K-Nearest Neighbours(KNN, K近鄰)是一種分類算法,本文介紹了其背後的概念,以及如何在代碼中實現它。

我們將使用Python中最常用的機器學習庫scikit-learn來實現KNN。
Scikit-Learn是一個非常強大的機器學習庫。它最初由David Cournapeau於2007年在Google Summer編程項目中開發。
該庫也包含一些數據集。這裏,我們將使用威斯康星州乳腺癌數據集(the Breast Cancer Wisconsin Dataset ),並研究如何實現KNN算法。
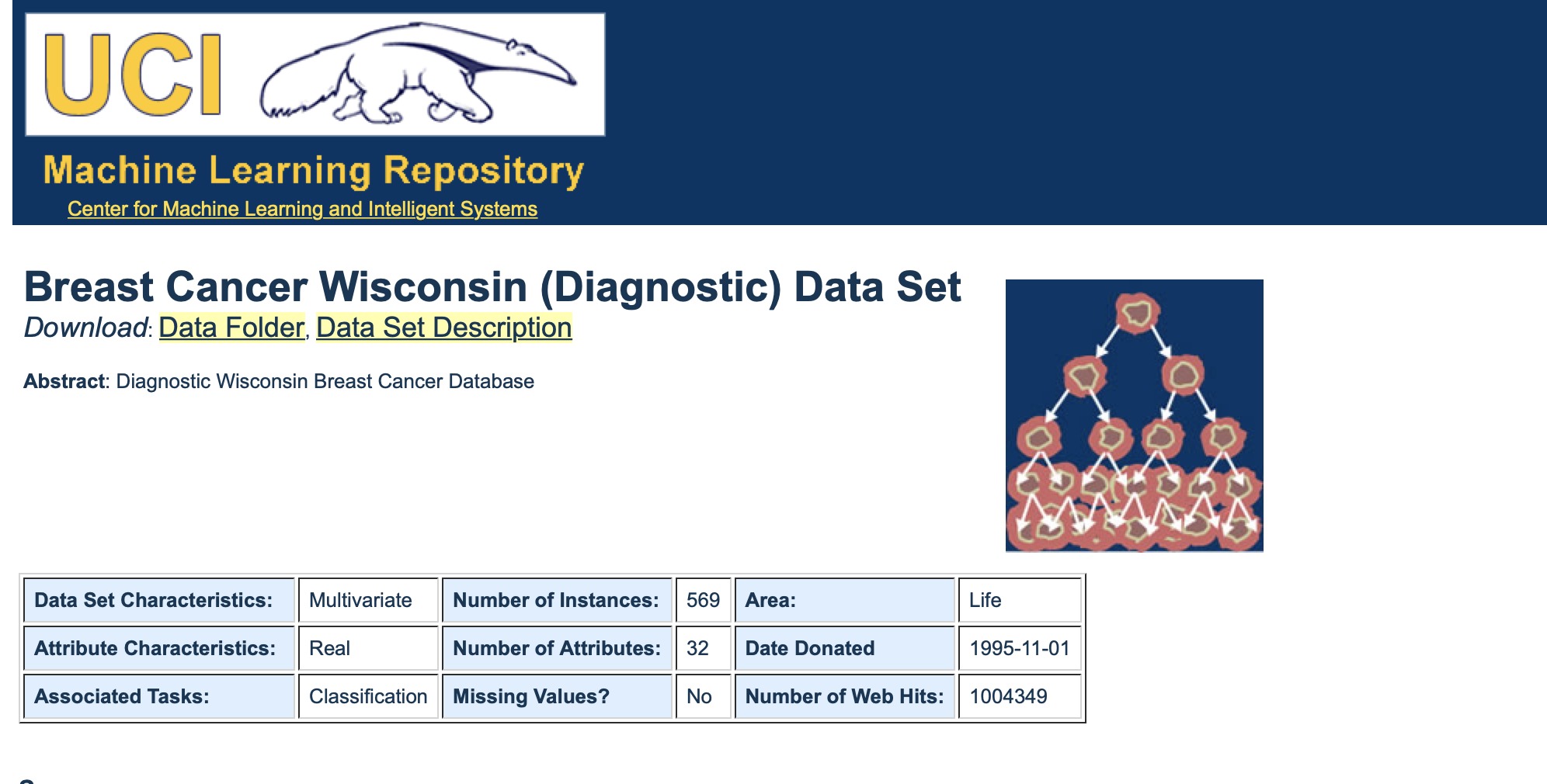
加載數據集
這是一個包含569個數據點的數據集。每個數據點都有30個特征值。這些特征共同決定一個人的細胞是惡性還是良性。
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
data = load_breast_cancer()了解數據集
# Print the information contained within the dataset
print(data.keys(),"\n")
#Print the feature names
count=0
for f in data.feature_names:
count+=1
print(count,"-",f)
#Print the classes
print(data.target_names,"\n")
#Printing the Initial Few Rows
print(data.data[0:3], "\n")
#Print the class values of first 30 datapoints
print(data.target[0:30], "\n")
#Print the dimensions of data
print(data.data.shape, "\n")數據中的信息(‘data’, ‘target’, ‘target_names’, ‘DESCR’, ‘feature_names’, ‘filename’)
- “data”-一個實際數據
- “target”-類值(標簽值或者目標值)
- ‘target_names’—類名稱(標簽名或目標名):惡性/良性
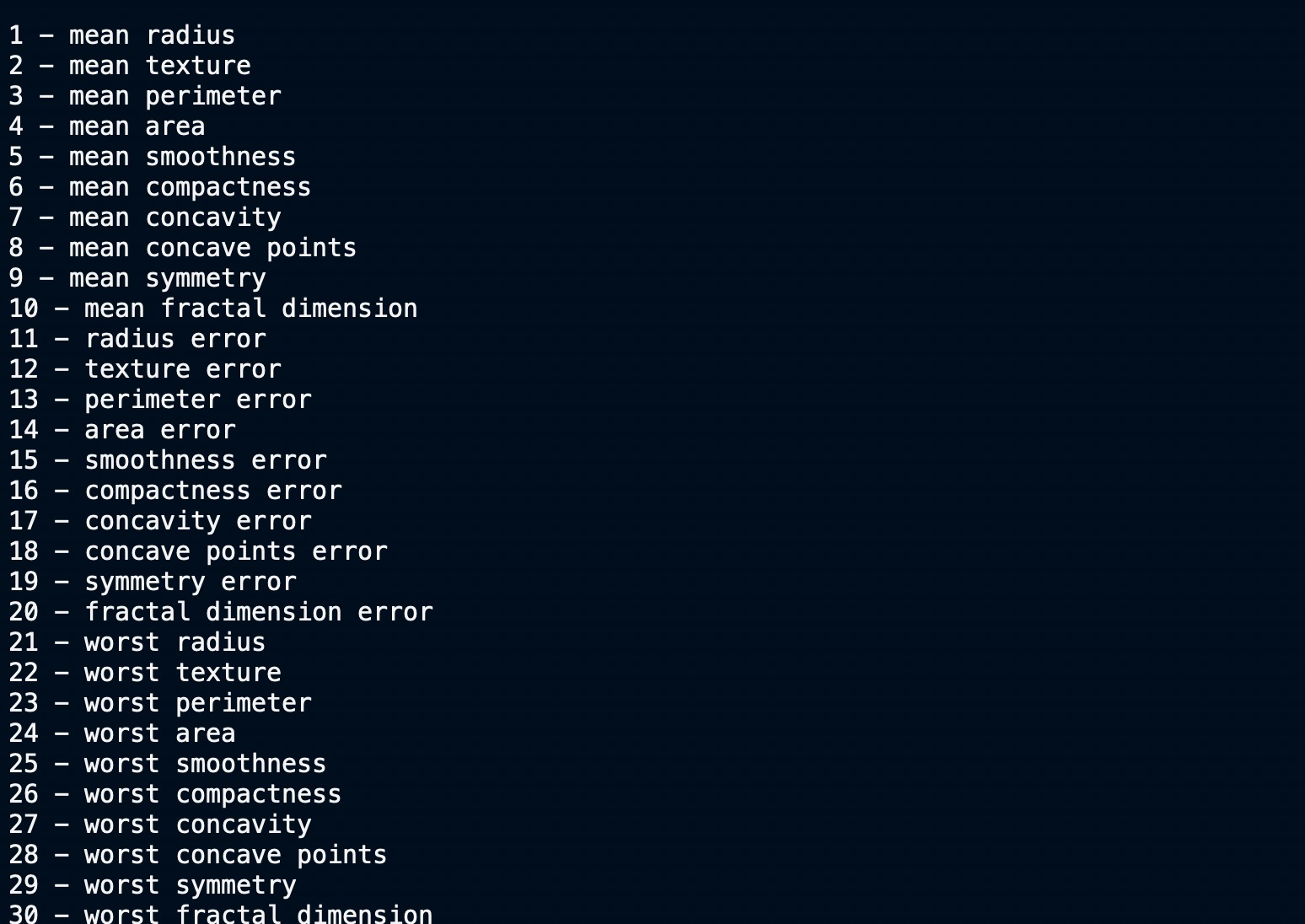
- ‘feature_names’—決定惡性的各種特征/屬性的名稱
特征名
目標值、名稱和數據維度
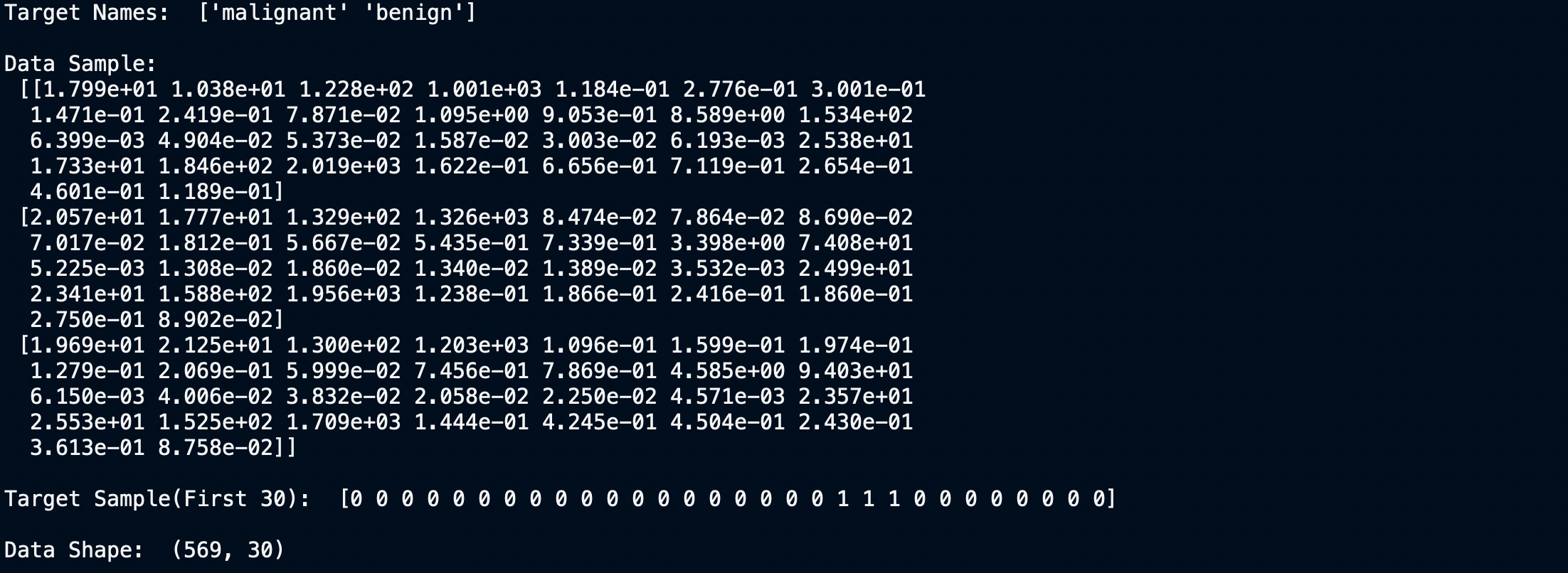
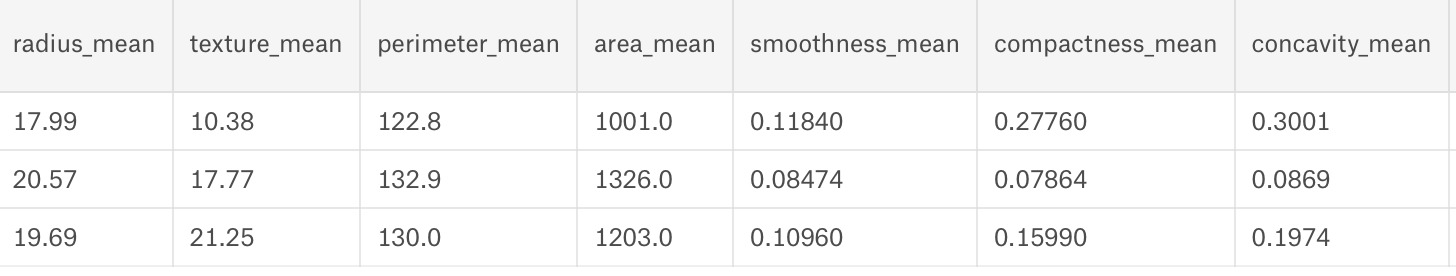
我們可以清楚地看到數據集有30列和569行。現在讓我們為其建立模型。
繪製數據
切分數據
要了解模型性能,我們需要首先將數據集分切分訓練集和測試集。
讓我們使用函數 train_test_split()拆分數據集。您需要傳遞3個參數:特征、目標和測試集的大小。您也可以(可選)使用random_state隨機選擇記錄。在我們的例子中,我們對訓練集和測試集按90:10進行分割。
# Import train_test_split function
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Split dataset into training set and test set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data, data.target, test_size=0.1) # 90% training and 10% test過濾掉無用的功能
我們有30個定義數據的屬性/特征,然而並非所有這些都是對我們的分類問題有用的。相關性(Correlation)很容易用來消除不重要的屬性。
如果2個要素高度相關,則它們傳達相同的信息。因此,可以刪除其中之一。
讓我們繪製一個熱圖來了解相關性。右對角線始終為1,因為特征與其自身的相關性為1。
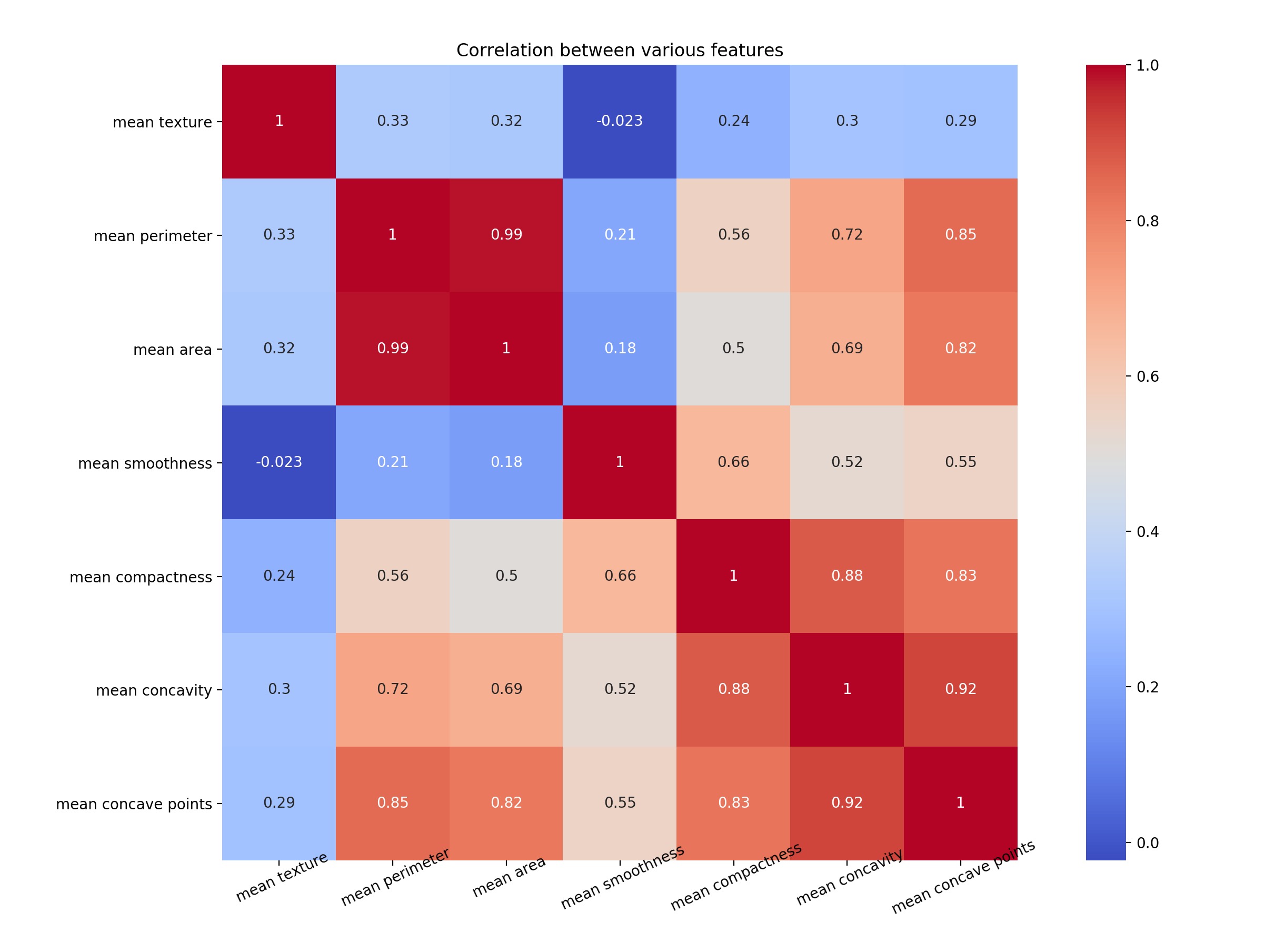
上圖的代碼如下
#Import the necessary libraries
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#Arrange the data as a dataframe
data1 = pd.DataFrame(data.data)
data1.columns = data.feature_names
# Plotting only 7 features out of 30
NUM_POINTS = 7
features_mean= list(data1.columns[1:NUM_POINTS+1])
feature_names = data.feature_names[1:NUM_POINTS+1]
print(feature_names)
f,ax = plt.subplots(1,1) #plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
sns.heatmap(data1[features_mean].corr(), annot=True, square=True, cmap='coolwarm')
# Set number of ticks for x-axis
ax.set_xticks([float(n)+0.5 for n in range(NUM_POINTS)])
# Set ticks labels for x-axis
ax.set_xticklabels(feature_names, rotation=25, rotation_mode="anchor",fontsize=10)
# Set number of ticks for y-axis
ax.set_yticks([float(n)+0.5 for n in range(NUM_POINTS)])
# Set ticks labels for y-axis
ax.set_yticklabels(feature_names, rotation='horizontal', fontsize=10)
plt.title("Correlation between various features")
plt.show()
plt.close()注意mean concave points特征與mean concavity/strong>特征具有0.92的相關性。
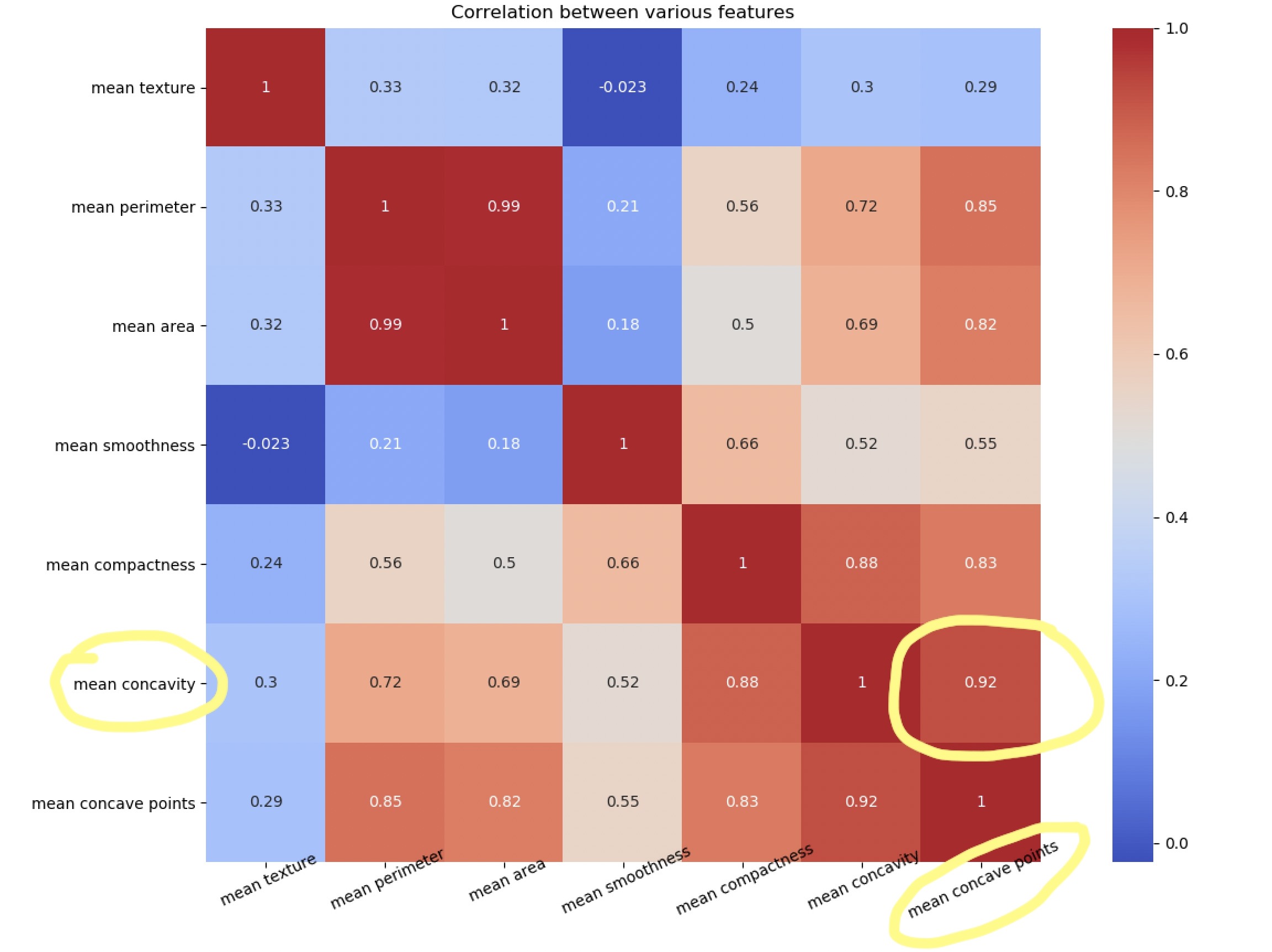
散點矩陣
查看高度相關特征的另一種方法是繪製散點矩陣
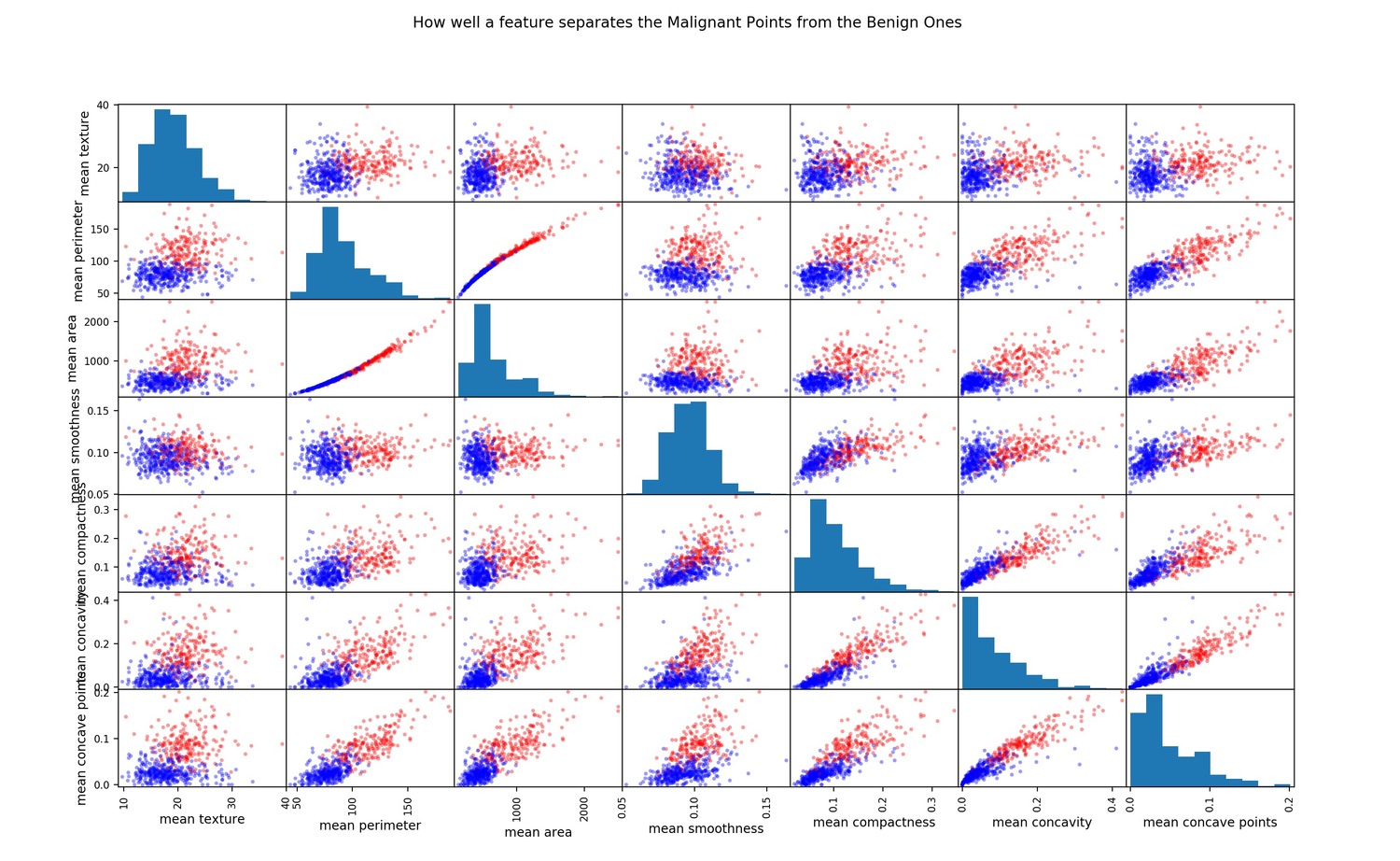
點分布得越多,特征關聯就越少。
散點矩陣的代碼如下
#Color Labels - 0 is benign and 1 is malignant
color_dic = {0:'red', 1:'blue'}
target_list = list(data['target'])
colors = list(map(lambda x: color_dic.get(x), target_list))
#Plotting the scatter matrix
sm = pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(data1[features_mean], c= colors, alpha=0.4, figsize=((10,10)))
plt.suptitle("How well a feature separates the Malignant Points from the Benign Ones")
plt.show()還可以進行其他類型的繪圖,以進一步分析每個特征和2個類別。
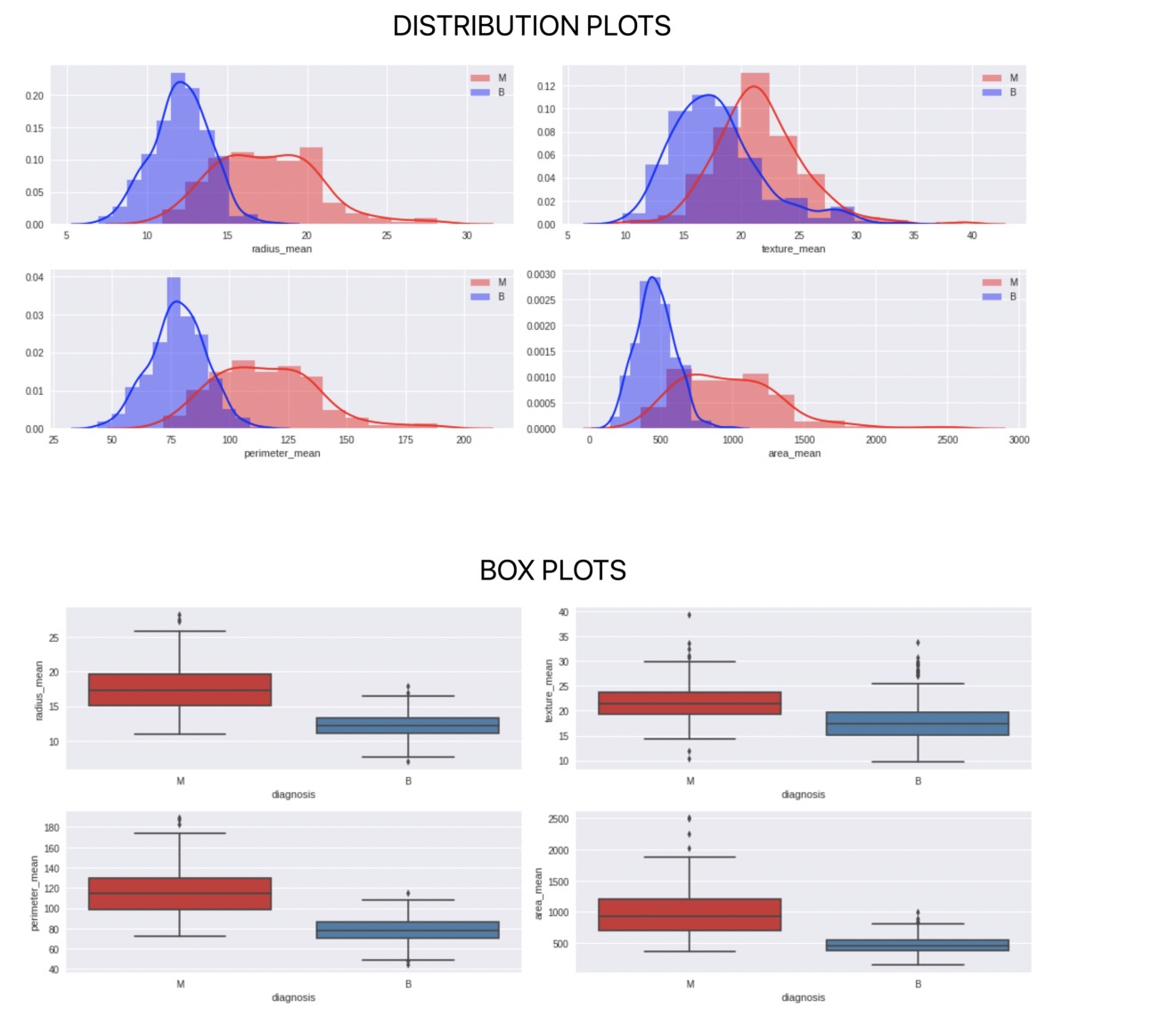
建立模型和測試準確性
最後,我們進入構建模型並測試模型準確性的階段。此處需要做的一件重要事情是確定K的值,我們分別使用K = 1、5和10並查看結果。

我們可以看到,K = 1的表現非常差,因為它沒有吸收很多鄰居的輸入,而K = 5和10的表現幾乎相似。
建立模型並獲得準確性的代碼如下
#Import knearest neighbors Classifier model
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
#Import scikit-learn metrics module for accuracy calculation
from sklearn import metrics
#Create KNN Classifiers
knn1 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)
knn5 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn10 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10)
#Train the model using the training sets
knn1.fit(X_train, Y_train)
#Predict the response for test dataset
Y_pred = knn1.predict(X_test)
# Model Accuracy, how often is the classifier correct?
print("\n\nK=1, Accuracy:",round(metrics.accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred)*100,1), "%")
#Train the model using the training sets
knn5.fit(X_train, y=Y_train)
#Predict the response for test dataset
Y_pred = knn5.predict(X_test)
# Model Accuracy, how often is the classifier correct?
print("K=5 Accuracy:",round(metrics.accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred)*100,1), "%")
#Train the model using the training sets
knn10.fit(X_train, Y_train)
#Predict the response for test dataset
Y_pred = knn10.predict(X_test)
# Model Accuracy, how often is the classifier correct?
print("K=10 Accuracy:",round(metrics.accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred)*100,1), "%")