Dateoffsets是用于Pandas中日期范围的标准日期增量。就我们传入的关键字args而言,它的工作方式与relativedelta完全相同。DateOffets的工作方式如下,每个偏移量指定一组符合DateOffset的日期。例如,“ Bday”将此集合定义为工作日的日期集合(M-F)。
可以创建DateOffsets以将日期向前移动给定数量的有效日期。例如,可以将Bday(2)添加到日期以将其向前移动两个工作日。如果日期不是从有效日期开始,则首先将其移动到有效日期,然后创建偏移量。
Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.name属性以字符串形式返回应用于给定偏移量的频率。
用法: pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.name
参数:没有
返回:频率作为字符串
范例1:采用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.name属性以字符串形式返回应用于给定偏移量的频率名称。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 11:15:00')
# Create an offset
bh = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour(n = 5)
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the Offset
print(bh)输出:
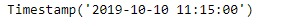
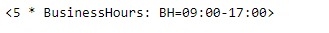
现在,我们将营业时间偏移量添加到给定的timestamp对象,以增加datetime值。我们还将以字符串形式打印在给定偏移量上应用的频率名称。
# Adding the Business hour offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bh
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# print the name of the frequency
# applied as string
print(bh.name)输出:
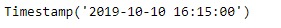

从输出中可以看到,我们已经成功创建了一个偏移并将其添加到给定的时间戳中。我们还以字符串形式打印了在给定偏移量上应用的频率名称。
范例2:采用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.name属性以字符串形式返回应用于给定偏移量的频率名称。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 11:15:00')
# Create an offset
bh = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour(offset = datetime.timedelta(hours = 1))
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the Offset
print(bh)输出:
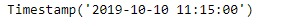

现在,我们将营业时间偏移量添加到给定的timestamp对象,以增加datetime值。我们还将以字符串形式打印在给定偏移量上应用的频率名称。
# Adding the Business hour offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bh
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# print the name of the frequency
# applied as string
print(bh.name)输出:
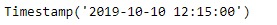

从输出中可以看到,我们已经成功创建了一个偏移并将其添加到给定的时间戳中。我们还以字符串形式打印了在给定偏移量上应用的频率名称。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.name。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
