Augment 接受模型對象和數據集,並添加有關數據集中每個觀察值的信息。最常見的是,這包括 .fitted 列中的預測值、.resid 列中的殘差以及 .se.fit 列中擬合值的標準誤差。新列始終以 . 前綴開頭,以避免覆蓋原始數據集中的列。
用戶可以通過 data 參數或 newdata 參數傳遞數據以進行增強。如果用戶將數據傳遞給 data 參數,則它必須正是用於擬合模型對象的數據。將數據集傳遞給 newdata 以擴充模型擬合期間未使用的數據。這仍然要求至少存在用於擬合模型的所有預測變量列。如果用於擬合模型的原始結果變量未包含在 newdata 中,則輸出中不會包含 .resid 列。
根據是否給出 data 或 newdata,增強的行為通常會有所不同。這是因為通常存在與訓練觀察(例如影響或相關)測量相關的信息,而這些信息對於新觀察沒有有意義的定義。
為了方便起見,許多增強方法提供默認的 data 參數,以便 augment(fit) 將返回增強的訓練數據。在這些情況下,augment 嘗試根據模型對象重建原始數據,並取得了不同程度的成功。
增強數據集始終以 tibble::tibble 形式返回,其行數與傳遞的數據集相同。這意味著傳遞的數據必須可強製轉換為 tibble。如果預測變量將模型作為協變量矩陣的一部分輸入,例如當模型公式使用 splines::ns() 、 stats::poly() 或 survival::Surv() 時,它會表示為矩陣列。
我們正在定義適合各種 na.action 參數的模型的行為,但目前不保證數據丟失時的行為。
用法
# S3 method for lm
augment(
x,
data = model.frame(x),
newdata = NULL,
se_fit = FALSE,
interval = c("none", "confidence", "prediction"),
...
)參數
- x
-
由
stats::lm()創建的lm對象。 - data
-
base::data.frame 或
tibble::tibble()包含用於生成對象x的原始數據。默認為stats::model.frame(x),以便augment(my_fit)返回增強的原始數據。不要將新數據傳遞給data參數。增強將報告傳遞給data參數的數據的影響和烹飪距離等信息。這些度量僅針對原始訓練數據定義。 - newdata
-
base::data.frame()或tibble::tibble()包含用於創建x的所有原始預測變量。默認為NULL,表示沒有任何內容傳遞給newdata。如果指定了newdata,則data參數將被忽略。 - se_fit
-
邏輯指示是否應將
.se.fit列添加到增強輸出中。對於某些模型,此計算可能有點耗時。默認為FALSE。 - interval
-
指示要添加到增強輸出的置信區間列類型的字符。傳遞給
predict(),默認為"none"。 - ...
-
附加參數。不曾用過。僅需要匹配通用簽名。注意:拚寫錯誤的參數將被吸收到
...中,並被忽略。如果拚寫錯誤的參數有默認值,則將使用默認值。例如,如果您傳遞conf.lvel = 0.9,所有計算將使用conf.level = 0.95進行。這裏有兩個異常:
細節
當使用 na.action = "na.omit" 執行建模時(這是典型的默認設置),初始數據中帶有 NA 的行將完全從增強 DataFrame 中省略。當使用 na.action = "na.exclude" 執行建模時,應提供原始數據作為第二個參數,此時增強數據將包含這些行(通常用 NA 代替新列)。如果未向 augment() 和 na.action = "na.exclude" 提供原始數據,則會引發警告並刪除不完整的行。
一些不尋常的 lm 對象(例如 MASS 中的 rlm)可能會省略 .cooksd 和 .std.resid 。 mgcv 中的 gam 省略 .sigma 。
當提供 newdata 時,僅返回 .fitted 、 .resid 和 .se.fit 列。
也可以看看
augment() , stats::predict.lm()
其他電影整理者:augment.glm() , glance.glm() , glance.lm() , glance.summary.lm() , glance.svyglm() , tidy.glm() , tidy.lm.beta() , tidy.lm() , tidy.mlm() , tidy.summary.lm()
值
帶有列的 tibble::tibble():
- .cooksd
-
廚師距離。
- .fitted
-
擬合值或預測值。
- .hat
-
帽子矩陣的對角線。
- .lower
-
擬合值的區間下限。
- .resid
-
觀察值和擬合值之間的差異。
- .se.fit
-
擬合值的標準誤差。
- .sigma
-
從模型中刪除相應觀測值時的估計殘差標準差。
- .std.resid
-
標準化殘差。
- .upper
-
擬合值的區間上限。
例子
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
mod <- lm(mpg ~ wt + qsec, data = mtcars)
tidy(mod)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 5
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 (Intercept) 19.7 5.25 3.76 7.65e- 4
#> 2 wt -5.05 0.484 -10.4 2.52e-11
#> 3 qsec 0.929 0.265 3.51 1.50e- 3
glance(mod)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 12
#> r.squared adj.r.squared sigma statistic p.value df logLik AIC
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0.826 0.814 2.60 69.0 9.39e-12 2 -74.4 157.
#> # ℹ 4 more variables: BIC <dbl>, deviance <dbl>, df.residual <int>,
#> # nobs <int>
# coefficient plot
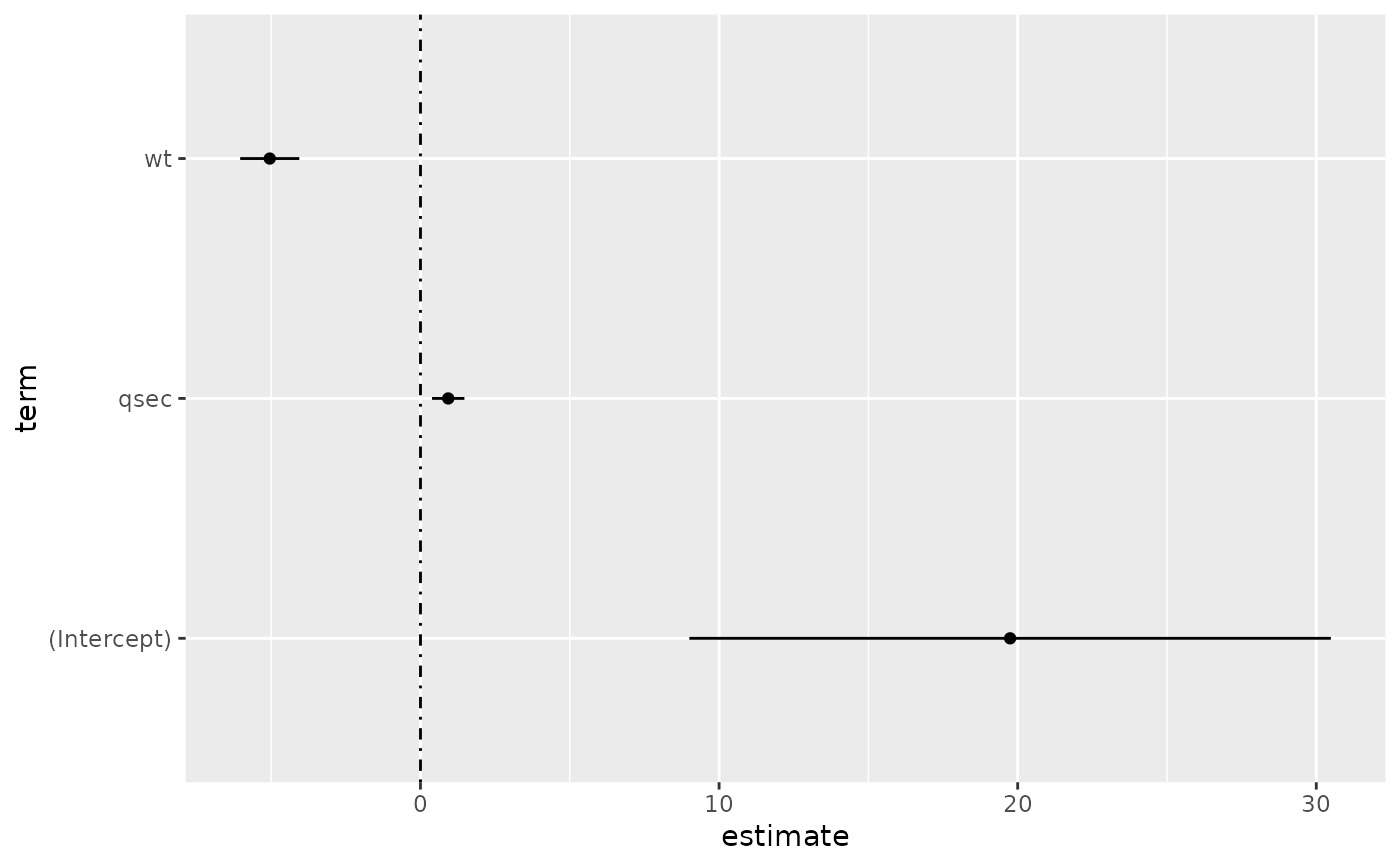
d <- tidy(mod, conf.int = TRUE)
ggplot(d, aes(estimate, term, xmin = conf.low, xmax = conf.high, height = 0)) +
geom_point() +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, lty = 4) +
geom_errorbarh()
 # aside: There are tidy() and glance() methods for lm.summary objects too.
# this can be useful when you want to conserve memory by converting large lm
# objects into their leaner summary.lm equivalents.
s <- summary(mod)
tidy(s, conf.int = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 7
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value conf.low conf.high
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 (Intercept) 19.7 5.25 3.76 7.65e- 4 9.00 30.5
#> 2 wt -5.05 0.484 -10.4 2.52e-11 -6.04 -4.06
#> 3 qsec 0.929 0.265 3.51 1.50e- 3 0.387 1.47
glance(s)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 8
#> r.squared adj.r.squared sigma statistic p.value df df.residual nobs
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 0.826 0.814 2.60 69.0 9.39e-12 2 29 32
augment(mod)
#> # A tibble: 32 × 10
#> .rownames mpg wt qsec .fitted .resid .hat .sigma .cooksd
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 2.62 16.5 21.8 -0.815 0.0693 2.64 2.63e-3
#> 2 Mazda RX4 Wag 21 2.88 17.0 21.0 -0.0482 0.0444 2.64 5.59e-6
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 2.32 18.6 25.3 -2.53 0.0607 2.60 2.17e-2
#> 4 Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 3.22 19.4 21.6 -0.181 0.0576 2.64 1.05e-4
#> 5 Hornet Sportab… 18.7 3.44 17.0 18.2 0.504 0.0389 2.64 5.29e-4
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 3.46 20.2 21.1 -2.97 0.0957 2.58 5.10e-2
#> 7 Duster 360 14.3 3.57 15.8 16.4 -2.14 0.0729 2.61 1.93e-2
#> 8 Merc 240D 24.4 3.19 20 22.2 2.17 0.0791 2.61 2.18e-2
#> 9 Merc 230 22.8 3.15 22.9 25.1 -2.32 0.295 2.59 1.59e-1
#> 10 Merc 280 19.2 3.44 18.3 19.4 -0.185 0.0358 2.64 6.55e-5
#> # ℹ 22 more rows
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: .std.resid <dbl>
augment(mod, mtcars, interval = "confidence")
#> # A tibble: 32 × 20
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 … 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 D… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spo… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> 7 Duster 360 14.3 8 360 245 3.21 3.57 15.8 0 0 3
#> 8 Merc 240D 24.4 4 147. 62 3.69 3.19 20 1 0 4
#> 9 Merc 230 22.8 4 141. 95 3.92 3.15 22.9 1 0 4
#> 10 Merc 280 19.2 6 168. 123 3.92 3.44 18.3 1 0 4
#> # ℹ 22 more rows
#> # ℹ 9 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .lower <dbl>,
#> # .upper <dbl>, .resid <dbl>, .hat <dbl>, .sigma <dbl>, .cooksd <dbl>,
#> # .std.resid <dbl>
# predict on new data
newdata <- mtcars %>%
head(6) %>%
mutate(wt = wt + 1)
augment(mod, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 14
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 W… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 Dr… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spor… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 3 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .resid <dbl>
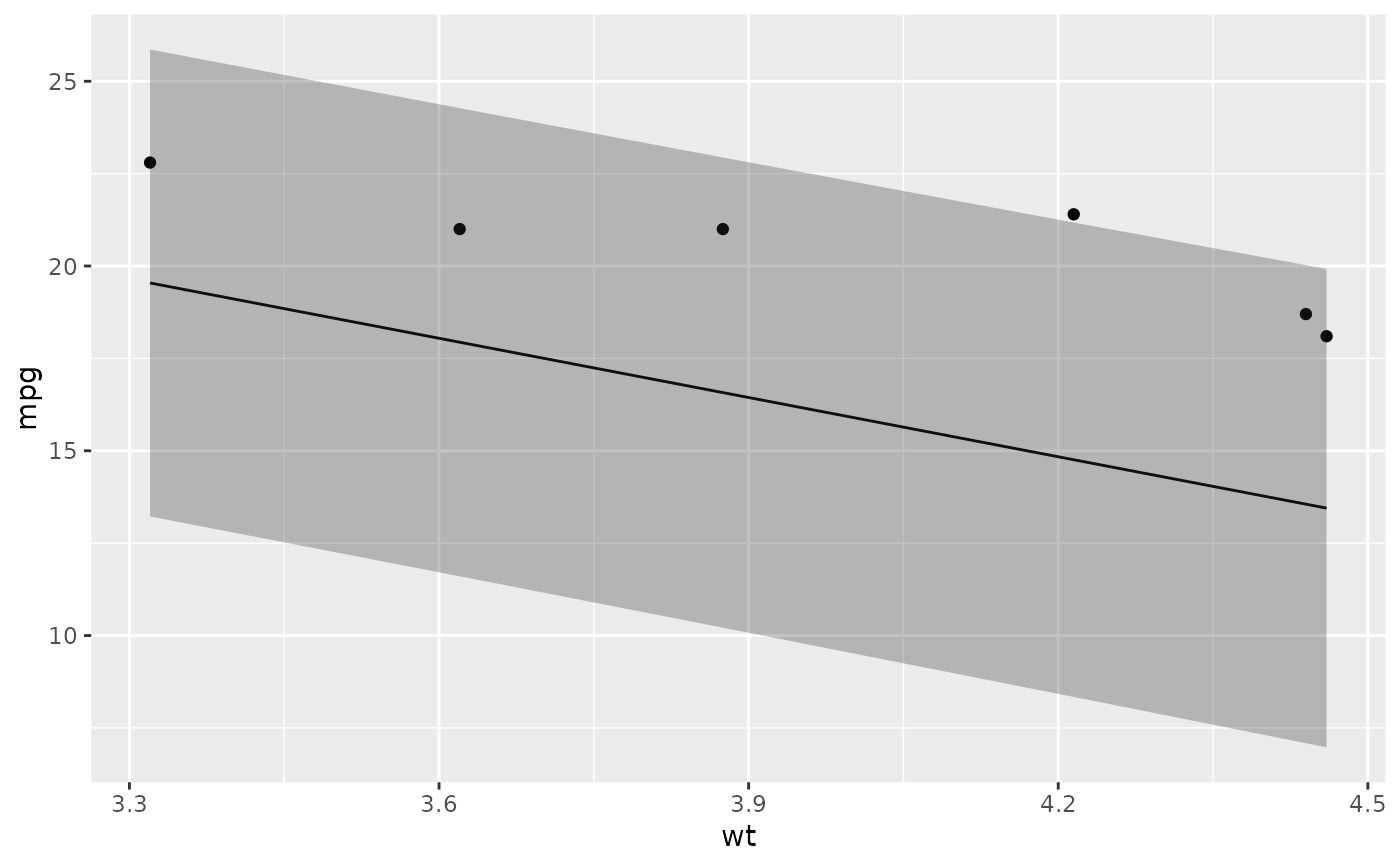
# ggplot2 example where we also construct 95% prediction interval
# simpler bivariate model since we're plotting in 2D
mod2 <- lm(mpg ~ wt, data = mtcars)
au <- augment(mod2, newdata = newdata, interval = "prediction")
ggplot(au, aes(wt, mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line(aes(y = .fitted)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = .lower, ymax = .upper), col = NA, alpha = 0.3)
# aside: There are tidy() and glance() methods for lm.summary objects too.
# this can be useful when you want to conserve memory by converting large lm
# objects into their leaner summary.lm equivalents.
s <- summary(mod)
tidy(s, conf.int = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 7
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value conf.low conf.high
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 (Intercept) 19.7 5.25 3.76 7.65e- 4 9.00 30.5
#> 2 wt -5.05 0.484 -10.4 2.52e-11 -6.04 -4.06
#> 3 qsec 0.929 0.265 3.51 1.50e- 3 0.387 1.47
glance(s)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 8
#> r.squared adj.r.squared sigma statistic p.value df df.residual nobs
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 0.826 0.814 2.60 69.0 9.39e-12 2 29 32
augment(mod)
#> # A tibble: 32 × 10
#> .rownames mpg wt qsec .fitted .resid .hat .sigma .cooksd
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 2.62 16.5 21.8 -0.815 0.0693 2.64 2.63e-3
#> 2 Mazda RX4 Wag 21 2.88 17.0 21.0 -0.0482 0.0444 2.64 5.59e-6
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 2.32 18.6 25.3 -2.53 0.0607 2.60 2.17e-2
#> 4 Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 3.22 19.4 21.6 -0.181 0.0576 2.64 1.05e-4
#> 5 Hornet Sportab… 18.7 3.44 17.0 18.2 0.504 0.0389 2.64 5.29e-4
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 3.46 20.2 21.1 -2.97 0.0957 2.58 5.10e-2
#> 7 Duster 360 14.3 3.57 15.8 16.4 -2.14 0.0729 2.61 1.93e-2
#> 8 Merc 240D 24.4 3.19 20 22.2 2.17 0.0791 2.61 2.18e-2
#> 9 Merc 230 22.8 3.15 22.9 25.1 -2.32 0.295 2.59 1.59e-1
#> 10 Merc 280 19.2 3.44 18.3 19.4 -0.185 0.0358 2.64 6.55e-5
#> # ℹ 22 more rows
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: .std.resid <dbl>
augment(mod, mtcars, interval = "confidence")
#> # A tibble: 32 × 20
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 … 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 D… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spo… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> 7 Duster 360 14.3 8 360 245 3.21 3.57 15.8 0 0 3
#> 8 Merc 240D 24.4 4 147. 62 3.69 3.19 20 1 0 4
#> 9 Merc 230 22.8 4 141. 95 3.92 3.15 22.9 1 0 4
#> 10 Merc 280 19.2 6 168. 123 3.92 3.44 18.3 1 0 4
#> # ℹ 22 more rows
#> # ℹ 9 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .lower <dbl>,
#> # .upper <dbl>, .resid <dbl>, .hat <dbl>, .sigma <dbl>, .cooksd <dbl>,
#> # .std.resid <dbl>
# predict on new data
newdata <- mtcars %>%
head(6) %>%
mutate(wt = wt + 1)
augment(mod, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 14
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 W… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 Dr… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spor… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 3 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .resid <dbl>
# ggplot2 example where we also construct 95% prediction interval
# simpler bivariate model since we're plotting in 2D
mod2 <- lm(mpg ~ wt, data = mtcars)
au <- augment(mod2, newdata = newdata, interval = "prediction")
ggplot(au, aes(wt, mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line(aes(y = .fitted)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = .lower, ymax = .upper), col = NA, alpha = 0.3)
 # predict on new data without outcome variable. Output does not include .resid
newdata <- newdata %>%
select(-mpg)
#> Error in select(., -mpg): unused argument (-mpg)
augment(mod, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 14
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 W… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 Dr… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spor… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 3 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .resid <dbl>
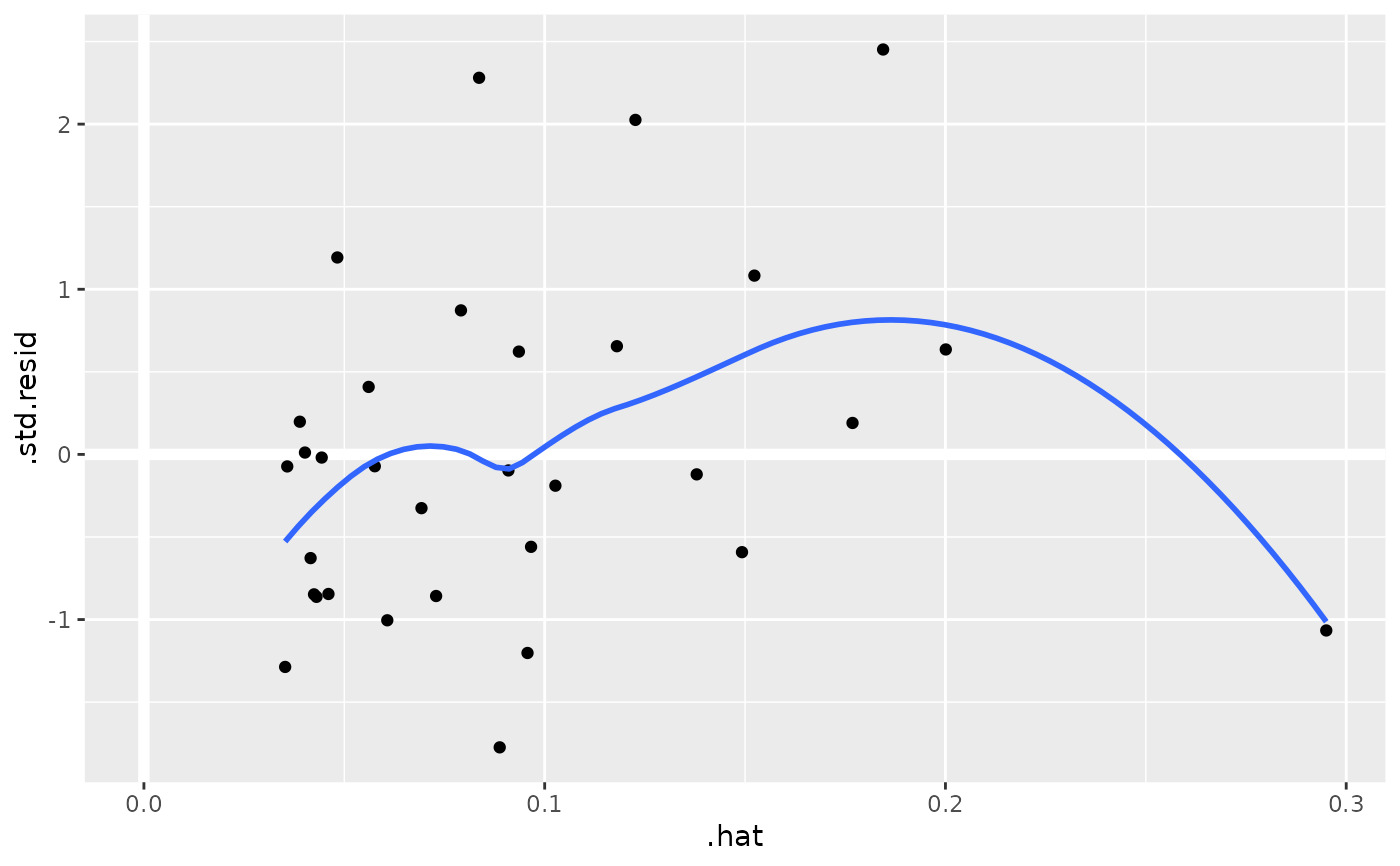
au <- augment(mod, data = mtcars)
ggplot(au, aes(.hat, .std.resid)) +
geom_vline(size = 2, colour = "white", xintercept = 0) +
geom_hline(size = 2, colour = "white", yintercept = 0) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE)
#> Warning: Using `size` aesthetic for lines was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
#> ℹ Please use `linewidth` instead.
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
# predict on new data without outcome variable. Output does not include .resid
newdata <- newdata %>%
select(-mpg)
#> Error in select(., -mpg): unused argument (-mpg)
augment(mod, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 14
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX4 W… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4 Dr… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet Spor… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 3 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>, .resid <dbl>
au <- augment(mod, data = mtcars)
ggplot(au, aes(.hat, .std.resid)) +
geom_vline(size = 2, colour = "white", xintercept = 0) +
geom_hline(size = 2, colour = "white", yintercept = 0) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE)
#> Warning: Using `size` aesthetic for lines was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
#> ℹ Please use `linewidth` instead.
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
 plot(mod, which = 6)
plot(mod, which = 6)
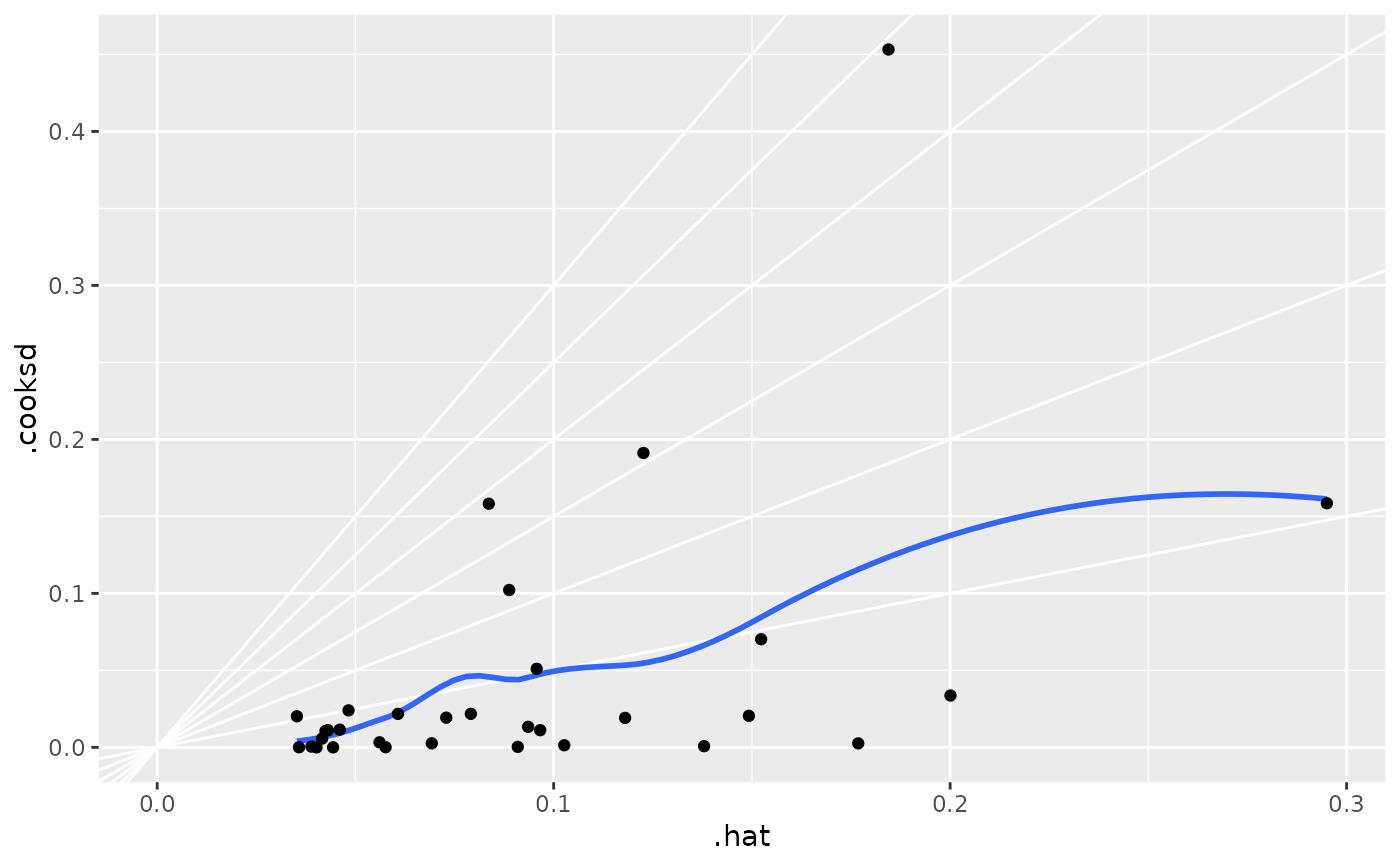
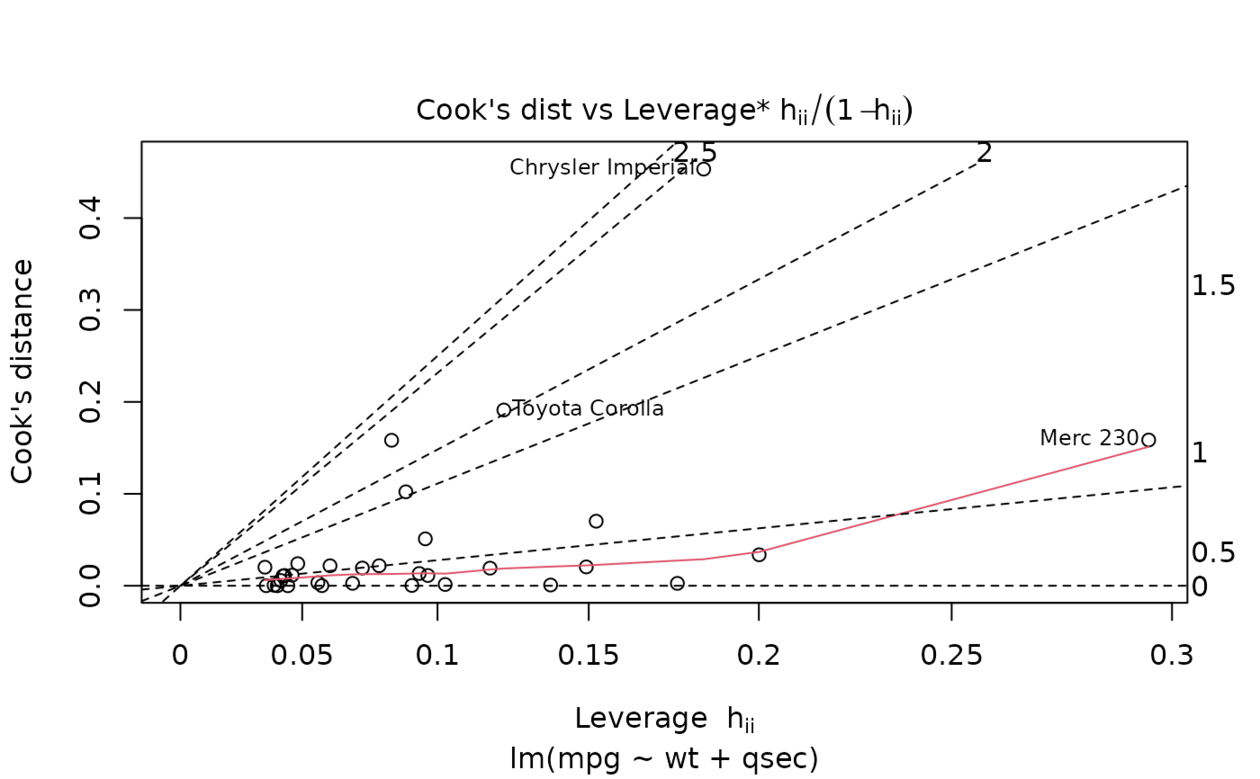 ggplot(au, aes(.hat, .cooksd)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, colour = NA) +
geom_abline(slope = seq(0, 3, by = 0.5), colour = "white") +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_point()
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
ggplot(au, aes(.hat, .cooksd)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, colour = NA) +
geom_abline(slope = seq(0, 3, by = 0.5), colour = "white") +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE) +
geom_point()
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
 # column-wise models
a <- matrix(rnorm(20), nrow = 10)
b <- a + rnorm(length(a))
result <- lm(b ~ a)
tidy(result)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 6
#> response term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Y1 (Intercept) -0.292 0.280 -1.04 0.332
#> 2 Y1 a1 1.28 0.232 5.50 0.000903
#> 3 Y1 a2 -0.519 0.187 -2.78 0.0274
#> 4 Y2 (Intercept) -0.0923 0.259 -0.357 0.732
#> 5 Y2 a1 -0.231 0.214 -1.08 0.317
#> 6 Y2 a2 0.768 0.172 4.45 0.00296
# column-wise models
a <- matrix(rnorm(20), nrow = 10)
b <- a + rnorm(length(a))
result <- lm(b ~ a)
tidy(result)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 6
#> response term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Y1 (Intercept) -0.292 0.280 -1.04 0.332
#> 2 Y1 a1 1.28 0.232 5.50 0.000903
#> 3 Y1 a2 -0.519 0.187 -2.78 0.0274
#> 4 Y2 (Intercept) -0.0923 0.259 -0.357 0.732
#> 5 Y2 a1 -0.231 0.214 -1.08 0.317
#> 6 Y2 a2 0.768 0.172 4.45 0.00296
相關用法
- R broom augment.lmRob 使用來自 lmRob 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.loess 整理 a(n) 黃土對象
- R broom augment.betamfx 使用來自 betamfx 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.robustbase.glmrob 使用來自 glmrob 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.rlm 使用來自 rlm 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.htest 使用來自(n)個 htest 對象的信息來增強數據
- R broom augment.clm 使用來自 clm 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.speedlm 使用來自 speedlm 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.felm 使用來自 (n) 個 felm 對象的信息來增強數據
- R broom augment.smooth.spline 整理一個(n)smooth.spline對象
- R broom augment.drc 使用來自 a(n) drc 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.decomposed.ts 使用來自 decomposed.ts 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.poLCA 使用來自 poLCA 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.rqs 使用來自 (n) 個 rqs 對象的信息來增強數據
- R broom augment.polr 使用來自 (n) 個 polr 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.plm 使用來自 plm 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.nls 使用來自 nls 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.gam 使用來自 gam 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.fixest 使用來自(n)個最固定對象的信息來增強數據
- R broom augment.survreg 使用來自 survreg 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.rq 使用來自 a(n) rq 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.Mclust 使用來自 Mclust 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.nlrq 整理 a(n) nlrq 對象
- R broom augment.robustbase.lmrob 使用來自 lmrob 對象的信息增強數據
- R broom augment.mlogit 使用來自 mlogit 對象的信息增強數據
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自等大神的英文原創作品 Augment data with information from a(n) lm object。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
