本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.spatial.Delaunay 的用法。
用法:
class scipy.spatial.Delaunay(points, furthest_site=False, incremental=False, qhull_options=None)#N 維的 Delaunay 細分。
- points: 浮點數數組,形狀(npoints,ndim)
要進行三角剖分的點坐標
- furthest_site: 布爾型,可選
是否計算furthest-site Delaunay 三角剖分。默認值:假
- incremental: 布爾型,可選
允許增量添加新點。這會占用一些額外的資源。
- qhull_options: str,可選
傳遞給 Qhull 的其他選項。有關詳細信息,請參閱 Qhull 手冊。選項“Qt” 始終啟用。默認值:ndim > 4 時為“Qbb Qc Qz Qx Q12”,否則為“Qbb Qc Qz Q12”。增量模式省略“Qz”。
- QhullError
當 Qhull 遇到錯誤條件時引發,例如在未啟用解決選項時出現幾何退化。
- ValueError
如果將不兼容的數組作為輸入給出,則引發。
參數 ::
拋出 ::
注意:
使用 Qhull 庫 Qhull library 計算曲麵細分。
注意
除非您傳入 Qhull 選項 “QJ”,否則 Qhull 不保證每個輸入點在 Delaunay 三角剖分中都顯示為一個頂點。省略的點列在共麵屬性中。
例子:
一組點的三角剖分:
>>> import numpy as np >>> points = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1.1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]) >>> from scipy.spatial import Delaunay >>> tri = Delaunay(points)我們可以繪製它:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.triplot(points[:,0], points[:,1], tri.simplices) >>> plt.plot(points[:,0], points[:,1], 'o') >>> plt.show()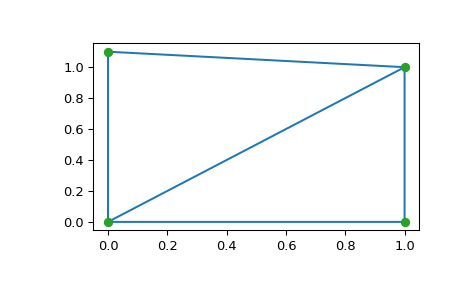
形成三角剖分的兩個三角形的點索引和坐標:
>>> tri.simplices array([[2, 3, 0], # may vary [3, 1, 0]], dtype=int32)請注意,根據舍入誤差的方式,單純形的順序可能與上述不同。
>>> points[tri.simplices] array([[[ 1. , 0. ], # may vary [ 1. , 1. ], [ 0. , 0. ]], [[ 1. , 1. ], [ 0. , 1.1], [ 0. , 0. ]]])三角形 0 是三角形 1 的唯一鄰居,它與三角形 1 的頂點 1 相對:
>>> tri.neighbors[1] array([-1, 0, -1], dtype=int32) >>> points[tri.simplices[1,1]] array([ 0. , 1.1])我們可以找出哪些三角形點在:
>>> p = np.array([(0.1, 0.2), (1.5, 0.5), (0.5, 1.05)]) >>> tri.find_simplex(p) array([ 1, -1, 1], dtype=int32)數組中返回的整數是對應點所在單純形的索引。如果返回 -1,則該點不在單純形中。請注意,以下示例中的快捷方式僅適用於有效點,因為無效點會導致 -1,而 -1 本身就是列表中最後一個單純形的有效索引。
>>> p_valids = np.array([(0.1, 0.2), (0.5, 1.05)]) >>> tri.simplices[tri.find_simplex(p_valids)] array([[3, 1, 0], # may vary [3, 1, 0]], dtype=int32)我們還可以為這些點計算三角形 1 中的重心坐標:
>>> b = tri.transform[1,:2].dot(np.transpose(p - tri.transform[1,2])) >>> np.c_[np.transpose(b), 1 - b.sum(axis=0)] array([[ 0.1 , 0.09090909, 0.80909091], [ 1.5 , -0.90909091, 0.40909091], [ 0.5 , 0.5 , 0. ]])第一個點的坐標均為正值,這意味著它確實在三角形內部。第三個點位於邊上,因此其第三個坐標為空。
- points: ndarray of double, shape (npoints, ndim)
輸入點的坐標。
- simplices: 整數的ndarray,形狀(nsimplex,ndim + 1)
在三角剖分中形成單純形的點的索引。對於二維,點是逆時針方向的。
- neighbors: 整數的ndarray,形狀(nsimplex,ndim + 1)
每個單純形的相鄰單純形的索引。第 k 個鄰居與第 k 個頂點相對。對於邊界處的單純形,-1 表示沒有鄰居。
- equations: ndarray of double, shape (nsimplex, ndim+2)
[正常,偏移] 形成拋物麵上刻麵的超平麵方程(更多信息請參見Qhull documentation)。
- paraboloid_scale, paraboloid_shift: 浮點數
額外拋物麵尺寸的縮放和移動(更多信息請參見Qhull documentation)。
transformndarray of double, shape (nsimplex, ndim+1, ndim)從
x到重心坐標c的仿射變換。vertex_to_simplexndarray int, shape (npoints,)查找數組,從一個頂點到它所屬的某個單純形。
convex_hullndarray int, shape (nfaces, ndim)構成點集凸包的麵的頂點。
- coplanar: int,形狀的ndarray(ncoplanar,3)
共麵點的索引以及最近小平麵和最近頂點的相應索引。共麵點是由於數值精度問題而未包含在三角剖分中的輸入點。
如果未指定選項“Qc”,則不計算此列表。
vertex_neighbor_vertices兩個 int ndarray 的元組; (indptr, index )頂點的相鄰頂點。
- furthest_site:
如果這是最遠的站點三角剖分,則為 True,否則為 False。
屬性 ::
相關用法
- Python SciPy spatial.tsearch用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.Voronoi用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.procrustes用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.SphericalVoronoi用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.minkowski_distance用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.HalfspaceIntersection用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.voronoi_plot_2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.minkowski_distance_p用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.geometric_slerp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.distance_matrix用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.ConvexHull用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.convex_hull_plot_2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy spatial.delaunay_plot_2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.save_npz用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.issparse用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.coo_matrix用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix_csc用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.isspmatrix_csr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.tril用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.coo_array用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.dia_array用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.bmat用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.hstack用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy sparse.rand用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.spatial.Delaunay。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
