Matplotlib是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的二维图。 Matplotlib是一个基于NumPy数组的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom
这个matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom class是用于处理批注的可调用帮助程序类。
用法: class matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom(artist, ref_coord, unit=’points’)
参数:
- artist:该对象用于计算偏移量。它通常是Artist,BboxBase或Transform。
- ref_coord:是长度2序列。如果是Artist或BboxBase,则此值是偏移量原点到位置的偏移量(以艺术家边界框的分数为单位),而如果Artist是Transform,则该偏移量原点是应用于此值的变换。
- unit:它用于管理要用于偏移输入的屏幕单位(像素或点)。
该类的方法:
- get_unit(self):它是__call__使用的转换输入的单位。
- set_unit(self, unit):它是__call__使用的转换输入的单位,其中,单位参数在‘points’或‘pixels’中。
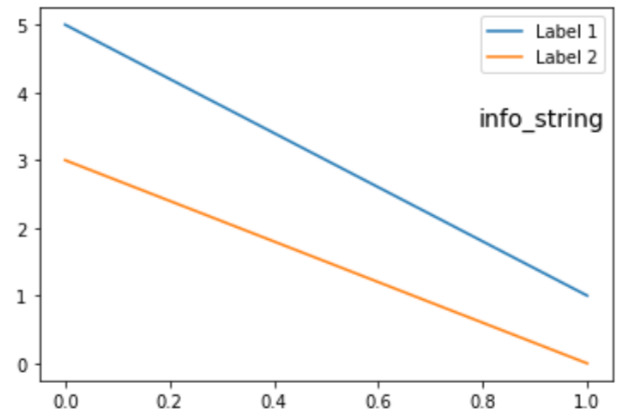
范例1:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.text
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([5,1], label="Label 1")
ax.plot([3,0], label="Label 2")
legend = ax.legend(loc="upper right")
# Create offset from lower right
# corner of legend box, (1.0,0) is
# the coordinates of the offset point
# in the legend coordinate system
offset = matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom(legend, (1.0, 0.0))
# Create annotation. Top right corner
# located -20 pixels below the offset
# point (lower right corner of legend).
ax.annotate("info_string",
xy = (0,0),
size = 14,
xycoords = 'figure fraction',
xytext = (0,-20),
textcoords = offset,
horizontalalignment = 'right',
verticalalignment = 'top')
# Draw the canvas for offset to take effect
fig.canvas.draw()
plt.show()输出:
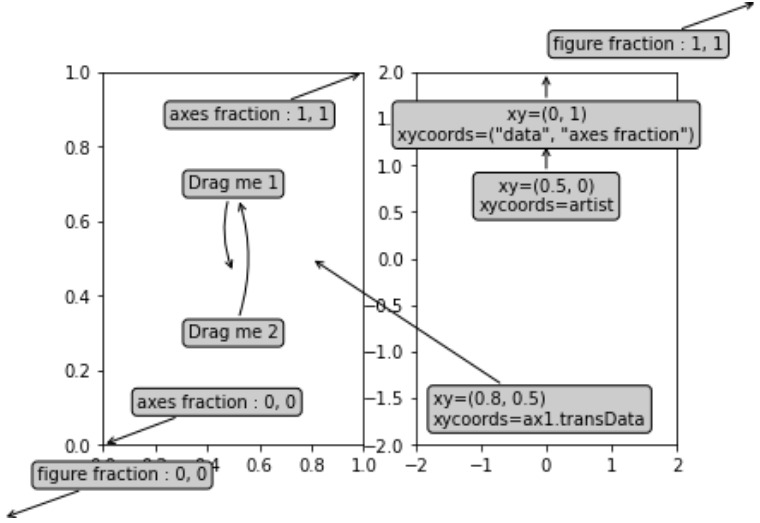
范例2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.text import OffsetFrom
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
bbox_args = dict(boxstyle ="round", fc ="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle ="->")
# Here we'll demonstrate the extents of the coordinate system and how
# we place annotating text.
ax1.annotate('figure fraction:0, 0',
xy =(0, 0),
xycoords ='figure fraction',
xytext =(20, 20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('figure fraction:1, 1',
xy =(1, 1),
xycoords ='figure fraction',
xytext = (-20, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "right",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('axes fraction:0, 0',
xy = (0, 0),
xycoords ='axes fraction',
xytext = (20, 20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax1.annotate('axes fraction:1, 1',
xy =(1, 1),
xycoords ='axes fraction',
xytext = (-20, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "right",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
# It is also possible to generate
# draggable annotations
an1 = ax1.annotate('Drag me 1', xy =(.5, .7),
xycoords ='data',
ha ="center", va ="center",
bbox = bbox_args,
)
an2 = ax1.annotate('Drag me 2', xy =(.5, .5),
xycoords = an1,
xytext =(.5, .3),
textcoords = 'axes fraction',
ha = "center",
va = "center",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = dict(patchB = an1.get_bbox_patch(),
connectionstyle = "arc3, rad = 0.2",
**arrow_args))
an1.draggable()
an2.draggable()
an3 = ax1.annotate('', xy =(.5, .5), xycoords = an2,
xytext =(.5, .5), textcoords = an1,
ha ="center", va ="center",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = dict(patchA = an1.get_bbox_patch(),
patchB = an2.get_bbox_patch(),
connectionstyle ="arc3, rad = 0.2",
**arrow_args))
# Finally we'll show off some more
# complex annotation and placement
text = ax2.annotate('xy =(0, 1)\nxycoords = ("data", "axes fraction")',
xy =(0, 1),
xycoords = ("data", 'axes fraction'),
xytext = (0, -20),
textcoords ='offset points',
ha = "center",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.annotate('xy =(0.5, 0)\nxycoords = artist',
xy =(0.5, 0.),
xycoords = text,
xytext = (0, -20),
textcoords = 'offset points',
ha = "center",
va = "top",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.annotate('xy =(0.8, 0.5)\nxycoords = ax1.transData',
xy =(0.8, 0.5),
xycoords = ax1.transData,
xytext = (10, 10),
textcoords = OffsetFrom(ax2.bbox, (0, 0), "points"),
ha = "left",
va = "bottom",
bbox = bbox_args,
arrowprops = arrow_args)
ax2.set(xlim =[-2, 2], ylim =[-2, 2])
plt.show()输出:
相关用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.Normalize用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.text.OffsetFrom class in python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
