本文简要介绍 python 语言中 numpy.random.power 的用法。
用法:
random.power(a, size=None)从具有正 index a - 1 的功率分布中抽取 [0, 1] 中的样本。
也称为幂函数分布。
注意
新代码应改为使用
default_rng()实例的power方法;请参阅快速入门。- a: 浮点数或类似数组的浮点数
分布参数。必须是非负数。
- size: int 或整数元组,可选
输出形状。例如,如果给定的形状是
(m, n, k),则绘制m * n * k样本。如果 size 为None(默认),如果a是标量,则返回单个值。否则,将抽取np.array(a).size样本。
- out: ndarray 或标量
从参数化的功率分布中抽取样本。
- ValueError
如果一个 <= 0。
参数:
返回:
抛出:
注意:
概率密度函数是
幂函数分布正好是帕累托分布的倒数。它也可以看作是 Beta 分布的一个特例。
例如,它用于对保险索赔的over-reporting 建模。
参考:
Christian Kleiber、Samuel Kotz,“经济学和精算学中的统计规模分布”,Wiley,2003 年。
Heckert, N. A. 和 Filliben, James J. “NIST Handbook 148: Dataplot Reference Manual, Volume 2: Let Subcommands and Library Functions”,美国国家标准与技术手册系列,2003 年 6 月。https://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/software/dataplot/refman2/auxillar/powpdf.pdf
1:
2:
例子:
从分布中抽取样本:
>>> a = 5. # shape >>> samples = 1000 >>> s = np.random.power(a, samples)显示样本的直方图以及概率密度函数:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, bins=30) >>> x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100) >>> y = a*x**(a-1.) >>> normed_y = samples*np.diff(bins)[0]*y >>> plt.plot(x, normed_y) >>> plt.show()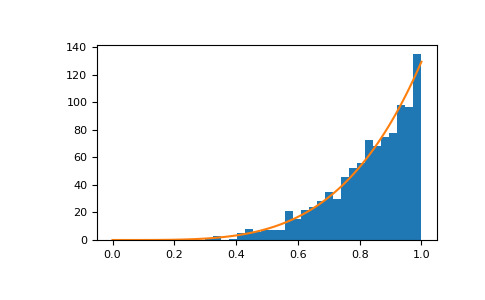
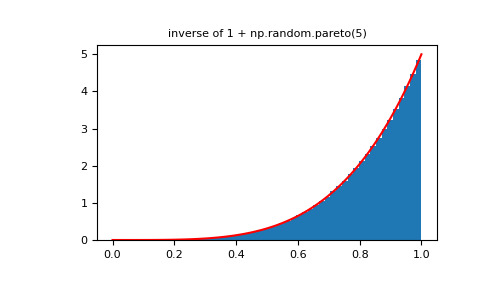
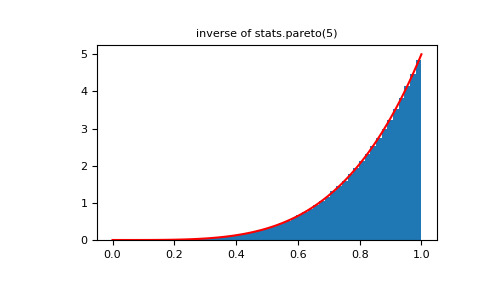
将幂函数分布与 Pareto 的倒数进行比较。
>>> from scipy import stats >>> rvs = np.random.power(5, 1000000) >>> rvsp = np.random.pareto(5, 1000000) >>> xx = np.linspace(0,1,100) >>> powpdf = stats.powerlaw.pdf(xx,5)>>> plt.figure() >>> plt.hist(rvs, bins=50, density=True) >>> plt.plot(xx,powpdf,'r-') >>> plt.title('np.random.power(5)')>>> plt.figure() >>> plt.hist(1./(1.+rvsp), bins=50, density=True) >>> plt.plot(xx,powpdf,'r-') >>> plt.title('inverse of 1 + np.random.pareto(5)')>>> plt.figure() >>> plt.hist(1./(1.+rvsp), bins=50, density=True) >>> plt.plot(xx,powpdf,'r-') >>> plt.title('inverse of stats.pareto(5)')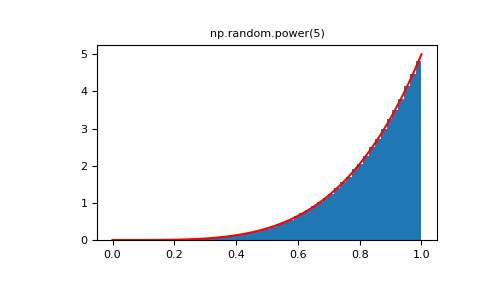
相关用法
- Python numpy random.poisson用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.permutation用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.pareto用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.wald用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.multivariate_normal用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.standard_exponential用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.gumbel用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.multinomial用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.rand用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.logistic用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.shuffle用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.triangular用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.noncentral_f用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.poisson用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.lognormal用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.seed用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.triangular用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.gumbel用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.weibull用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.shuffle用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.geometric用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.multinomial用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.logseries用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.rand用法及代码示例
- Python numpy random.mtrand.RandomState.power用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自numpy.org大神的英文原创作品 numpy.random.power。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
