Python是進行數據分析的一種出色語言,主要是因為以數據為中心的python軟件包具有奇妙的生態係統。 Pandas是其中的一種,使導入和分析數據更加容易。
Pandas MultiIndex.from_product()函數根據多個可迭代項的笛卡爾積生成MultiIndex。
用法: MultiIndex.from_product(iterables, sortorder=None, names=None)
參數:
iterables:每個可迭代的索引的每個級別都有唯一的標簽。
sortorder:排序級別(必須按字典級別按該級別排序)。
names:索引中級別的名稱。
返回:索引:MultiIndex
範例1:采用MultiIndex.from_product()函數根據多個可迭代項的笛卡爾積構造一個MultiIndex。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the first iterable
Price =[20, 35, 60, 85]
# Create the second iterable
Name =['Vanilla', 'Strawberry']
# Print the first iterable
print(Price)
# Print the second iterable
print("\n", Name)輸出:
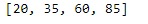
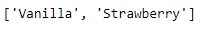
現在,讓我們使用以上兩個可迭代項來創建MultiIndex。
# Creating the MultiIndex
midx = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([Name, Price],
names =['Name', 'Price'])
# Print the MultiIndex
print(midx)輸出:

正如我們在輸出中看到的,該函數使用這兩個可迭代對象的笛卡爾積創建了一個MultiIndex對象。
範例2:采用MultiIndex.from_product()函數根據多個可迭代項的笛卡爾積構造一個MultiIndex。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the first iterable
Snake =['Viper', 'Cobra']
# Create the second iterable
Variety =['Brown', 'Yellow', 'Black']
# Print the first iterable
print(Snake)
# Print the second iterable
print("\n", Variety)輸出:
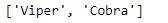
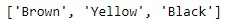
現在,讓我們使用以上兩個可迭代項來創建MultiIndex。
# Creating the MultiIndex
midx = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([Snake, Variety],
names =['Snake', 'Variety'])
# Print the MultiIndex
print(midx)輸出:

該函數使用兩個可迭代對象創建了一個MultiIndex。
相關用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas MultiIndex.from_product()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
