本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.signal.minimum_phase 的用法。
用法:
scipy.signal.minimum_phase(h, method='homomorphic', n_fft=None)#將linear-phase FIR 濾波器轉換為最小相位
- h: 數組
Linear-phase FIR 濾波器係數。
- method: {‘hilbert’, ‘homomorphic’}
使用方法:
- ‘homomorphic’ (default)
This method [4] [5] works best with filters with an odd number of taps, and the resulting minimum phase filter will have a magnitude response that approximates the square root of the original filter’s magnitude response.
- ‘hilbert’
This method [1] is designed to be used with equiripple filters (e.g., from
remez) with unity or zero gain regions.
- n_fft: int
用於 FFT 的點數。應該至少比信號長度大幾倍(見注釋)。
- h_minimum: 數組
過濾器的 minimum-phase 版本,長度為
(length(h) + 1) // 2。
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
Hilbert [1] 或同態 [4] [5] 方法都需要選擇 FFT 長度來估計濾波器的複倒譜。
在 Hilbert 方法的情況下,與理想頻譜
epsilon的偏差與阻帶零點的數量n_stop和 FFT 長度n_fft相關,如下所示:epsilon = 2. * n_stop / n_fft例如,對於 100 個阻帶零點和 2048 的 FFT 長度,
epsilon = 0.0976。如果我們保守地假設阻帶零點的數量比濾波器長度小一,我們可以將 FFT 長度取為滿足epsilon=0.01的 2 的下一個冪:n_fft = 2 ** int(np.ceil(np.log2(2 * (len(h) - 1) / 0.01)))這為希爾伯特和同態方法提供了合理的結果,並給出了
n_fft=None時使用的值。存在用於創建 minimum-phase 濾波器的替代實現,包括零反轉 [2] 和頻譜分解 [3] [4]。有關更多信息,請參閱:
參考:
[1] (1,2)N. Damera-Venkata 和 BL Evans,“實數和複數最小相位數字 FIR 濾波器的優化設計”,聲學、語音和信號處理,1999 年。論文集,1999 年 IEEE 國際會議,亞利桑那州鳳凰城,1999 年,第1145-1148 卷 3。 DOI:10.1109/ICASSP.1999.756179
[2]X. Chen 和 T. W. Parks,“通過直接分解設計最優最小相位 FIR 濾波器”,信號處理,卷。 10,沒有。 4,第 369-383 頁,1986 年 6 月。
[3]T. Saramaki,“有限脈衝響應濾波器設計”,數字信號處理手冊,第 4 章,紐約:Wiley-Interscience,1993 年。
[4] (1,2,3)J. S. Lim,信號處理高級主題。新澤西州恩格爾伍德懸崖:普倫蒂斯霍爾,1988 年。
[5] (1,2)A. V. Oppenheim、R. W. Schafer 和 J. R. Buck,“Discrete-Time 信號處理”,第 2 版。新澤西州上馬鞍河:Prentice Hall,1999 年。
例子:
創建一個最佳的linear-phase 過濾器,然後將其轉換為最小相位:
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.signal import remez, minimum_phase, freqz, group_delay >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> freq = [0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0] >>> desired = [1, 0] >>> h_linear = remez(151, freq, desired, fs=2.)將其轉換為最小相位:
>>> h_min_hom = minimum_phase(h_linear, method='homomorphic') >>> h_min_hil = minimum_phase(h_linear, method='hilbert')比較三個過濾器:
>>> fig, axs = plt.subplots(4, figsize=(4, 8)) >>> for h, style, color in zip((h_linear, h_min_hom, h_min_hil), ... ('-', '-', '--'), ('k', 'r', 'c')): ... w, H = freqz(h) ... w, gd = group_delay((h, 1)) ... w /= np.pi ... axs[0].plot(h, color=color, linestyle=style) ... axs[1].plot(w, np.abs(H), color=color, linestyle=style) ... axs[2].plot(w, 20 * np.log10(np.abs(H)), color=color, linestyle=style) ... axs[3].plot(w, gd, color=color, linestyle=style) >>> for ax in axs: ... ax.grid(True, color='0.5') ... ax.fill_between(freq[1:3], *ax.get_ylim(), color='#ffeeaa', zorder=1) >>> axs[0].set(xlim=[0, len(h_linear) - 1], ylabel='Amplitude', xlabel='Samples') >>> axs[1].legend(['Linear', 'Min-Hom', 'Min-Hil'], title='Phase') >>> for ax, ylim in zip(axs[1:], ([0, 1.1], [-150, 10], [-60, 60])): ... ax.set(xlim=[0, 1], ylim=ylim, xlabel='Frequency') >>> axs[1].set(ylabel='Magnitude') >>> axs[2].set(ylabel='Magnitude (dB)') >>> axs[3].set(ylabel='Group delay') >>> plt.tight_layout()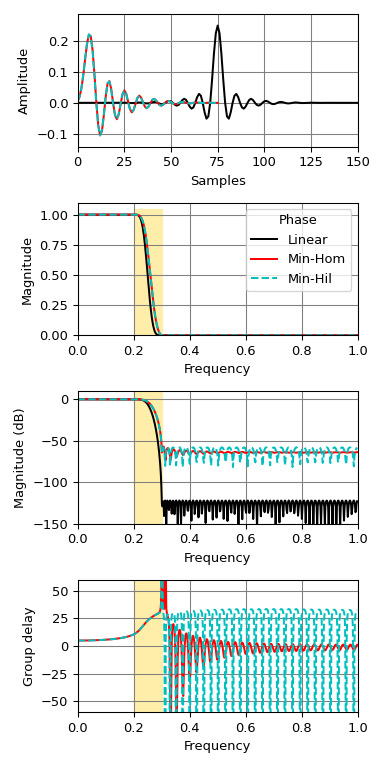
相關用法
- Python SciPy signal.max_len_seq用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.morlet用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.medfilt2d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.morlet2用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.czt_points用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.chirp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.residue用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.iirdesign用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.kaiser_atten用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.oaconvolve用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.hilbert用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.ricker用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.group_delay用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.cheb2ord用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.get_window用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.lfilter用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.coherence用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.dfreqresp用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.TransferFunction用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.dbode用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.residuez用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.bilinear_zpk用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.firls用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.impulse用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy signal.buttord用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.signal.minimum_phase。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
