根据索引从参数轴axis 收集切片。 (不推荐使用的参数)
用法
tf.compat.v1.gather(
params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None, axis=None, batch_dims=0
)参数
-
params从中收集值的Tensor。必须至少排名axis + 1。 -
indices索引Tensor。必须是以下类型之一:int32,int64。这些值必须在[0, params.shape[axis])范围内。 -
validate_indices已弃用,什么都不做。索引总是在 CPU 上验证,从不在 GPU 上验证。警告:在 CPU 上,如果发现超出范围的索引,则会引发错误。在 GPU 上,如果发现超出范围的索引,则将 0 存储在相应的输出值中。
-
axis一个Tensor。必须是以下类型之一:int32,int64。params中的axis从中收集indices。必须大于或等于batch_dims。默认为第一个非批量维度。支持负索引。 -
batch_dims一个integer。批次维度的数量。必须小于或等于rank(indices)。 -
name操作的名称(可选)。
返回
-
一个
Tensor。具有与params相同的类型。
警告:不推荐使用某些参数:(validate_indices)。它们将在未来的版本中被删除。更新说明:validate_indices 参数无效。索引总是在 CPU 上验证,从不在 GPU 上验证。
根据 indices 从 params 轴 axis 收集切片。 indices 必须是任何维度的整数张量(通常是一维)。
Tensor.getitem 适用于标量、tf.newaxis 和 python 切片
tf.gather 扩展索引以处理索引张量。
在最简单的情况下,它与标量索引相同:
params = tf.constant(['p0', 'p1', 'p2', 'p3', 'p4', 'p5'])
params[3].numpy()
b'p3'
tf.gather(params, 3).numpy()
b'p3'最常见的情况是传递索引的单轴张量(这不能表示为 python 切片,因为索引不是连续的):
indices = [2, 0, 2, 5]
tf.gather(params, indices).numpy()
array([b'p2', b'p0', b'p2', b'p5'], dtype=object)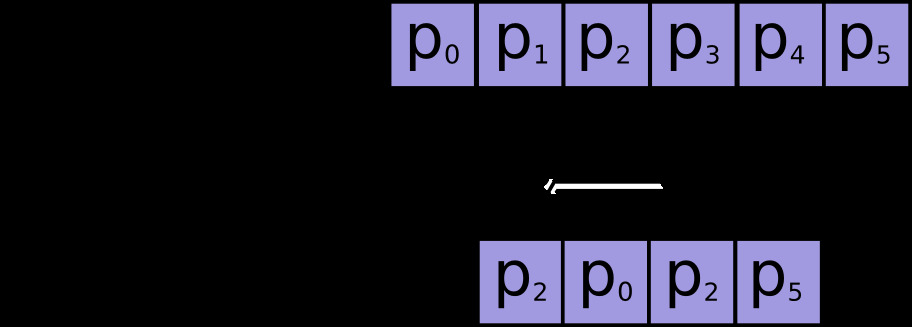
索引可以具有任何形状。当params 有 1 个轴时,输出形状等于输入形状:
tf.gather(params, [[2, 0], [2, 5]]).numpy()
array([[b'p2', b'p0'],
[b'p2', b'p5']], dtype=object)params 也可以具有任何形状。 gather 可以根据 axis 参数(默认为 0)跨任何轴选择切片。下面它用于从矩阵中收集第一行,然后是列:
params = tf.constant([[0, 1.0, 2.0],
[10.0, 11.0, 12.0],
[20.0, 21.0, 22.0],
[30.0, 31.0, 32.0]])
tf.gather(params, indices=[3,1]).numpy()
array([[30., 31., 32.],
[10., 11., 12.]], dtype=float32)
tf.gather(params, indices=[2,1], axis=1).numpy()
array([[ 2., 1.],
[12., 11.],
[22., 21.],
[32., 31.]], dtype=float32)更一般地说:输出形状与输入形状相同,indexed-axis 被索引的形状替换。
def result_shape(p_shape, i_shape, axis=0):
return p_shape[:axis] + i_shape + p_shape[axis+1:]
result_shape([1, 2, 3], [], axis=1)
[1, 3]
result_shape([1, 2, 3], [7], axis=1)
[1, 7, 3]
result_shape([1, 2, 3], [7, 5], axis=1)
[1, 7, 5, 3]这里有些例子:
params.shape.as_list()
[4, 3]
indices = tf.constant([[0, 2]])
tf.gather(params, indices=indices, axis=0).shape.as_list()
[1, 2, 3]
tf.gather(params, indices=indices, axis=1).shape.as_list()
[4, 1, 2]params = tf.random.normal(shape=(5, 6, 7, 8))
indices = tf.random.uniform(shape=(10, 11), maxval=7, dtype=tf.int32)
result = tf.gather(params, indices, axis=2)
result.shape.as_list()
[5, 6, 10, 11, 8]这是因为每个索引都从 params 中获取一个切片,并将其放置在输出中的相应位置。对于上面的例子
# For any location in indices
a, b = 0, 1
tf.reduce_all(
# the corresponding slice of the result
result[:,:, a, b,:] ==
# is equal to the slice of `params` along `axis` at the index.
params[:,:, indices[a, b],:]
).numpy()
True批处理:
batch_dims 参数允许您从批次的每个元素中收集不同的项目。
使用 batch_dims=1 相当于在 params 和 indices 的第一个轴上有一个外循环:
params = tf.constant([
[0, 0, 1, 0, 2],
[3, 0, 0, 0, 4],
[0, 5, 0, 6, 0]])
indices = tf.constant([
[2, 4],
[0, 4],
[1, 3]])tf.gather(params, indices, axis=1, batch_dims=1).numpy()
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]], dtype=int32)这相当于:
def manually_batched_gather(params, indices, axis):
batch_dims=1
result = []
for p,i in zip(params, indices):
r = tf.gather(p, i, axis=axis-batch_dims)
result.append(r)
return tf.stack(result)
manually_batched_gather(params, indices, axis=1).numpy()
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]], dtype=int32)batch_dims 的较高值相当于 params 和 indices 的外轴上的多个嵌套循环。所以整体形函数为
def batched_result_shape(p_shape, i_shape, axis=0, batch_dims=0):
return p_shape[:axis] + i_shape[batch_dims:] + p_shape[axis+1:]
batched_result_shape(
p_shape=params.shape.as_list(),
i_shape=indices.shape.as_list(),
axis=1,
batch_dims=1)
[3, 2]tf.gather(params, indices, axis=1, batch_dims=1).shape.as_list()
[3, 2]如果您需要使用诸如 tf.argsort 或 tf.math.top_k 之类的操作的索引,其中索引的最后一个维度在相应位置索引到输入的最后一个维度,这自然会出现。在这种情况下,您可以使用 tf.gather(values, indices, batch_dims=-1) 。
也可以看看:
tf.Tensor.getitem:直接张量索引操作(t[]),处理标量和python-slicestensor[..., 7, 1:-1]tf.scatter:类似于__setitem__(t[i] = x)的操作集合tf.gather_nd:类似于tf.gather的操作,但一次收集多个轴(它可以收集矩阵的元素而不是行或列)tf.boolean_mask,tf.where:二进制索引。tf.slice和tf.strided_slice:用于对__getitem__的 python-slice 处理(t[1:-1:2])的实现的较低级别访问
相关用法
- Python tf.compat.v1.gather_nd用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.gfile.Copy用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.gfile.Exists用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.gradients用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.get_variable_scope用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.get_local_variable用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.get_variable用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.gfile.FastGFile.close用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.get_session_tensor用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.get_session_handle用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.distributions.Multinomial.stddev用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.distribute.MirroredStrategy.experimental_distribute_dataset用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.data.TFRecordDataset.interleave用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.distributions.Bernoulli.cross_entropy用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.Variable.eval用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.train.FtrlOptimizer.compute_gradients用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.layers.conv3d用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.strings.length用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.data.Dataset.snapshot用法及代码示例
- Python tf.compat.v1.data.experimental.SqlDataset.reduce用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自tensorflow.org大神的英文原创作品 tf.compat.v1.gather。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
