Pandas 索引是一个不变的ndarray,它实现了有序的,可切片的集合。它是存储所有 Pandas 对象的轴标签的基本对象。
Pandas Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性返回True如果给定Index对象中的基础数据单调增加,则返回False。
用法: Index.is_monotonic_increasing
参数:没有
返回:布尔值
范例1:采用Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性以确定给定Index对象中的基础数据是否单调增加。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the index
idx = pd.Index([100, 200, 420, 888, 924])
# Print the index
print(idx)输出:
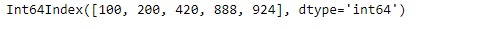
现在我们将使用Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性以确定给定Index对象中的基础数据是否单调增加。
# check if the values in the Index
# are monotonically increasing
result = idx.is_monotonic_increasing
# Print the result
print(result)输出:
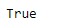
正如我们在输出中看到的,Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性已返回True指示给定Index对象的基础数据正在单调增加。
范例2:采用Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性以确定给定Index对象中的基础数据是否单调增加。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the index
idx = pd.Index(['2012-12-12', None, '2002-1-10', None])
# Print the index
print(idx)输出:
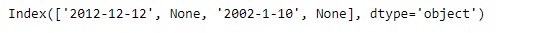
现在我们将使用Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性以确定给定Index对象中的基础数据是否单调增加。
# check if the values in the Index
# are monotonically increasing
result = idx.is_monotonic_increasing
# Print the result
print(result)输出:
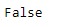
正如我们在输出中看到的,Index.is_monotonic_increasing属性已返回False指示给定Index对象的基础数据不是单调增加的。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas Index.is_monotonic_increasing。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
