Pandas 系列是带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不必是唯一的,但必须是可哈希的类型。该对象同时支持基于整数和基于标签的索引,并提供了许多方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.rank()函数计算沿轴的数值数据等级(1到n)。相等的值被分配一个等级,该等级是这些值的等级的平均值。
用法: Series.rank(axis=0, method=’average’, numeric_only=None, na_option=’keep’, ascending=True, pct=False)
参数:
axis:直接排名索引
method:{“平均”,“最小”,“最大”,“第一”,“密集”}
numeric_only:仅包含float,int,boolean数据。仅对DataFrame或Panel对象有效
na_option:{“保持”,“顶部”,“底部”}
ascending:从高(1)到低(N)的等级错误
pct:计算数据的百分比等级
返回:等级:与来电者类型相同
范例1:采用Series.rank()函数对给定Series对象的基础数据进行排名。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6])
# Create the Index
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:

现在我们将使用Series.rank()函数返回给定Series对象的基础数据的等级。
# assign rank
result = sr.rank()
# Print the result
print(result)输出:
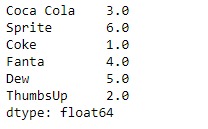
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.rank()函数已将排名分配给给定Series对象的每个元素。
范例2:采用Series.rank()函数对给定Series对象的基础数据进行排名。给定的数据还包含一些相等的值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6, 25])
# Create the Index
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp', 'Appy']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:
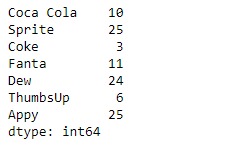
现在我们将使用Series.rank()函数返回给定Series对象的基础数据的等级。
# assign rank
result = sr.rank()
# Print the result
print(result)输出:
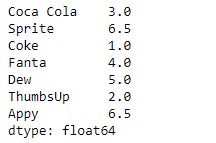
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.rank()函数已将排名分配给给定Series对象的每个元素。注意,为相等的值分配了一个等级,该等级是其等级的平均值。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas Series.rank()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
