Processing, bezierTangent()用法介绍。
用法
bezierTangent(a, b, c, d, t)
参数
a(float)曲线上第一个点的坐标b(float)第一个控制点坐标c(float)第二控制点坐标d(float)曲线上第二点的坐标t(float)0 到 1 之间的值
返回
float
说明
计算贝塞尔曲线上一点的切线。维基百科上有一个很好的切线定义。
例子
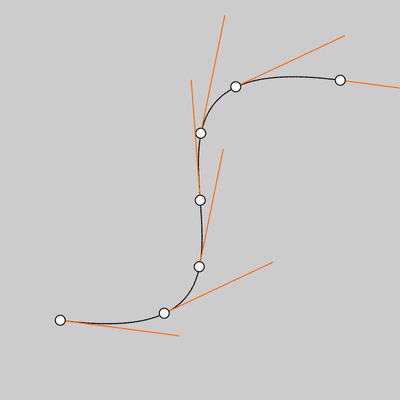
size(400,400);
noFill();
bezier(340, 80, 40, 40, 360, 360, 60, 320);
int steps = 6;
fill(255);
for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) {
float t = i / float(steps);
// Get the location of the point
float x = bezierPoint(340, 40, 360, 60, t);
float y = bezierPoint(80, 40, 360, 320, t);
// Get the tangent points
float tx = bezierTangent(340, 40, 360, 60, t);
float ty = bezierTangent(80, 40, 360, 320, t);
// Calculate an angle from the tangent points
float a = atan2(ty, tx);
a += PI;
stroke(255, 102, 0);
line(x, y, cos(a)*120 + x, sin(a)*120 + y);
// The following line of code makes a line
// inverse of the above line
//line(x, y, cos(a)*-30 + x, sin(a)*-30 + y);
stroke(0);
ellipse(x, y, 10, 10);
}
size(400,400);
noFill();
bezier(340, 80, 40, 40, 360, 360, 60, 320);
stroke(255, 102, 0);
int steps = 16;
for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) {
float t = i / float(steps);
float x = bezierPoint(340, 40, 360, 60, t);
float y = bezierPoint(80, 40, 360, 320, t);
float tx = bezierTangent(340, 40, 360, 60, t);
float ty = bezierTangent(80, 40, 360, 320, t);
float a = atan2(ty, tx);
a -= HALF_PI;
line(x, y, cos(a)*32 + x, sin(a)*32 + y);
}
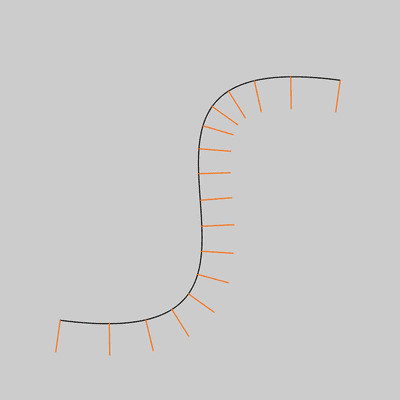
相关用法
- Processing bezierPoint()用法及代码示例
- Processing bezierDetail()用法及代码示例
- Processing bezierVertex()用法及代码示例
- Processing bezier()用法及代码示例
- Processing beginShape()用法及代码示例
- Processing beginRaw()用法及代码示例
- Processing beginRecord()用法及代码示例
- Processing beginCamera()用法及代码示例
- Processing beginContour()用法及代码示例
- Processing box()用法及代码示例
- Processing binary()用法及代码示例
- Processing blendMode()用法及代码示例
- Processing boolean()用法及代码示例
- Processing break用法及代码示例
- Processing boolean用法及代码示例
- Processing background()用法及代码示例
- Processing brightness()用法及代码示例
- Processing blue()用法及代码示例
- Processing byte()用法及代码示例
- Processing blend()用法及代码示例
- Processing byte用法及代码示例
- Processing FFT用法及代码示例
- Processing SawOsc.pan()用法及代码示例
- Processing FloatDict用法及代码示例
- Processing FFT.stop()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自processing.org大神的英文原创作品 bezierTangent()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
