random 是 NumPy 库中的一个模块。该模块包含用于生成随机数的函数。该模块包含一些简单的随机数据生成方法、一些排列和分布函数以及随机生成器函数。
random 模块中的所有函数如下:
简单的随机数据
简单随机数据有以下函数:
1) p.random.rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)
random 模块的这个函数用于生成给定形状的随机数或值。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.rand(5,2)
a输出:
array([[0.74710182, 0.13306399],
[0.01463718, 0.47618842],
[0.98980426, 0.48390004],
[0.58661785, 0.62895758],
[0.38432729, 0.90384119]])
2) np.random.randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)
random 模块的这个函数从 "standard normal" 分布返回一个样本。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.randn(2,2)
a输出:
array([[ 1.43327469, -0.02019121],
[ 1.54626422, 1.05831067]])
b=np.random.randn()
b
-0.3080190768904835
3) np.random.randint(low[, high, size, dtype])
random模块的这个函数用于生成从inclusive(low)到exclusive(high)的随机整数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.randint(3, size=10)
a输出:
array([1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
4) np.random.random_integers(low[, high, size])
random 模块的这个函数用于生成低和高之间的 np.int 类型的随机整数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.random_integers(3)
a
b=type(np.random.random_integers(3))
b
c=np.random.random_integers(5, size=(3,2))
c输出:
2
<type 'numpy.int32'>
array([[1, 1],
[2, 5],
[1, 3]])
5) np.random.random_sample([大小])
random 模块的该函数用于在半开区间 [0.0, 1.0) 内生成随机浮点数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.random_sample()
a
b=type(np.random.random_sample())
b
c=np.random.random_sample((5,))
c输出:
0.09250360565571492 <type 'float'> array([0.34665418, 0.47027209, 0.75944969, 0.37991244, 0.14159746])
6) np.random.random([大小])
random 模块的该函数用于在半开区间 [0.0, 1.0) 内生成随机浮点数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.random()
a
b=type(np.random.random())
b
c=np.random.random((5,))
c输出:
0.008786953974334155 <type 'float'> array([0.05530122, 0.59133394, 0.17258794, 0.6912388 , 0.33412534])
7) np.random.ranf([大小])
random 模块的该函数用于在半开区间 [0.0, 1.0) 内生成随机浮点数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.ranf()
a
b=type(np.random.ranf())
b
c=np.random.ranf((5,))
c输出:
0.2907792098474542 <type 'float'> array([0.34084881, 0.07268237, 0.38161256, 0.46494681, 0.88071377])
8) np.random.sample([大小])
random 模块的该函数用于在半开区间 [0.0, 1.0) 内生成随机浮点数。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.sample()
a
b=type(np.random.sample())
b
c=np.random.sample((5,))
c输出:
0.012298209913766511 <type 'float'> array([0.71878544, 0.11486169, 0.38189074, 0.14303308, 0.07217287])
9) np.random.choice(a[, size, replace, p])
random 模块的这个函数用于从给定的一维数组中生成随机样本。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.choice(5,3)
a
b=np.random.choice(5,3, p=[0.2, 0.1, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1])
b输出:
array([0, 3, 4]) array([2, 2, 2], dtype=int64)
10)np.random.bytes(长度)
random 模块的这个函数用于生成随机字节。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.bytes(7)
a输出:
'nQ\x08\x83\xf9\xde\x8a'
排列
排列的函数如下:
1) np.random.shuffle()
此函数用于通过改组其内容来就地修改序列。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.arange(12)
a
np.random.shuffle(a)
a输出:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) array([10, 3, 2, 4, 5, 8, 0, 9, 1, 11, 7, 6])
2) np.random.permutation()
此函数随机排列一个序列或返回一个排列后的范围。
例:
import numpy as np
a=np.random.permutation(12)
a输出:
array([ 8, 7, 3, 11, 6, 0, 9, 10, 2, 5, 4, 1])
分布
排列的函数如下:
1) beta(a, b[, size])
此函数用于从 Beta 分布中抽取样本。
例:
def setup(self):
self.dist = dist.beta
self.cargs = []
self.ckwd = dict(alpha=2, beta=3)
self.np_rand_fxn = numpy.random.beta
self.np_args = [2, 3]
self.np_kwds = dict()2) 二项式(n, p[, size])
此函数用于从二项分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
n, p = 10, .6
s1= np.random.binomial(n, p, 10)
s1输出:
array([6, 7, 7, 9, 3, 7, 8, 6, 6, 4])
3) chisquare(df[, size])
此函数用于从二项分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
np.random.chisquare(2,4)
sum(np.random.binomial(9, 0.1, 20000) == 0)/20000.输出:
array([6, 7, 7, 9, 3, 7, 8, 6, 6, 4])
4)狄利克雷(阿尔法[,大小])
此函数用于从 Dirichlet 分布中抽取样本。
例:
Import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
s1 = np.random.dirichlet((10, 5, 3), 20).transpose()
plt.barh(range(20), s1[0])
plt.barh(range(20), s1[1], left=s1[0], color='g')
plt.barh(range(20), s1[2], left=s1[0]+s1[1], color='r')
plt.title("Lengths of Strings")
plt.show()输出:
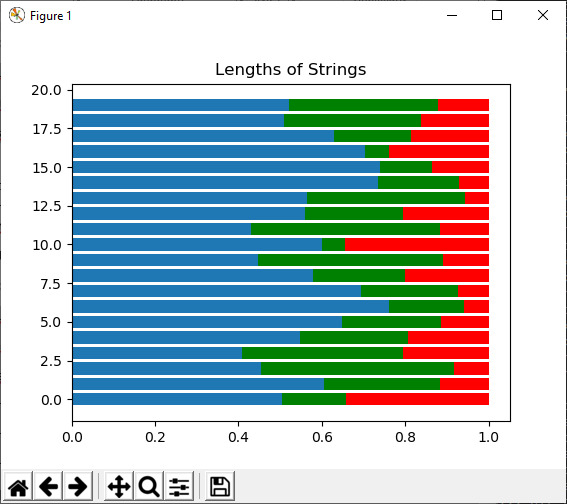
5) index ([比例,大小])
此函数用于从 index 分布中抽取样本。
例:
def __init__(self, sourceid, targetid):
self.__type = 'Transaction'
self.id = uuid4()
self.source = sourceid
self.target = targetid
self.date = self._datetime.date(start=2015, end=2019)
self.time = self._datetime.time()
if random() < 0.05:
self.amount = self._numbers.between(100000, 1000000)
self.amount = npr.exponential(10)
if random() < 0.15:
self.currency = self._business.currency_iso_code()
else:
self.currency = None6) f(dfnum, dfden[, size])
该函数用于从 F 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
dfno= 1.
dfden = 48.
s1 = np.random.f(dfno, dfden, 10)
np.sort(s1)输出:
array([0.00264041, 0.04725478, 0.07140803, 0.19526217, 0.23979 ,
0.24023478, 0.63141254, 0.95316446, 1.40281789, 1.68327507])
7)伽玛(形状[,比例,大小])
此函数用于从 Gamma 分布中抽取样本
例:
import numpy as np
shape, scale = 2., 2.
s1 = np.random.gamma(shape, scale, 1000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.special as spss
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True)
a = bins**(shape-1)*(np.exp(-bins/scale) /
(spss.gamma(shape)*scale**shape))
plt.plot(bins, a, linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()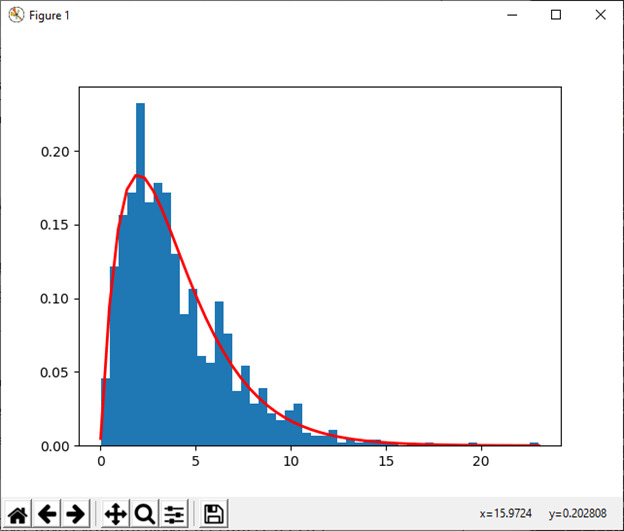
8)几何(p [,大小])
该函数用于从几何分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
a = np.random.geometric(p=0.35, size=10000)
(a == 1).sum() / 1000输出:
3.
9)gumbel([位置,比例,大小])
此函数用于从 Gumble 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
lov, scale = 0, 0.2
s1 = np.random.gumbel(loc, scale, 1000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 30, density=True)
plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*np.exp(-(bins - loc)/beta)* np.exp( -np.exp( -(bins - loc) /beta) ),linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
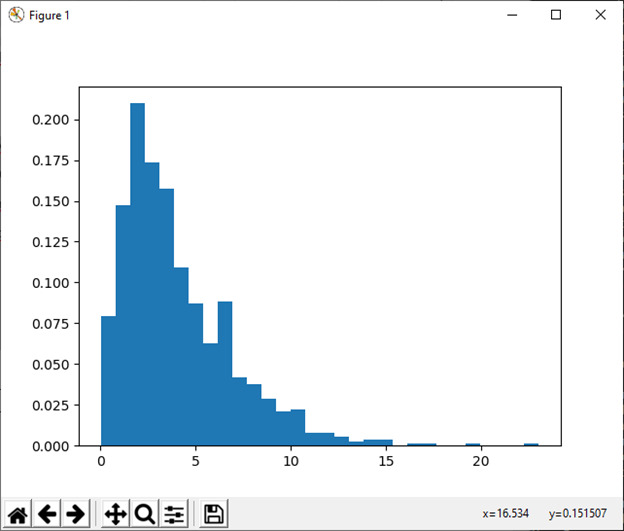
10) 超几何(ngood, nbad, nsample[, size])
此函数用于从超几何分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
good, bad, samp = 100, 2, 10
s1 = np.random.hypergeometric(good, bad, samp, 1000)
plt.hist(s1)
plt.show()输出:
(array([ 13., 0., 0., 0., 0., 163., 0., 0., 0., 824.]), array([ 8. , 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8, 9. , 9.2, 9.4, 9.6, 9.8, 10. ]), <a list of 10 Patch objects>)
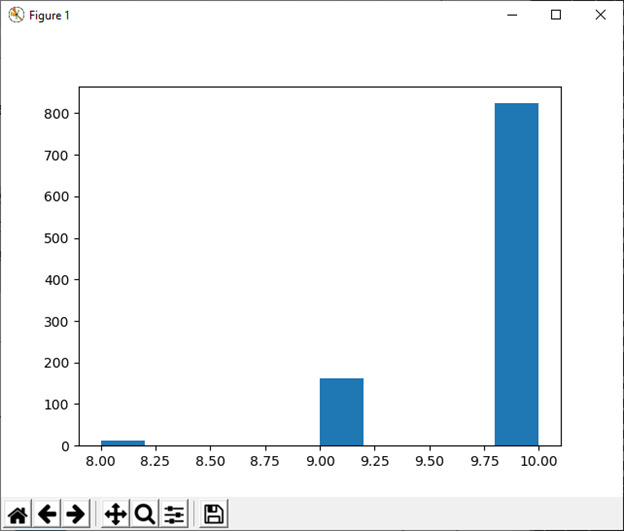
11) laplace([位置,比例,大小])
该函数用于从具有指定位置和尺度的拉普拉斯或双 index 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
location, scale = 0., 2.
s = np.random.laplace(location, scale, 10)
s输出:
array([-2.77127948, -1.46401453, -0.03723516, -1.61223942, 2.29590691,
1.74297722, 1.49438411, 0.30325513, -0.15948891, -4.99669747])
12) 逻辑([位置,比例,大小])
该函数用于从逻辑分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
location, scale = 10, 1
s1 = np.random.logistic(location, scale, 10000)
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=50)
count
bins
ignored
plt.show()输出:
array([1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 1.000e+00,
1.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 7.000e+00, 1.100e+01, 1.800e+01, 3.500e+01,
5.300e+01, 6.700e+01, 1.150e+02, 1.780e+02, 2.300e+02, 3.680e+02,
4.910e+02, 6.400e+02, 8.250e+02, 9.100e+02, 9.750e+02, 1.039e+03,
9.280e+02, 8.040e+02, 6.530e+02, 5.240e+02, 3.380e+02, 2.470e+02,
1.650e+02, 1.150e+02, 8.500e+01, 6.400e+01, 3.300e+01, 1.600e+01,
2.400e+01, 1.400e+01, 4.000e+00, 5.000e+00, 2.000e+00, 2.000e+00,
1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00,
0.000e+00, 1.000e+00])
array([ 0.50643911, 0.91891814, 1.33139717, 1.7438762 , 2.15635523,
2.56883427, 2.9813133 , 3.39379233, 3.80627136, 4.2187504 ,
4.63122943, 5.04370846, 5.45618749, 5.86866652, 6.28114556,
6.69362459, 7.10610362, 7.51858265, 7.93106169, 8.34354072,
8.75601975, 9.16849878, 9.58097781, 9.99345685, 10.40593588,
10.81841491, 11.23089394, 11.64337298, 12.05585201, 12.46833104,
12.88081007, 13.2932891 , 13.70576814, 14.11824717, 14.5307262 ,
14.94320523, 15.35568427, 15.7681633 , 16.18064233, 16.59312136,
17.00560039, 17.41807943, 17.83055846, 18.24303749, 18.65551652,
19.06799556, 19.48047459, 19.89295362, 20.30543265, 20.71791168,
21.13039072])
<a list of 50 Patch objects>
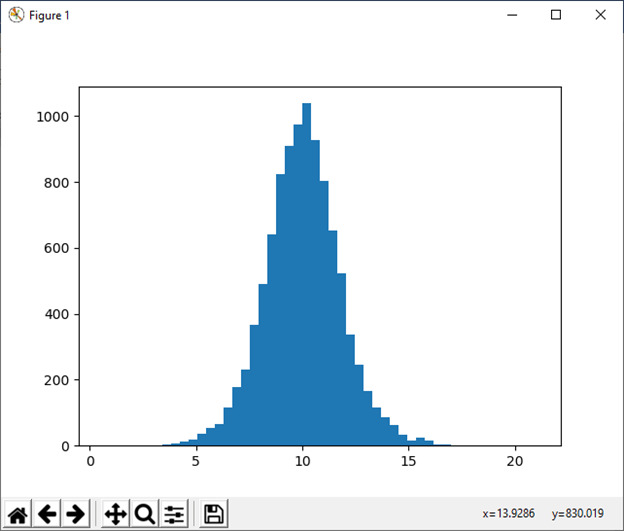
13)对数正态([均值,西格玛,大小])
该函数用于从 log-normal 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
mu, sigma = 2., 1.
s1 = np.random.lognormal(mu, sigma, 1000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True, align='mid')
a = np.linspace(min(bins), max(bins), 10000)
pdf = (np.exp(-(np.log(a) - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2))/ (a * sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)))
plt.plot(a, pdf, linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()输出:
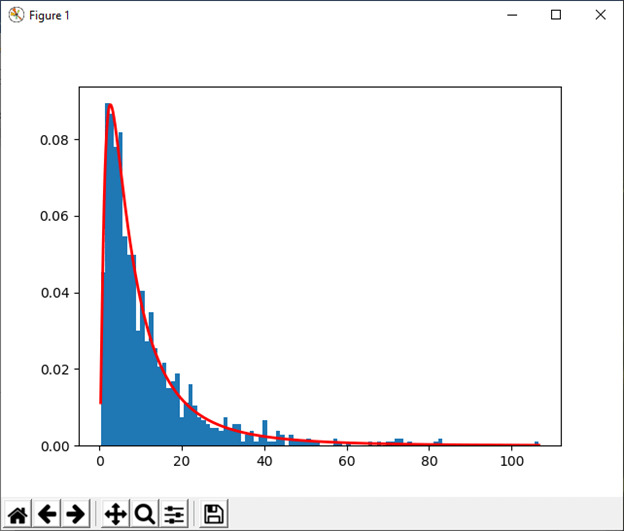
14) 日志系列(p[, 大小])
此函数用于从对数分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
x = .6
s1 = np.random.logseries(x, 10000)
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1)
def logseries(k, p):
return -p**k/(k*log(1-p))
plt.plot(bins, logseries(bins, x)*count.max()/logseries(bins, a).max(), 'r')
plt.show()输出:
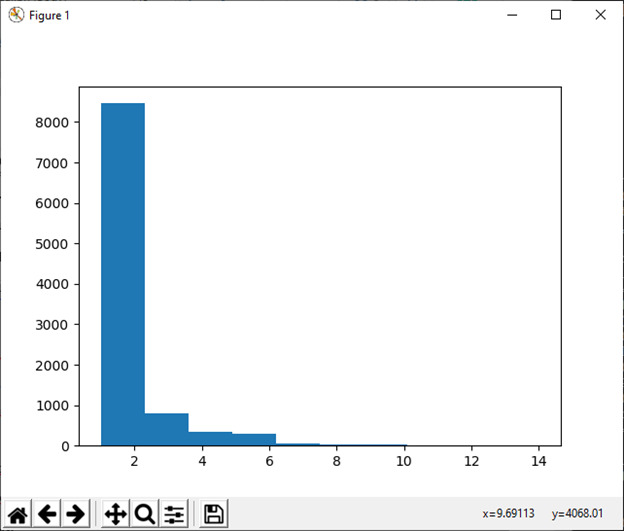
15) 多项式(n, pvals[, size])
此函数用于从多项分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
np.random.multinomial(20, [1/6.]*6, size=1)输出:
array([[4, 2, 5, 5, 3, 1]])
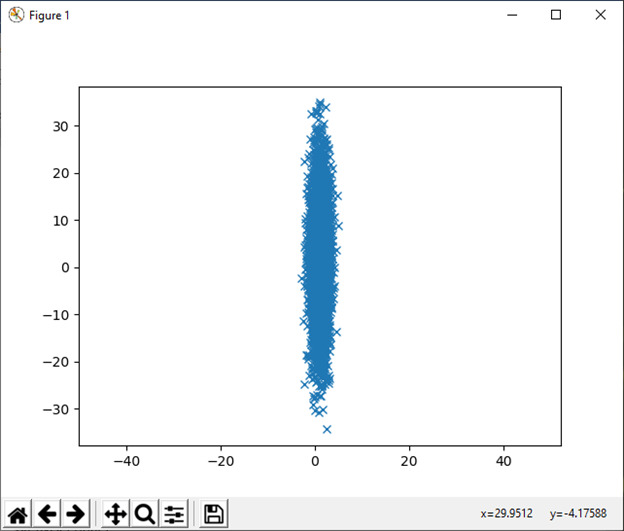
16)multivariate_normal(平均值,cov[,大小,...)
该函数用于从多元正态分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
mean = (1, 2)
coveriance = [[1, 0], [0, 100]]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a, b = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, coveriance, 5000).T
plt.plot(a, b, 'x')
plt.axis('equal'023
030
)
plt.show()输出:
17) negative_binomial(n, p[, 大小])
此函数用于从负二项式分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
s1 = np.random.negative_binomial(1, 0.1, 100000)
for i in range(1, 11):
probability = sum(s1<i) / 100000.
print i, "wells drilled, probability of one success =", probability输出:
1 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 2 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 3 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 4 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 5 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 6 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 7 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 8 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 9 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0 10 wells drilled, probability of one success = 0
18) noncentral_chisquare(df, nonc[, size])
此函数用于从非中心 chi-square 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
val = plt.hist(np.random.noncentral_chisquare(3, 25, 100000), bins=200, normed=True)
plt.show()输出:
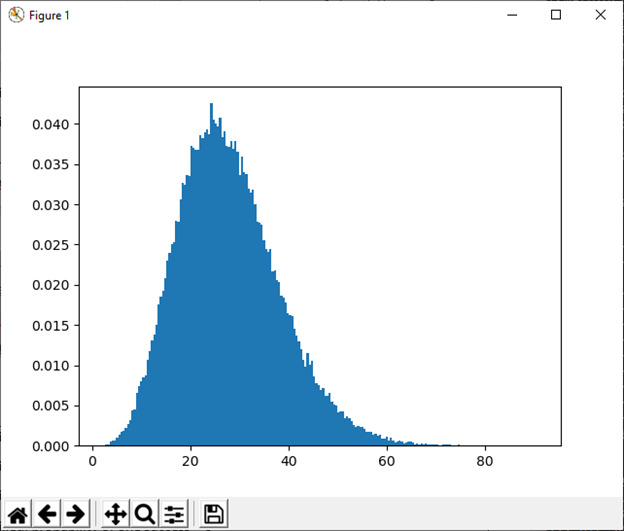
19)正常([位置,比例,大小])
此函数用于从正态分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mu, sigma = 0, 0.2 # mean and standard deviation
s1 = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 1000)
abs(mu - np.mean(s1)) < 0.01
abs(sigma - np.std(s1, ddof=1)) < 0.01
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 30, density=True)
plt.plot(bins, 1/(sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)) *np.exp( - (bins - mu)**2 / (2 * sigma**2) ), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
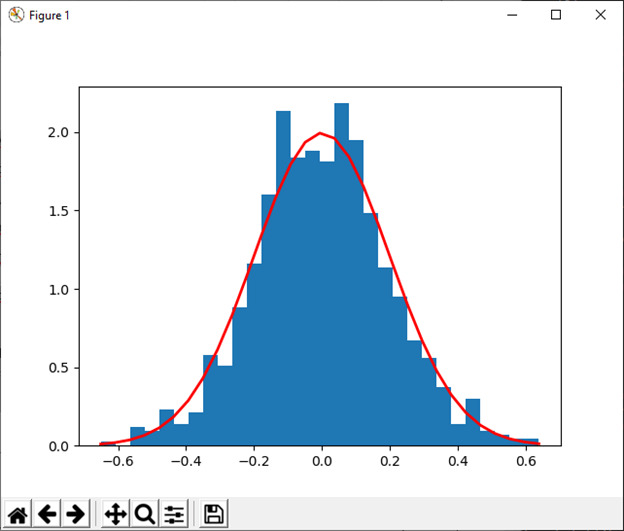
20) 帕累托 (a[, 大小])
此函数用于从具有指定形状的 Lomax 或 Pareto II 中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
b, m1 = 3., 2. # shape and mode
s1 = (np.random.pareto(b, 1000) + 1) * m1
count, bins, _ = plt.hist(s1, 100, density=True)
fit = b*m**b / bins**(b+1)
plt.plot(bins, max(count)*fit/max(fit), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
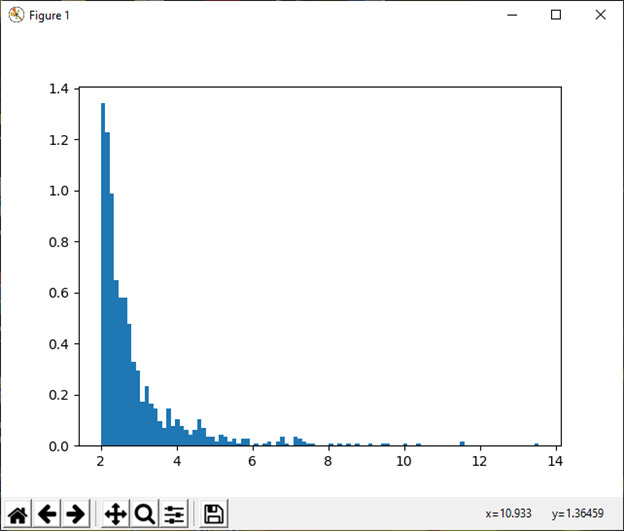
21) 功率(a[, 大小])
此函数用于从具有正 index a-1 的幂分布中抽取 [0, 1] 中的样本。
例:
import numpy as np
x = 5. # shape
samples = 1000
s1 = np.random.power(x, samples)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, bins=30)
a = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
b = x*a**(x-1.)
density_b = samples*np.diff(bins)[0]*b
plt.plot(a, density_b)
plt.show()输出:
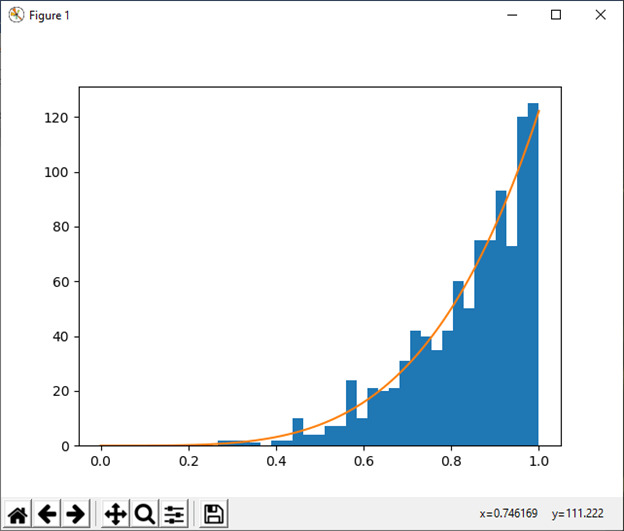
22) rayleigh([比例, 大小])
此函数用于从瑞利分布中抽取样本。
例:
val = hist(np.random.rayleigh(3, 100000), bins=200, density=True)
meanval = 1
modeval = np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * meanval
s1 = np.random.rayleigh(modeval, 1000000)
100.*sum(s1>3)/1000000.输出:
0.087300000000000003
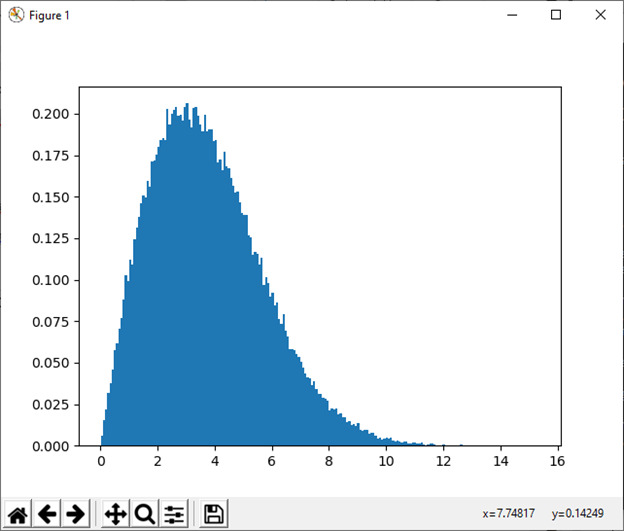
23) standard_cauchy([尺寸])
该函数用于从众数=0 的标准柯西分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
s1 = np.random.standard_cauchy(1000000)
s1 = s1[(s1>-25) & (s1<25)] # truncate distribution so it plots well
plt.hist(s1, bins=100)
plt.show()输出:
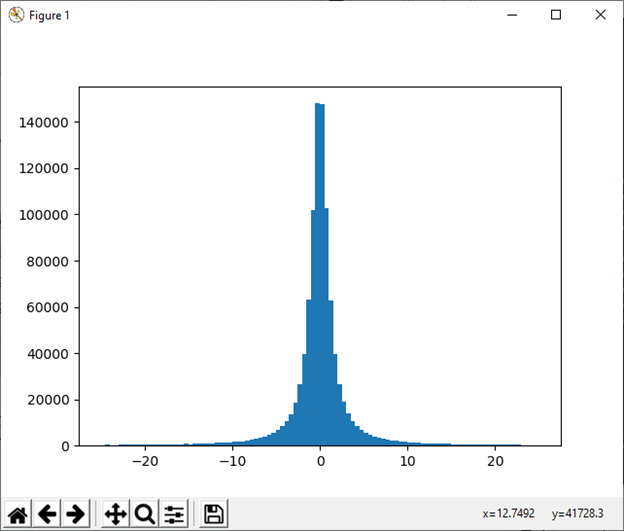
24) standard_exponential([尺寸])
此函数用于从标准 index 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
n = np.random.standard_exponential((2, 7000))输出:
array([[0.53857931, 0.181262 , 0.20478701, ..., 3.66232881, 1.83882709,
1.77963295],
[0.65163973, 1.40001955, 0.7525986 , ..., 0.76516523, 0.8400617 ,
0.88551011]])
25) standard_gamma([尺寸])
此函数用于从标准 Gamma 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
shape, scale = 2., 1.
s1 = np.random.standard_gamma(shape, 1000000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.special as sps
count1, bins1, ignored1 = plt.hist(s, 50, density=True)
y = bins1**(shape-1) * ((np.exp(-bins1/scale))/ (sps.gamma(shape) * scale**shape))
plt.plot(bins1, y, linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
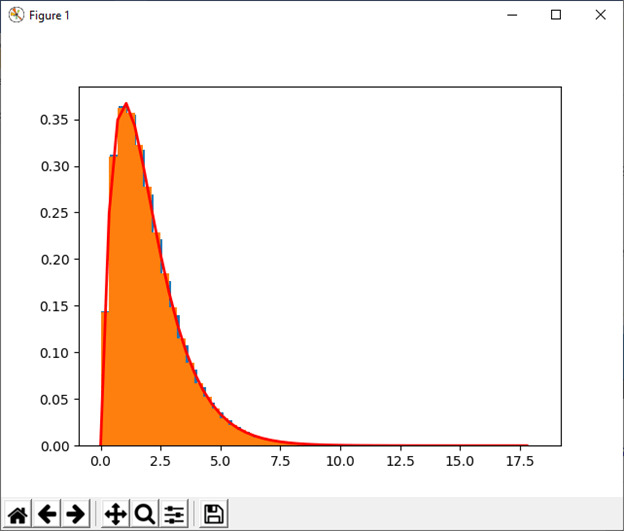
26) standard_normal([尺寸])
此函数用于从标准正态分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
s1= np.random.standard_normal(8000)
s1
q = np.random.standard_normal(size=(3, 4, 2))
q输出:
array([-3.14907597, 0.95366265, -1.20100026, ..., 3.47180222,
0.9608679 , 0.0774319 ])
array([[[ 1.55635461, -1.29541713],
[-1.50534663, -0.02829194],
[ 1.03949348, -0.26128132],
[ 1.51921798, 0.82136178]],
[[-0.4011052 , -0.52458858],
[-1.31803814, 0.37415379],
[-0.67077365, 0.97447018],
[-0.20212115, 0.67840888]],
[[ 1.86183474, 0.19946562],
[-0.07376021, 0.84599701],
[-0.84341386, 0.32081667],
[-3.32016062, -1.19029818]]])
27) 标准_t(df[, 大小])
此函数用于从具有 df 自由度的标准学生分布中抽取样本。
例:
intake = np.array([5260., 5470, 5640, 6180, 6390, 6515, 6805, 7515,8230,8770])
s1 = np.random.standard_t(10, size=100000)
np.mean(intake)
intake.std(ddof=1)
t = (np.mean(intake)-7725)/(intake.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(len(intake)))
h = plt.hist(s1, bins=100, density=True)
np.sum(s1<t) / float(len(s1))
plt.show()输出:
6677.5 1174.1101831694598 0.00864
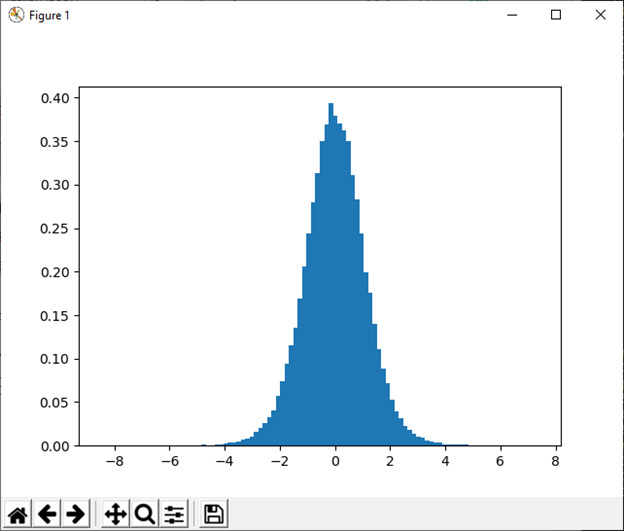
28)三角形(左,模式,右[,大小])
此函数用于从区间上的三角形分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
h = plt.hist(np.random.triangular(-4, 0, 8, 1000000), bins=300,density=True)
plt.show()输出:
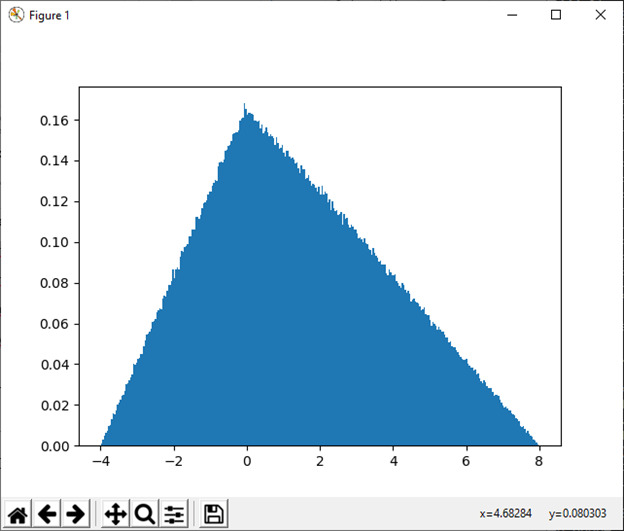
29)制服([低,高,大小])
此函数用于从均匀分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
s1 = np.random.uniform(-1,0,1000)
np.all(s1 >= -1)
np.all(s1 < 0)
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s1, 15, density=True)
plt.plot(bins, np.ones_like(bins), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
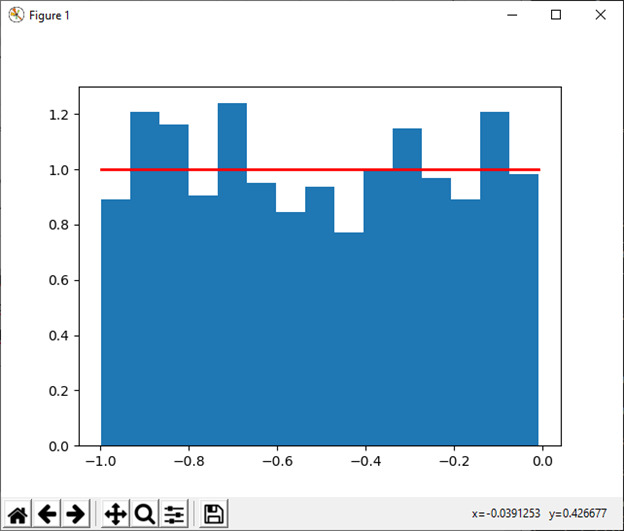
30) vonmises(m1, m2[, size])
此函数用于从 von Mises 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
m1, m2 = 0.0, 4.0
s1 = np.random.vonmises(m1, m2, 1000)
from scipy.special import i0
plt.hist(s1, 50, density=True)
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, num=51)
y = np.exp(m2*np.cos(x-m1))/(2*np.pi*i0(m2))
plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
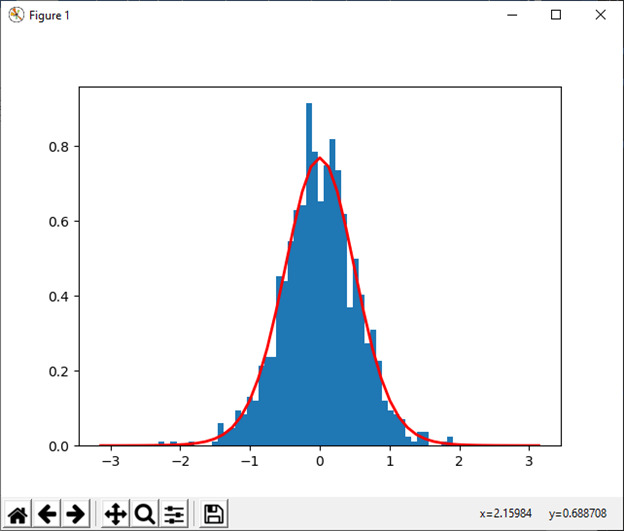
31) wald(mean, scale[, size])
此函数用于从 Wald 或逆高斯分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
h = plt.hist(np.random.wald(3, 3, 100000), bins=250, density=True)
plt.show()输出:
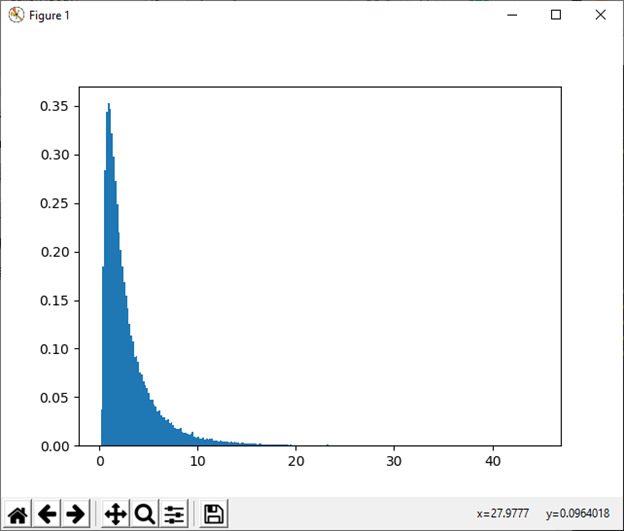
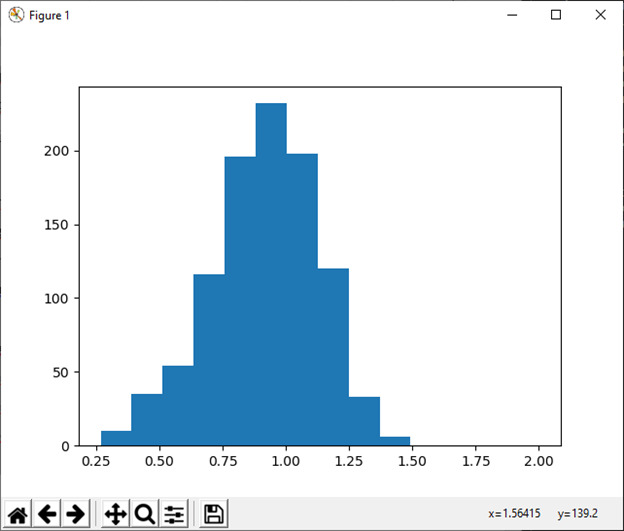
32) 威布尔 (a[, 大小])
此函数用于从威布尔分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import special
x=2.0
s=np.random.weibull(x, 1000)
a = np.arange(1, 100.)/50.
def weib(x, n, a):
return (a/n)*(x/n)**np.exp(-(x/n)**a)
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(np.random.weibull(5.,1000))
a= np.arange(1,100.)/50.
scale = count.max()/weib(x, 1., 5.).max()
scale = count.max()/weib(a, 1., 5.).max()
plt.plot(x, weib(x, 1., 5.)*scale)
plt.show()输出:
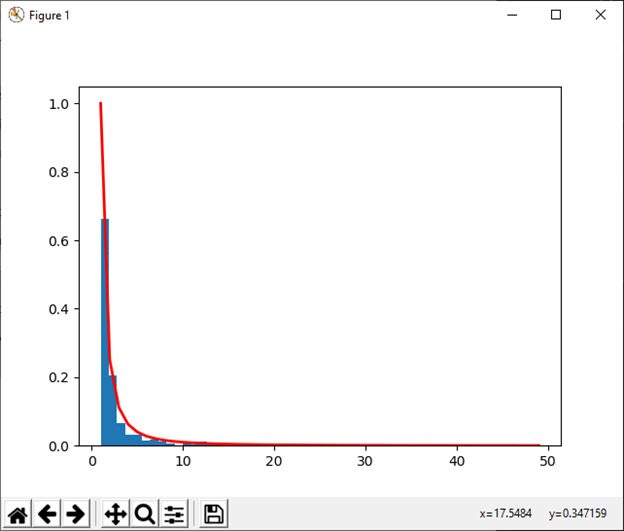
33) zipf(a[, 大小])
此函数用于从 Zipf 分布中抽取样本。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import special
x=2.0
s=np.random.zipf(x, 1000)
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s[s<50], 50, density=True)
a = np.arange(1., 50.)
b= a**(-x) / special.zetac(x)
plt.plot(a, b/max(b), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.show()输出:
相关用法
- Python numpy.random.standard_normal()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.weibull()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.uniform()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.shuffle()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.poisson()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.standard_gamma()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.wald()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.vonmises()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.standard_t()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.choice()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.noncentral_chisquare()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.triangular()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.geometric()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.chisquare()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.pareto()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.randn()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.dirichlet()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.f()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.gamma()用法及代码示例
- Python numpy.random.rayleigh()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 numpy.random() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
