Matplotlib是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的二维图。 Matplotlib是一个基于NumPy数组的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.ticker.LogLocator
这个matplotlib.ticker.LogLocator类用于确定对数轴的刻度位置。在此类中,刻度线的位置为:subs [j] * base ** i。
用法: class matplotlib.ticker.LogLocator(base=10.0, subs=(1.0, ), numdecs=4, numticks=None)
参数:
- subs:它是一个可选参数,可以为None,也可以为字符串或浮点数序列。默认为(1.0,)。它提供了用于放置刻度的基数的整数次幂。仅在基数的整数次幂时,默认位置才会打勾。 auto和all是此处唯一接受的字符串值。刻度线正好位于‘auto’的整数次幂之间,而“全部”则接受整数次幂。在此,无值等于‘auto’。
该类的方法:
- base(self, base):此方法用于设置对数刻度的底数。
- nonsingular(self, vmin, vmax):它用于根据需要扩展范围以避免奇异。
- set_params(self, base=None, subs=None, numdecs=None, numticks=None):用于在刻度内设置参数。
- tick_values(self, vmin, vmax):此方法返回位于vmin和vmax范围之间的刻度线的值。
- subs(self, subs):它用于为每个基数i * subs [j]设置日志刻度的次要刻度。
- view_limit(self, vmin, vmax):该方法在智能选择竞争限制时派上用场。
范例1:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator, LogLocator
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
y = [0.32, 0.30, 0.28, 0.26,
0.24, 0.22, 0.20, 0.18,
0.16, 0.14, 0.12, 0.10]
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
x_major = MultipleLocator(4)
x_minor = MultipleLocator(1)
ax1.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major)
ax1.xaxis.set_minor_locator(x_minor)
ax1.set_yscale("log")
y_major = LogLocator(base = 10)
y_minor = LogLocator(base = 10, subs =[1.1, 1.2, 1.3])
ax1.yaxis.set_major_locator(y_major)
ax1.yaxis.set_minor_locator(y_minor)
ax1.plot(x, y)
plt.show()输出:
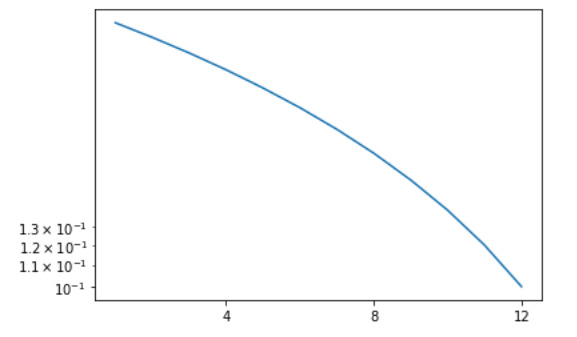
范例2:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import LogLocator
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 10)
y = 2**x
f = plt.figure()
ax = f.add_subplot(111)
plt.yscale('log')
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(LogLocator(base = 100))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.show()输出:
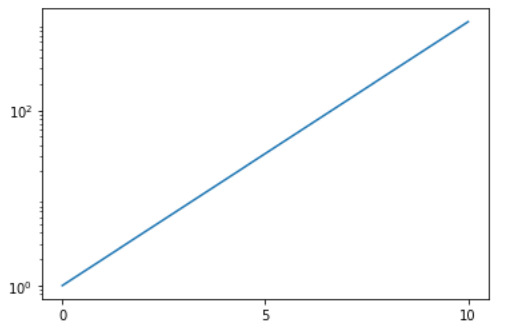
相关用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.Normalize用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.ticker.LogLocator Class in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
