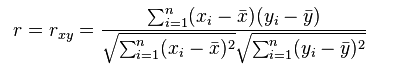下麵是章節基礎統計的目錄(其他內容參見全文目錄)
- 匯總統計(Summary statistics)
- 相關係數(Correlations)
- 分層抽樣(Stratified sampling)
- 假設檢驗(Hypothesis testing)
- 隨機數據生成(Random data generation)
匯總統計(Summary statistics)
使用Statistics中的colStats方法,我們可以對RDD[Vector]做列匯總統計。
在Python中,colStats() 返回MultivariateStatisticalSummary的實例,它包括按列計算的最大值、最小值、平均值、方差、非0值數量以及總數。
from pyspark.mllib.stat import Statistics
sc = ... # SparkContext
mat = ... # an RDD of Vectors
# Compute column summary statistics.
summary = Statistics.colStats(mat)
print summary.mean()
print summary.variance()
print summary.numNonzeros()相關係數(Correlations)
計算兩個序列的相關性是統計中的一個常用操作。MLlib為計算多種序列之間的相關性提供了足夠的靈活度。當前支持的關聯計算方法是Pearson和Spearman相關係數。
注:Pearson相關係數表達的是兩個數值變量的線性相關性, 它一般適用於正態分布。其取值範圍是[-1, 1], 當取值為0表示不相關,取值為(0~-1]表示負相關,取值為(0, 1]表示正相關。例如有趣的實驗:人的收入和看電視時長相關性調查,就可以使用Pearson相關係數來度量。其常用的計算公式為:
其中, xi/yi是變量值,n是樣本數量。帶上劃線的x, y分別是所有xi和yi的均值。
Spearman相關係數也用來表達兩個變量的相關性,但是它沒有Pearson相關係數對變量的分布要求那麽嚴格,另外Spearman相關係數可以更好地用於測度變量的排序關係。例如:Pearson適用於衡量一個班級語文成績和數學成績的關係,Spearman適用於衡量語文成績排名和數學成績排名的關係。Spearman相關係數可以認為是等級變量之間的相關係數。其計算公式為:
類 Statistics 提供了計算序列之間相關性的計算方法。依賴於輸入的類型,兩個RDD[Double]或者一個RDD[Vector],輸出分別是Double或者相關性矩陣。
from pyspark.mllib.stat import Statistics
sc = ... # SparkContext
seriesX = ... # a series
seriesY = ... # must have the same number of partitions and cardinality as seriesX
# Compute the correlation using Pearson's method. Enter "spearman" for Spearman's method. If a
# method is not specified, Pearson's method will be used by default.
print Statistics.corr(seriesX, seriesY, method="pearson")
data = ... # an RDD of Vectors
# calculate the correlation matrix using Pearson's method. Use "spearman" for Spearman's method.
# If a method is not specified, Pearson's method will be used by default.
print Statistics.corr(data, method="pearson")
分層抽樣(Stratified sampling)
跟其他的統計方法不一樣,MLlib中的分層抽樣方法:sampleByKey和sampleByKeyExact,可以在包含key-value對的RDD上執行。對分層抽樣來說,key可以認為是標簽而value是特定的屬性。例如,key可以是男人、女人或者文檔ID,相應的values就是人群中人的年齡序列或者文檔中的單詞序列。方法sampleByKey會像拋硬幣一樣去判斷每個實例是否被抽出,因此需要遍曆一次數據,並且需要提供一個期望的樣本大小。sampleByKeyExact比sampleByKey的每層簡單隨機抽樣需要更多的資源,但是在抽樣大小上有99.99%的準確度。不過sampleByKeyExact目前在python中不支持。
sampleByKey()允許用戶抽取大約 ⌈fk⋅nk⌉∀k∈K 個樣本,其中fk是希望對k(鍵)抽取的比例,nk是k(鍵)中的key-value對數量,K是key(鍵)集合。
sc = ... # SparkContext
fractions = {"a": 0.2, "b": 0.1, "c": 0.2, ...}
data = ... # an RDD of any key(a/b/c...) value pairs
fractions = ... # specify the exact fraction desired from each key as a dictionary
approxSample = data.sampleByKey(False, fractions);假設檢驗(Hypothesis testing)
假設檢驗是一個強大的統計工具,它可以用來判斷一個事件是否有顯劇的統計特征,以及這個事件是不是偶然發生的。MLlib當前支持用於判斷擬合度或者獨立性的Pearson卡方(chi-squared ( χ2) )檢驗。不同的輸入類型決定了是做擬合度檢驗還是獨立性檢驗。擬合度檢驗要求輸入為Vector, 獨立性檢驗要求輸入是Matrix。
MLlib也支持輸入類型是RDD[LabeledPoint]時,通過卡方獨立性檢驗做特征選擇。
類 Statistics 提供了進行Pearson卡方檢驗的方法。下麵的例子展示了怎樣運行和解釋假設檢驗。
from pyspark import SparkContext
from pyspark.mllib.linalg import Vectors, Matrices
from pyspark.mllib.regresssion import LabeledPoint
from pyspark.mllib.stat import Statistics
sc = SparkContext()
vec = Vectors.dense(...) # a vector composed of the frequencies of events
# compute the goodness of fit. If a second vector to test against is not supplied as a parameter,
# the test runs against a uniform distribution.
goodnessOfFitTestResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(vec)
print goodnessOfFitTestResult # summary of the test including the p-value, degrees of freedom,
# test statistic, the method used, and the null hypothesis.
mat = Matrices.dense(...) # a contingency matrix
# conduct Pearson's independence test on the input contingency matrix
independenceTestResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(mat)
print independenceTestResult # summary of the test including the p-value, degrees of freedom...
obs = sc.parallelize(...) # LabeledPoint(feature, label) .
# The contingency table is constructed from an RDD of LabeledPoint and used to conduct
# the independence test. Returns an array containing the ChiSquaredTestResult for every feature
# against the label.
featureTestResults = Statistics.chiSqTest(obs)
for i, result in enumerate(featureTestResults):
print "Column $d:" % (i + 1)
print result隨機數據生成(Random data generation)
隨機數據生成在隨機算法、原型開發、性能測試中比較有用。MLlib支持生成的隨機的RDD[(int, int, double)],數據服從下列分別:均勻分布、標準正態分布、泊鬆分布。
類RandomRDDs 提供了工廠方法來生成隨機的RDD[double]或者RDD[vector]。下麵的代碼中,生成了一個RDD[double], 它服從標準正態分布,然後轉成了N(1, 4)分布。
from pyspark.mllib.random import RandomRDDs
sc = ... # SparkContext
# Generate a random double RDD that contains 1 million i.i.d. values drawn from the
# standard normal distribution `N(0, 1)`, evenly distributed in 10 partitions.
u = RandomRDDs.uniformRDD(sc, 1000000L, 10)
# Apply a transform to get a random double RDD following `N(1, 4)`.
v = u.map(lambda x: 1.0 + 2.0 * x)參考:
[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson_product-moment_correlation_coefficient
[2] http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%96%AF%E7%9A%AE%E5%B0%94%E6%9B%BC%E7%AD%89%E7%BA%A7%E7%9B%B8%E5%85%B3%E7%B3%BB%E6%95%B0