facet_wrap() 将一维面板序列包装为二维面板。这通常比 facet_grid() 更好地利用屏幕空间,因为大多数显示器大致呈矩形。
用法
facet_wrap(
facets,
nrow = NULL,
ncol = NULL,
scales = "fixed",
shrink = TRUE,
labeller = "label_value",
as.table = TRUE,
switch = deprecated(),
drop = TRUE,
dir = "h",
strip.position = "top"
)参数
- facets
-
由
vars()引用并在行或列维度上定义分面组的一组变量或表达式。可以命名变量(名称传递给labeller)。为了与经典接口兼容,也可以是公式或字符向量。使用单边公式
~a + b或字符向量c("a", "b")。 - nrow, ncol
-
行数和列数。
- scales
-
比例应该是固定的(
"fixed",默认值)、自由的("free")还是一维自由的("free_x"、"free_y")? - shrink
-
如果
TRUE,将缩小比例以适应统计数据的输出,而不是原始数据。如果是FALSE,则为统计汇总前的原始数据范围。 - labeller
-
一种函数,它采用一个标签数据帧并返回字符向量列表或数据帧。每个输入列对应一个因子。因此,将有多个
vars(cyl, am)。每个输出列在条带标签中显示为单独的一行。此函数应继承自 "labeller" S3 类,以便与labeller()兼容。您可以对不同类型的标签使用不同的标签函数,例如使用label_parsed()格式化构面标签。默认情况下使用label_value(),检查它以获取更多详细信息和指向其他选项的指针。 - as.table
-
如果是
TRUE(默认值),则各个方面的布局就像表格一样,最高值位于右下角。如果是FALSE,则各个方面的布局就像绘图一样,最高值位于右上角。 - switch
-
默认情况下,标签显示在图的顶部和右侧。如果
"x",顶部标签将显示在底部。如果是"y",右侧标签将显示在左侧。也可以设置为"both"。 - drop
-
如果默认为
TRUE,则数据中未使用的所有因子水平将自动删除。如果是FALSE,则将显示所有因子水平,无论它们是否出现在数据中。 - dir
-
方向:默认为
"h"表示水平方向,或"v"表示垂直方向。 - strip.position
-
默认情况下,标签显示在图的顶部。使用
strip.position,可以通过设置strip.position = c("top", "bottom", "left", "right")将标签放置在四个侧面的任意一侧
例子
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) + geom_point()
# Use vars() to supply faceting variables:
p + facet_wrap(vars(class))
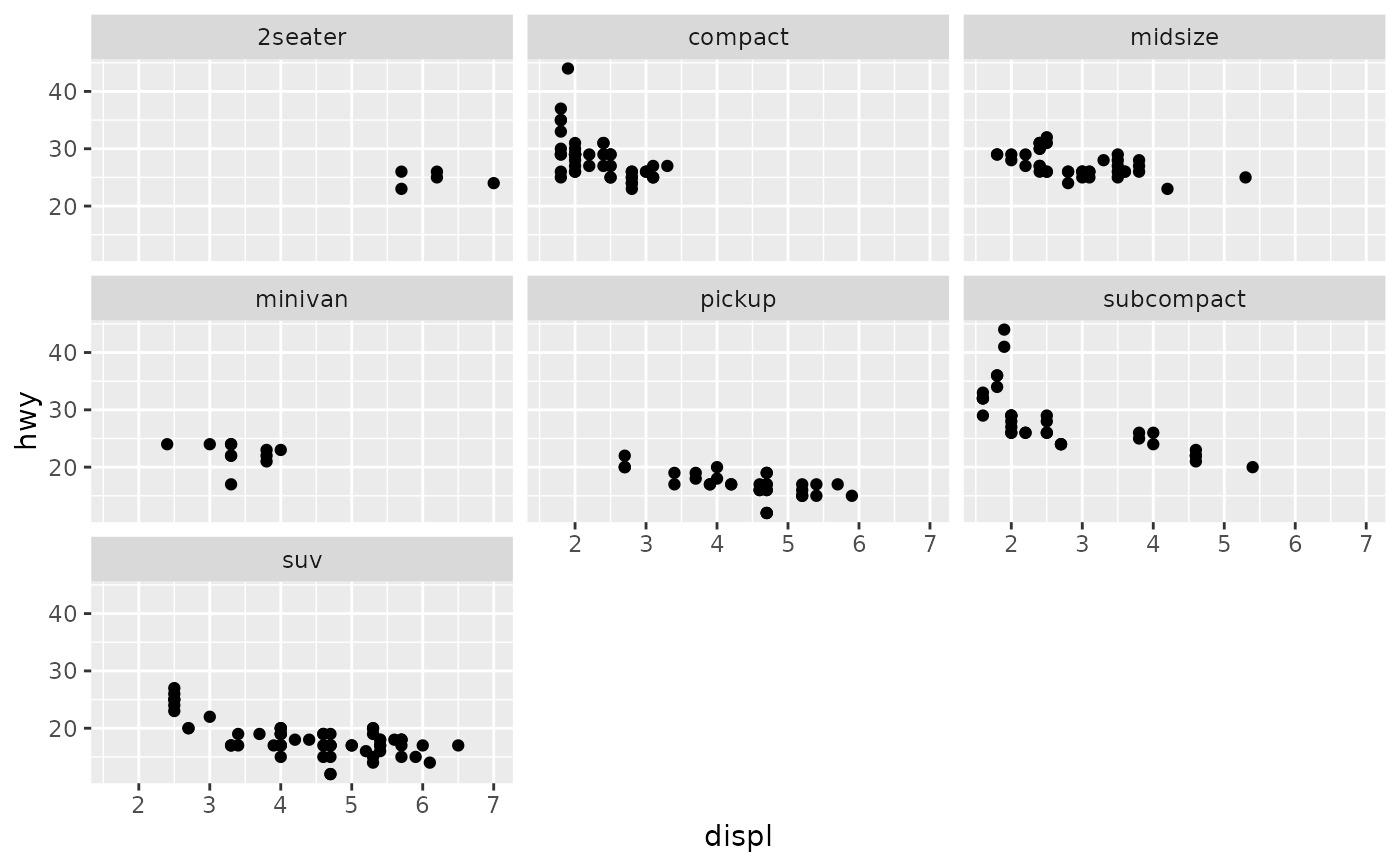 # Control the number of rows and columns with nrow and ncol
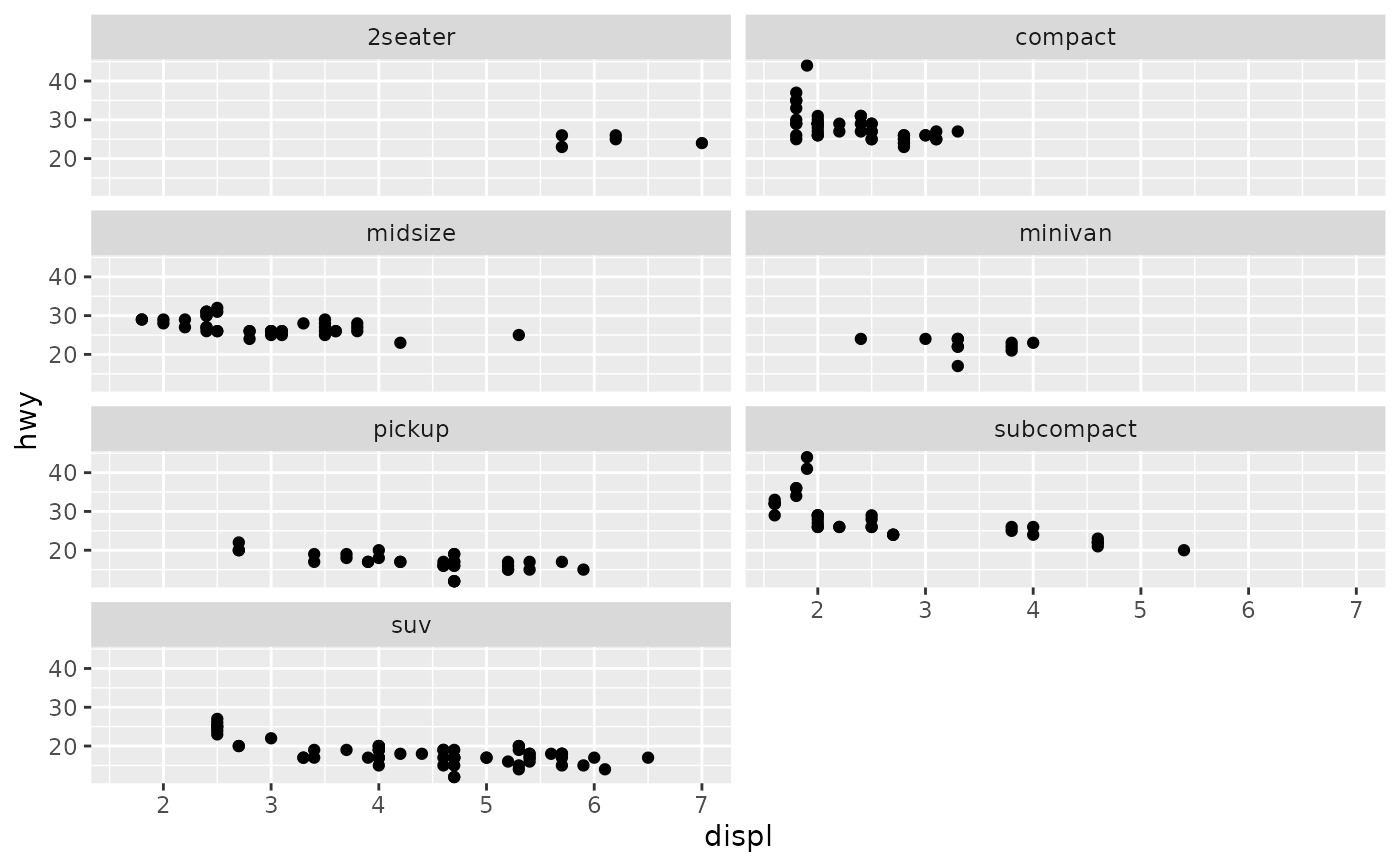
p + facet_wrap(vars(class), nrow = 4)
# Control the number of rows and columns with nrow and ncol
p + facet_wrap(vars(class), nrow = 4)
 # \donttest{
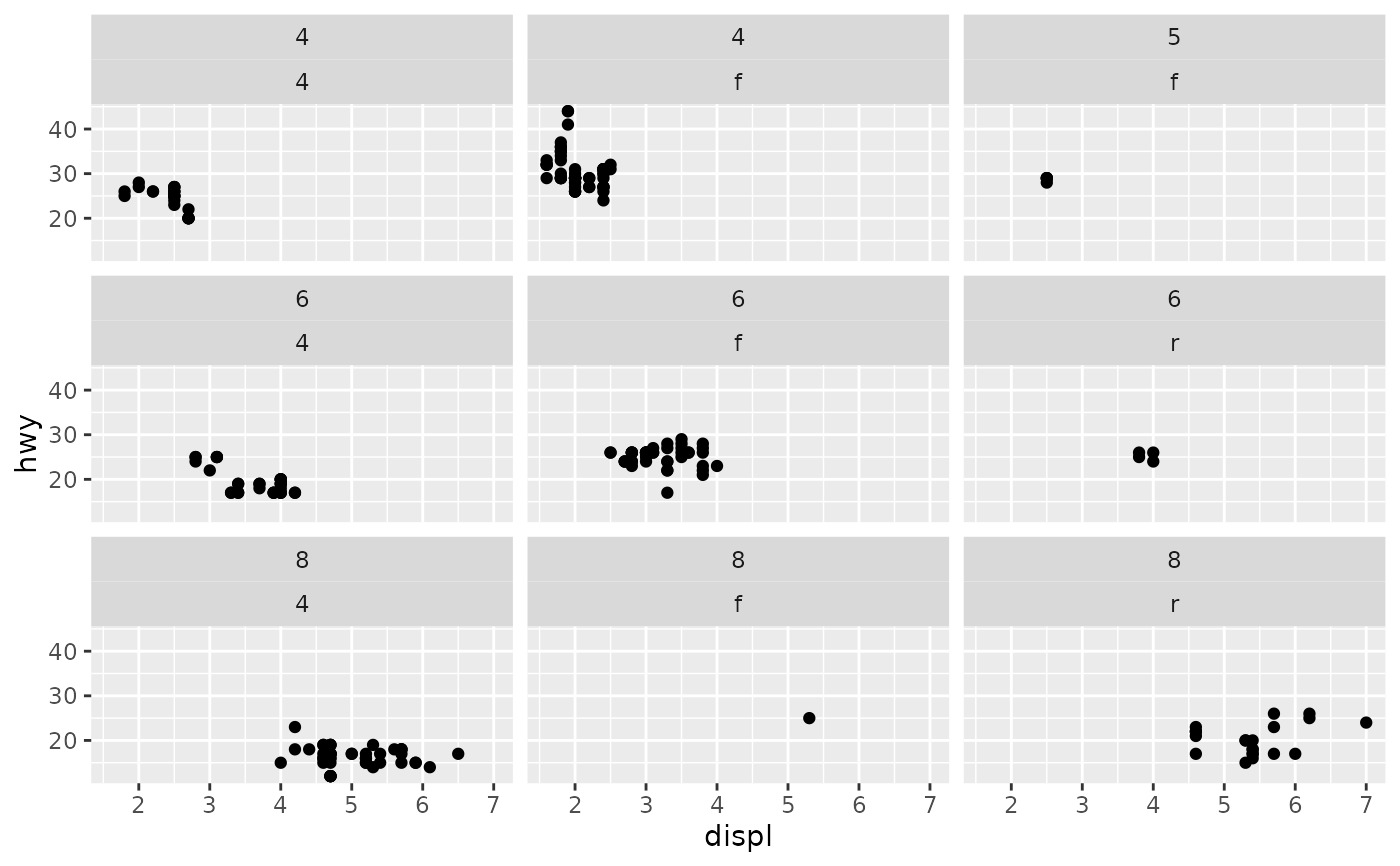
# You can facet by multiple variables
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(cyl, drv))
# \donttest{
# You can facet by multiple variables
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(cyl, drv))
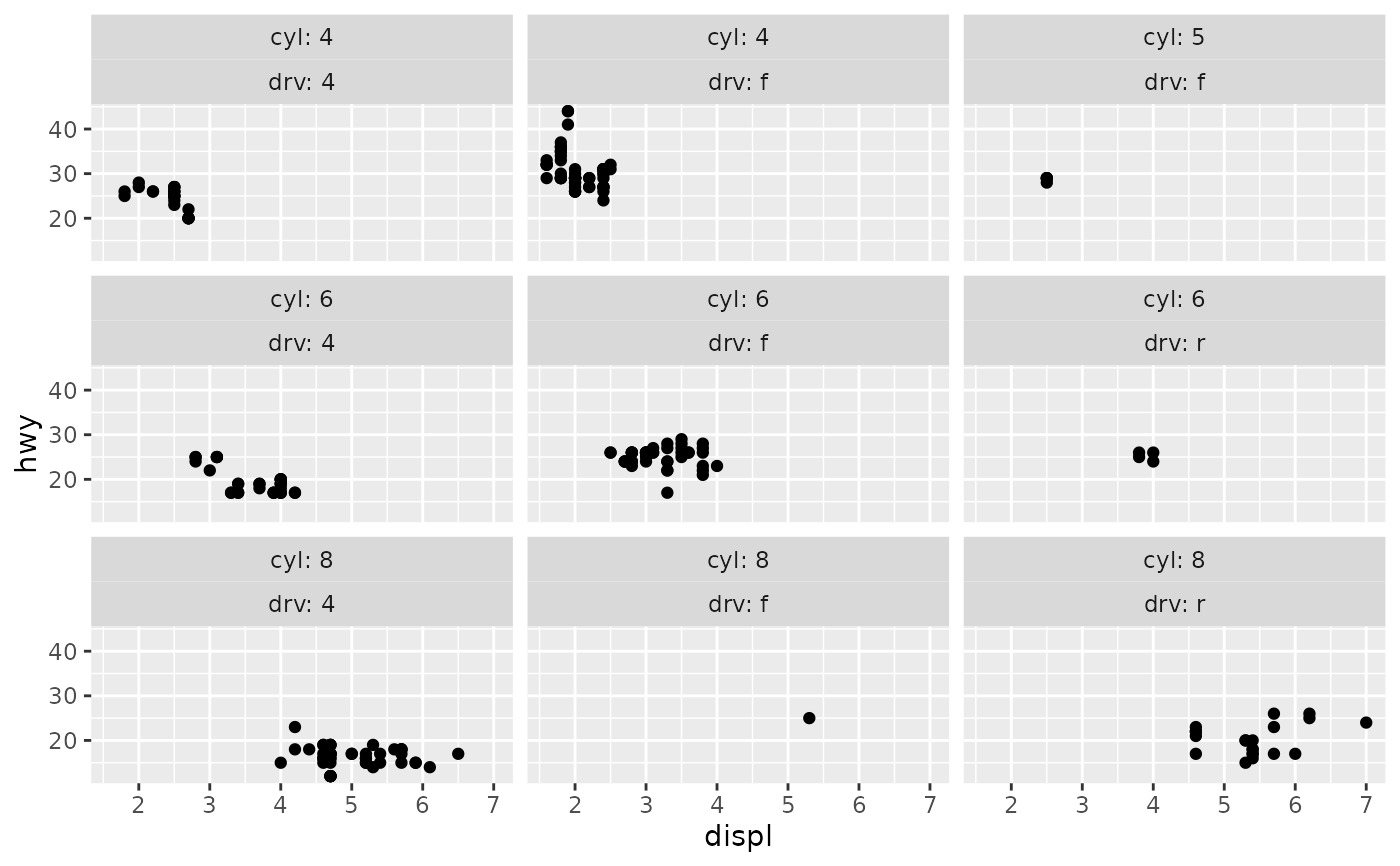
 # Use the `labeller` option to control how labels are printed:
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(cyl, drv), labeller = "label_both")
# Use the `labeller` option to control how labels are printed:
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(cyl, drv), labeller = "label_both")
 # To change the order in which the panels appear, change the levels
# of the underlying factor.
mpg$class2 <- reorder(mpg$class, mpg$displ)
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class2))
# To change the order in which the panels appear, change the levels
# of the underlying factor.
mpg$class2 <- reorder(mpg$class, mpg$displ)
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class2))
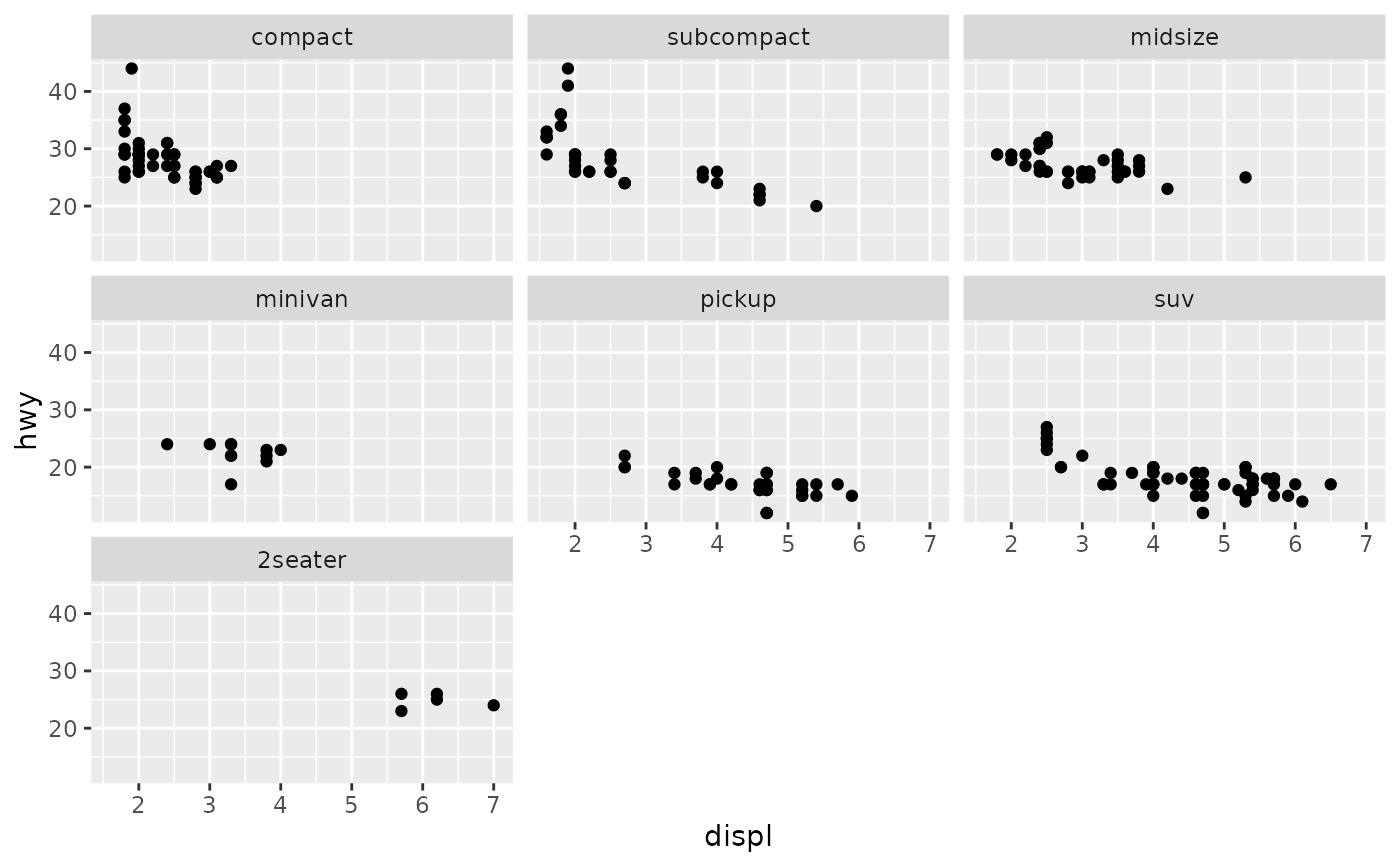 # By default, the same scales are used for all panels. You can allow
# scales to vary across the panels with the `scales` argument.
# Free scales make it easier to see patterns within each panel, but
# harder to compare across panels.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class), scales = "free")
# By default, the same scales are used for all panels. You can allow
# scales to vary across the panels with the `scales` argument.
# Free scales make it easier to see patterns within each panel, but
# harder to compare across panels.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class), scales = "free")
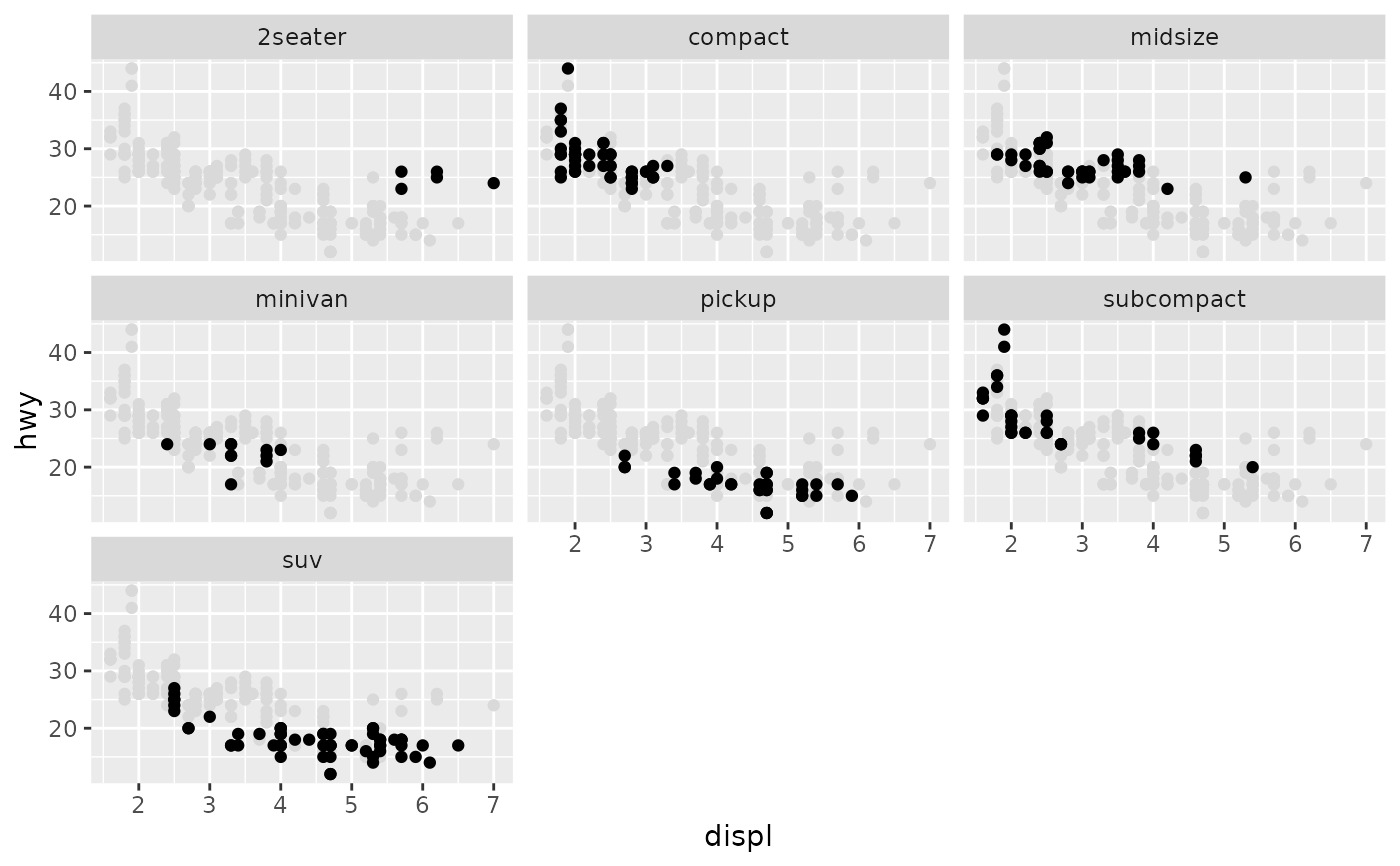
 # To repeat the same data in every panel, simply construct a data frame
# that does not contain the faceting variable.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point(data = transform(mpg, class = NULL), colour = "grey85") +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class))
# To repeat the same data in every panel, simply construct a data frame
# that does not contain the faceting variable.
ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy)) +
geom_point(data = transform(mpg, class = NULL), colour = "grey85") +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(class))
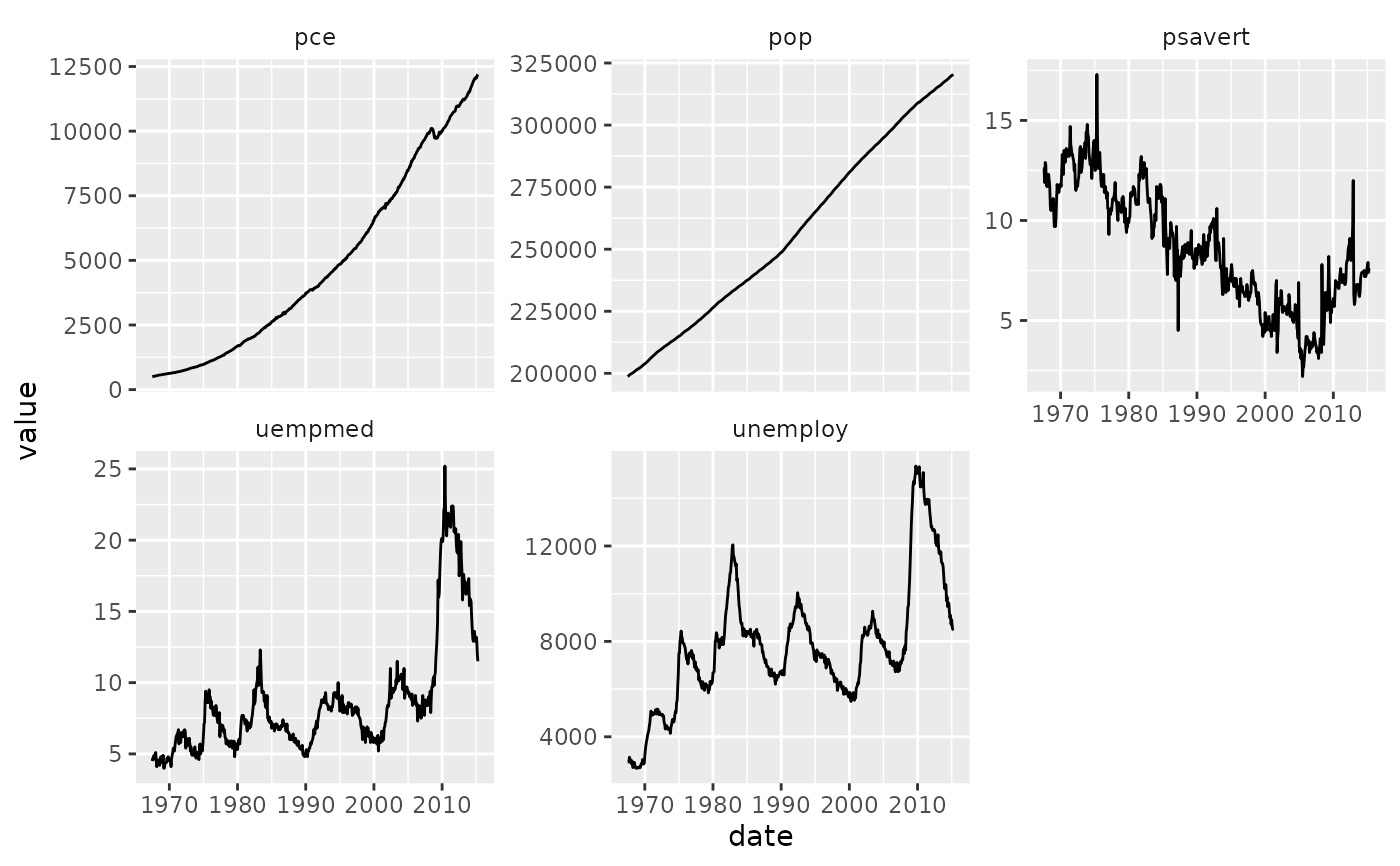
 # Use `strip.position` to display the facet labels at the side of your
# choice. Setting it to `bottom` makes it act as a subtitle for the axis.
# This is typically used with free scales and a theme without boxes around
# strip labels.
ggplot(economics_long, aes(date, value)) +
geom_line() +
facet_wrap(vars(variable), scales = "free_y", nrow = 2, strip.position = "top") +
theme(strip.background = element_blank(), strip.placement = "outside")
# Use `strip.position` to display the facet labels at the side of your
# choice. Setting it to `bottom` makes it act as a subtitle for the axis.
# This is typically used with free scales and a theme without boxes around
# strip labels.
ggplot(economics_long, aes(date, value)) +
geom_line() +
facet_wrap(vars(variable), scales = "free_y", nrow = 2, strip.position = "top") +
theme(strip.background = element_blank(), strip.placement = "outside")
 # }
# }
相关用法
- R ggplot2 facet_grid 将面板布置在网格中
- R ggplot2 fortify.lm 使用模型拟合统计数据补充拟合到线性模型的数据。
- R ggplot2 annotation_logticks 注释:记录刻度线
- R ggplot2 vars 引用分面变量
- R ggplot2 position_stack 将重叠的对象堆叠在一起
- R ggplot2 geom_qq 分位数-分位数图
- R ggplot2 geom_spoke 由位置、方向和距离参数化的线段
- R ggplot2 geom_quantile 分位数回归
- R ggplot2 geom_text 文本
- R ggplot2 get_alt_text 从绘图中提取替代文本
- R ggplot2 annotation_custom 注释:自定义grob
- R ggplot2 geom_ribbon 函数区和面积图
- R ggplot2 stat_ellipse 计算法行数据椭圆
- R ggplot2 resolution 计算数值向量的“分辨率”
- R ggplot2 geom_boxplot 盒须图(Tukey 风格)
- R ggplot2 lims 设置规模限制
- R ggplot2 geom_hex 二维箱计数的六边形热图
- R ggplot2 scale_gradient 渐变色阶
- R ggplot2 scale_shape 形状比例,又称字形
- R ggplot2 geom_bar 条形图
- R ggplot2 draw_key 图例的关键字形
- R ggplot2 annotate 创建注释层
- R ggplot2 label_bquote 带有数学表达式的标签
- R ggplot2 annotation_map 注释:Map
- R ggplot2 scale_viridis 来自 viridisLite 的 Viridis 色标
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Hadley Wickham等大神的英文原创作品 Wrap a 1d ribbon of panels into 2d。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
