本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.cluster.vq.kmeans 的用法。
用法:
scipy.cluster.vq.kmeans(obs, k_or_guess, iter=20, thresh=1e-05, check_finite=True, *, seed=None)#對形成 k 個簇的一組觀察向量執行 k-means。
k-means 算法將觀測值的分類調整為聚類並更新聚類質心,直到質心的位置在連續迭代中穩定。在該算法的實現中,通過將觀測值與其對應的質心之間的平均歐幾裏得距離變化的絕對值與閾值進行比較來確定質心的穩定性。這產生了將質心映射到代碼的代碼簿,反之亦然。
- obs: ndarray
M×N 數組的每一行都是一個觀察向量。列是每次觀察期間看到的特征。必須首先使用
whiten函數對特征進行白化。- k_or_guess: int 或 ndarray
要生成的質心數。為每個質心分配一個代碼,這也是該質心在生成的code_book 矩陣中的行索引。
通過從觀察矩陣中隨機選擇觀察值來選擇初始 k 個質心。或者,通過 N 數組傳遞 k 指定初始 k 質心。
- iter: 整數,可選
運行k-means的次數,返回失真最低的碼本。如果使用
k_or_guess參數的數組指定初始質心,則忽略此參數。該參數不代表k-means算法的迭代次數。- thresh: 浮點數,可選
如果自上次 k-means 迭代以來的失真變化小於或等於閾值,則終止 k-means 算法。
- check_finite: 布爾型,可選
是否檢查輸入矩陣是否僅包含有限數。禁用可能會提高性能,但如果輸入確實包含無窮大或 NaN,則可能會導致問題(崩潰、非終止)。默認值:真
- seed: {無,int,
numpy.random.Generator,numpy.random.RandomState},可選 用於初始化偽隨機數生成器的種子。如果種子是無(或
numpy.random), 這numpy.random.RandomState使用單例。如果種子是一個 int,一個新的RandomState使用實例,播種種子.如果種子已經是一個Generator或者RandomState實例然後使用該實例。默認值為無。
- codebook: ndarray
由 k 個質心組成的 k × N 數組。第 i 個質心 codebook[i] 用代碼 i 表示。生成的質心和代碼代表看到的最低失真,不一定是全局最小失真。請注意,質心的數量不一定與
k_or_guess參數相同,因為在迭代期間會刪除分配給無觀測值的質心。- distortion: 浮點數
通過的觀測值和生成的質心之間的平均(非平方)歐幾裏得距離。請注意與k-means 算法上下文中失真的標準定義的差異,它是距離平方和。
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
要獲得更多函數或最佳性能,您可以使用 sklearn.cluster.KMeans 。 This 是多個實現的基準測試結果。
例子:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.cluster.vq import vq, kmeans, whiten >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> features = np.array([[ 1.9,2.3], ... [ 1.5,2.5], ... [ 0.8,0.6], ... [ 0.4,1.8], ... [ 0.1,0.1], ... [ 0.2,1.8], ... [ 2.0,0.5], ... [ 0.3,1.5], ... [ 1.0,1.0]]) >>> whitened = whiten(features) >>> book = np.array((whitened[0],whitened[2])) >>> kmeans(whitened,book) (array([[ 2.3110306 , 2.86287398], # random [ 0.93218041, 1.24398691]]), 0.85684700941625547)>>> codes = 3 >>> kmeans(whitened,codes) (array([[ 2.3110306 , 2.86287398], # random [ 1.32544402, 0.65607529], [ 0.40782893, 2.02786907]]), 0.5196582527686241)>>> # Create 50 datapoints in two clusters a and b >>> pts = 50 >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> a = rng.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[4, 1], [1, 4]], size=pts) >>> b = rng.multivariate_normal([30, 10], ... [[10, 2], [2, 1]], ... size=pts) >>> features = np.concatenate((a, b)) >>> # Whiten data >>> whitened = whiten(features) >>> # Find 2 clusters in the data >>> codebook, distortion = kmeans(whitened, 2) >>> # Plot whitened data and cluster centers in red >>> plt.scatter(whitened[:, 0], whitened[:, 1]) >>> plt.scatter(codebook[:, 0], codebook[:, 1], c='r') >>> plt.show()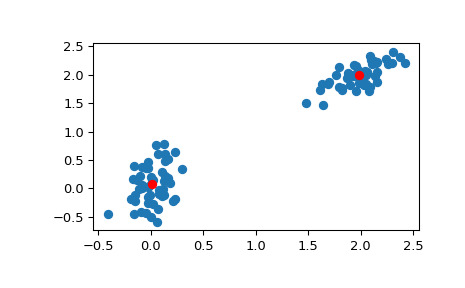
相關用法
- Python SciPy vq.kmeans2用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy vq.whiten用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy vq.vq用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy interpolate.make_interp_spline用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.anderson用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ClusterNode.pre_order用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.iqr用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy FortranFile.read_record用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.correlate用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.exp1用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy special.expn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.czt_points用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy interpolate.krogh_interpolate用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.morphological_gradient用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy distance.sokalmichener用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy linalg.eigvalsh_tridiagonal用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy linalg.cdf2rdf用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy csc_array.diagonal用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy fft.idctn用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy linalg.LaplacianNd用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy linalg.solve_circulant用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy hierarchy.ward用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.chirp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy stats.genpareto用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.variance用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.cluster.vq.kmeans。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
