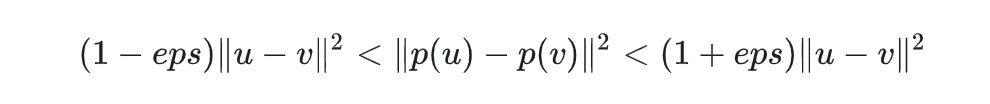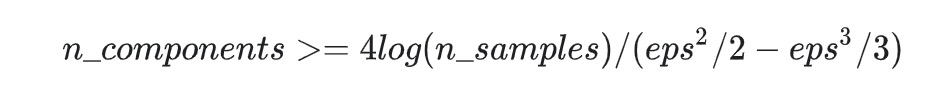Johnson-Lindenstrauss綁定為帶有隨機投影的嵌入簡介
Johnson-Lindenstrauss引理(簡稱JL引理)指出,任何高維數據集都可以隨機投影到低維歐氏空間中,同時控製點的兩兩距離的失真度。也就說將點從高維空間映射到低維空間之後,新舊空間點的距離是可以近似相等的。
理論界限
隨機投影引起的失真度p,如下式所示:
其中u和v是從大小為[n_samples,n_features]的數據集中獲取的任意行,而p是形狀為[n_components,n_features](或稀疏Achlioptas矩陣)的隨機高斯N(0,1)矩陣的投影。
保證eps-embedding的最小組件數量為:
注:見後文代碼執行的圖,
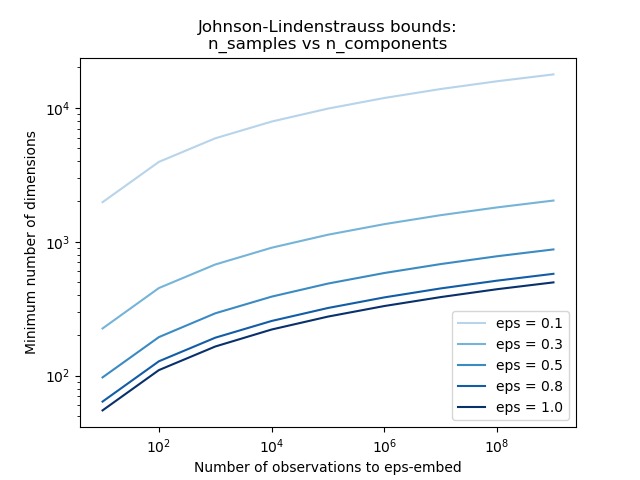
- 第一個圖顯示隨著樣本數量n_samples的增加,最小尺寸
n_components對數增加以保證eps-embedding。 - 第二個圖顯示了對於給定數量的樣本
n_samples,容許失真的增加eps可以大幅減少最小維度n_components
實證驗證
我們在手寫數字數據集或20個新聞組文本文檔(TF-IDF詞頻)數據集上驗證上述界限:
- 對於手寫數字數據集,將500張手寫數字圖片的一些8×8灰度像素數據隨機投影到各種較大維度n_components的空間。
- 對於20個新聞組數據集,使用稀疏隨機矩陣將總共500個具有10萬個特征的文檔投影到較小的歐幾裏得空間,並為目標維數n_components設置不同的值。
示例中默認數據集是數字數據集。要在二十個新聞組數據集上運行該示例,請將–twenty-newsgroups命令行參數傳遞給此腳本。
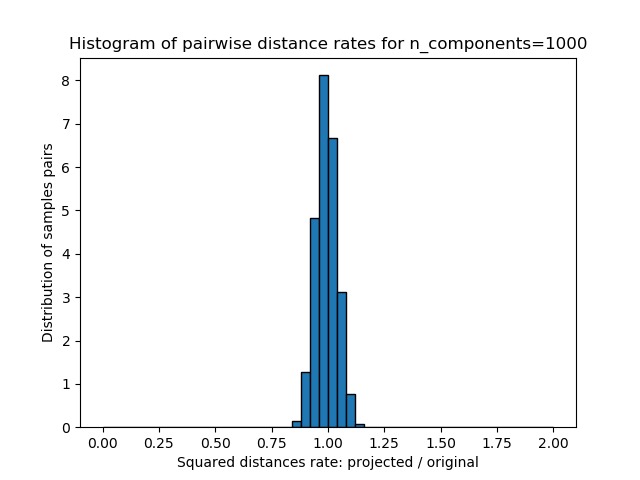
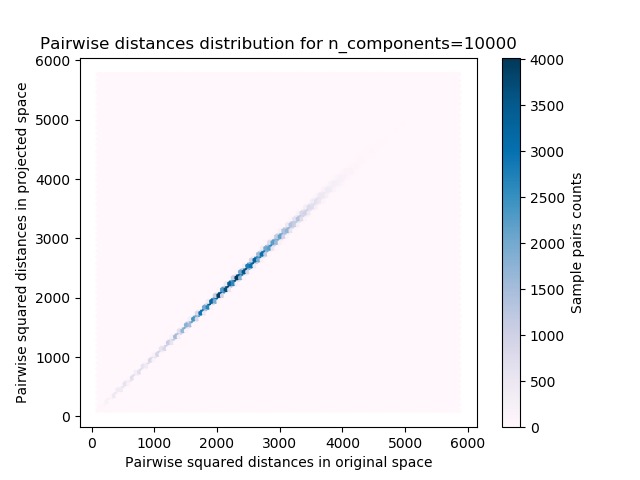
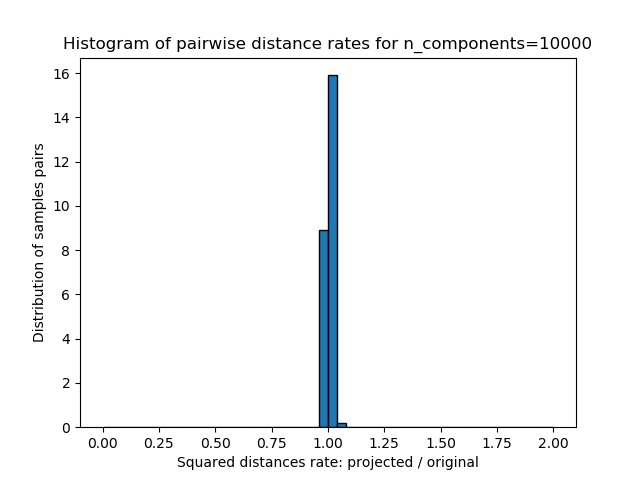
對於每個值n_components,我們繪製:
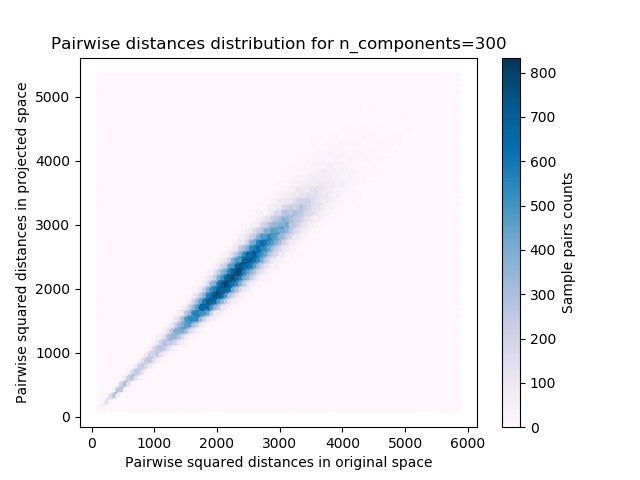
- 原始空間和投影空間中成對距離的樣本對的2D分布(2D分別為x和y軸)。
- 這些距離的比例的一維直方圖(投影/原始)。
我們可以看到,對於較小的n_components,分布較寬,有許多扭曲的對和偏斜的分布(由於左側的零比率的硬性限製,因為距離始終為正值);而對於較大的n_components值,則可以控製失真,並且通過隨機投影可以很好地保留距離。
備注
根據JL引理,無論原始數據集的特征數量如何,投影500個樣本而不會產生太多失真都將至少需要數千個維度。
因此,對在輸入空間中僅具有64個特征的數字數據集使用隨機投影是沒有意義的:在這種情況下,它不允許降維。所以在這個手寫數字數據集上我們實驗用的是增加維度。而另一方麵,在二十個新聞組數據集中,維數可以從56436降低到10000,同時合理地保持點對的距離。
代碼實現[Python]
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
print(__doc__)
import sys
from time import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from distutils.version import LooseVersion
from sklearn.random_projection import johnson_lindenstrauss_min_dim
from sklearn.random_projection import SparseRandomProjection
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups_vectorized
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import euclidean_distances
# `normed` is being deprecated in favor of `density` in histograms
if LooseVersion(matplotlib.__version__) >= '2.1':
density_param = {'density': True}
else:
density_param = {'normed': True}
# Part 1: 繪製n_components_min和n_samples之間的理論依賴性
# 容許失真的範圍
eps_range = np.linspace(0.1, 0.99, 5)
colors = plt.cm.Blues(np.linspace(0.3, 1.0, len(eps_range)))
# range of number of samples (observation) to embed
n_samples_range = np.logspace(1, 9, 9)
plt.figure()
for eps, color in zip(eps_range, colors):
min_n_components = johnson_lindenstrauss_min_dim(n_samples_range, eps=eps)
plt.loglog(n_samples_range, min_n_components, color=color)
plt.legend(["eps = %0.1f" % eps for eps in eps_range], loc="lower right")
plt.xlabel("Number of observations to eps-embed")
plt.ylabel("Minimum number of dimensions")
plt.title("Johnson-Lindenstrauss bounds:\nn_samples vs n_components")
# 容許失真的範圍
eps_range = np.linspace(0.01, 0.99, 100)
# range of number of samples (observation) to embed
n_samples_range = np.logspace(2, 6, 5)
colors = plt.cm.Blues(np.linspace(0.3, 1.0, len(n_samples_range)))
plt.figure()
for n_samples, color in zip(n_samples_range, colors):
min_n_components = johnson_lindenstrauss_min_dim(n_samples, eps=eps_range)
plt.semilogy(eps_range, min_n_components, color=color)
plt.legend(["n_samples = %d" % n for n in n_samples_range], loc="upper right")
plt.xlabel("Distortion eps")
plt.ylabel("Minimum number of dimensions")
plt.title("Johnson-Lindenstrauss bounds:\nn_components vs eps")
# Part 2: 對維數很低且密度高的某些數字圖像或對維數高且稀疏的20個新聞組數據集執行稀疏隨機投影
if '--twenty-newsgroups' in sys.argv:
# Need an internet connection hence not enabled by default
data = fetch_20newsgroups_vectorized().data[:500]
else:
data = load_digits().data[:500]
n_samples, n_features = data.shape
print("Embedding %d samples with dim %d using various random projections"
% (n_samples, n_features))
n_components_range = np.array([300, 1000, 10000])
dists = euclidean_distances(data, squared=True).ravel()
# 僅選擇不相同的樣本對
nonzero = dists != 0
dists = dists[nonzero]
for n_components in n_components_range:
t0 = time()
rp = SparseRandomProjection(n_components=n_components)
projected_data = rp.fit_transform(data)
print("Projected %d samples from %d to %d in %0.3fs"
% (n_samples, n_features, n_components, time() - t0))
if hasattr(rp, 'components_'):
n_bytes = rp.components_.data.nbytes
n_bytes += rp.components_.indices.nbytes
print("Random matrix with size: %0.3fMB" % (n_bytes / 1e6))
projected_dists = euclidean_distances(
projected_data, squared=True).ravel()[nonzero]
plt.figure()
plt.hexbin(dists, projected_dists, gridsize=100, cmap=plt.cm.PuBu)
plt.xlabel("Pairwise squared distances in original space")
plt.ylabel("Pairwise squared distances in projected space")
plt.title("Pairwise distances distribution for n_components=%d" %
n_components)
cb = plt.colorbar()
cb.set_label('Sample pairs counts')
rates = projected_dists / dists
print("Mean distances rate: %0.2f (%0.2f)"
% (np.mean(rates), np.std(rates)))
plt.figure()
plt.hist(rates, bins=50, range=(0., 2.), edgecolor='k', **density_param)
plt.xlabel("Squared distances rate: projected / original")
plt.ylabel("Distribution of samples pairs")
plt.title("Histogram of pairwise distance rates for n_components=%d" %
n_components)
# TODO: compute the expected value of eps and add them to the previous plot
# as vertical lines / region
plt.show()
代碼執行
代碼運行時間大約:0分1.837秒。
運行代碼輸出的文本內容如下:
Embedding 500 samples with dim 64 using various random projections Projected 500 samples from 64 to 300 in 0.016s Random matrix with size: 0.028MB Mean distances rate: 0.97 (0.08) Projected 500 samples from 64 to 1000 in 0.048s Random matrix with size: 0.096MB Mean distances rate: 0.99 (0.05) Projected 500 samples from 64 to 10000 in 0.594s Random matrix with size: 0.964MB Mean distances rate: 1.01 (0.01)
運行代碼輸出的圖片內容如下:



源碼下載
- Python版源碼文件: plot_johnson_lindenstrauss_bound.py
- Jupyter Notebook版源碼文件: plot_johnson_lindenstrauss_bound.ipynb