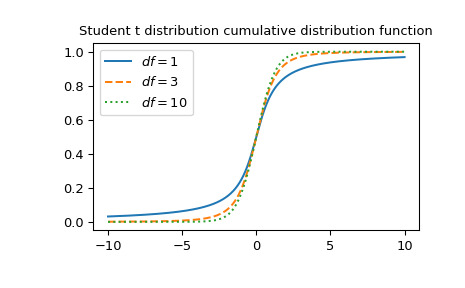
通過為 df 提供 NumPy 數組或列表,可以同時計算多個自由度的函數:
>>> stdtr([1, 2, 3], 1) array([0.75 , 0.78867513, 0.80449889])通過提供數組,可以同時計算多個不同自由度的多個點的函數df和t具有與廣播兼容的形狀。計算
stdtr3 個自由度的 4 個點,形成 3x4 形狀的數組。>>> dfs = np.array([[1], [2], [3]]) >>> t = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8]) >>> dfs.shape, t.shape ((3, 1), (4,))>>> stdtr(dfs, t) array([[0.85241638, 0.92202087, 0.94743154, 0.96041658], [0.90824829, 0.97140452, 0.98666426, 0.99236596], [0.93033702, 0.98599577, 0.99536364, 0.99796171]])t 分布也可用作
scipy.stats.t。直接調用stdtr比調用scipy.stats.t的cdf方法要快得多。為了獲得相同的結果,必須使用以下參數化:scipy.stats.t(df).cdf(x) = stdtr(df, x)。>>> from scipy.stats import t >>> df, x = 3, 1 >>> stdtr_result = stdtr(df, x) # this can be faster than below >>> stats_result = t(df).cdf(x) >>> stats_result == stdtr_result # test that results are equal True
相關用法
- Python SciPy special.stdtridf用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.stdtrit用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.struve用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.stirling2用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.smirnovi用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.seterr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.shichi用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.smirnov用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.softmax用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.sinc用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.sindg用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.spherical_kn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.spherical_yn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.sici用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.spherical_in用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.spherical_jn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.spence用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.exp1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.expn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ncfdtri用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.gamma用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.y1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.y0用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.ellip_harm_2用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.i1e用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.special.stdtr。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
