Processing, pushStyle()用法介绍。
用法
pushStyle()
返回
void
说明
pushStyle() 函数保存当前样式设置,popStyle() 恢复之前的设置。请注意,这些函数总是一起使用。它们允许您更改样式设置,然后返回到您所拥有的。当使用 pushStyle() 启动新样式时,它会建立在当前样式信息的基础上。可以嵌入 pushStyle() 和 popStyle() 函数以提供更多控制(参见上面的第二个示例进行演示。)
样式中包含以下函数控制的样式信息:fill(), stroke(), tint(), strokeWeight(), strokeCap(),strokeJoin(),
imageMode(), rectMode(), ellipseMode(), shapeMode(), colorMode(),
textAlign(), textFont(), textMode(), textSize(), textLeading(),
emissive(), specular(), shininess(), ambient()
例子
size(400, 400);
ellipse(0, 200, 132, 132); // Left circle
pushStyle(); // Start a new style
strokeWeight(40);
fill(204, 153, 0);
ellipse(200, 200, 132, 132); // Middle circle
popStyle(); // Restore original style
ellipse(400, 200, 132, 132); // Right circle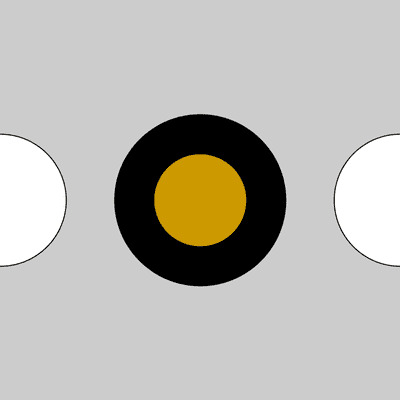
size(400, 400);
ellipse(0, 200, 132, 132); // Left circle
pushStyle(); // Start a new style
strokeWeight(40);
fill(204, 153, 0);
ellipse(132, 200, 132, 132); // Left-middle circle
pushStyle(); // Start another new style
stroke(0, 102, 153);
ellipse(264, 200, 132, 132); // Right-middle circle
popStyle(); // Restore the previous style
popStyle(); // Restore original style
ellipse(400, 200, 132, 132); // Right circle
有关的
相关用法
- Processing push()用法及代码示例
- Processing pushMatrix()用法及代码示例
- Processing parseJSONArray()用法及代码示例
- Processing parseJSONObject()用法及代码示例
- Processing popStyle()用法及代码示例
- Processing pmouseY用法及代码示例
- Processing pop()用法及代码示例
- Processing perspective()用法及代码示例
- Processing pixelDensity()用法及代码示例
- Processing pixelWidth用法及代码示例
- Processing printArray()用法及代码示例
- Processing pointLight()用法及代码示例
- Processing pixelHeight用法及代码示例
- Processing popMatrix()用法及代码示例
- Processing parseXML()用法及代码示例
- Processing printProjection()用法及代码示例
- Processing pmouseX用法及代码示例
- Processing print()用法及代码示例
- Processing printMatrix()用法及代码示例
- Processing pow()用法及代码示例
- Processing printCamera()用法及代码示例
- Processing pixels[]用法及代码示例
- Processing point()用法及代码示例
- Processing println()用法及代码示例
- Processing FFT用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自processing.org大神的英文原创作品 pushStyle()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
