Matplotlib是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的二维图。 Matplotlib是一个基于NumPy数组的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.colors.Colormap
matplotlib.colors.Colormap类属于matplotlib.colors模块。 matplotlib.colors模块用于将颜色或数字参数转换为RGBA或RGB。此模块用于将数字映射到颜色或以一维颜色数组(也称为colormap)进行颜色规格转换。
matplotlib.colors.Colormap类是所有标量到RGBA映射的基类。通常,色图实例用于将数据值(浮点数)从间隔0-1转换为它们各自的RGBA颜色。这里,matplotlib.colors.Normalize类用于缩放数据。 matplotlib.cm.ScalarMappable子类将其大量用于data-> normalize-> map-to-color处理链。
用法:
matplotlib.colors.Colormap类(名称,N = 256)
Parameters:
- name:它接受一个代表颜色名称的字符串。
- N:它是一个整数值,代表rgb量化级别的数量。
类的方法:
- colorbar_extend = None:如果颜色映射存在于标量可映射对象上并且colorbar_extend设置为false,则创建颜色条将选择colorbar_extend作为matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar构造函数中的extend关键字的默认值。
- is_gray(self):返回一个布尔值,以检查plt是否为灰色。
- reversed(self, name=None):用于制作Colormap的反向实例。基类未实现此函数。它具有一个参数,即name是可选参数,并接受反向色图的字符串名称。如果设置为None,则成为父色图+ “r”的名称。
- set_bad(自我,颜色=“ k”,字母=无):它设置用于遮罩值的颜色。
- set_over(self, color=’k’,, alpha=None):它用于设置颜色以用于超出范围的高值。它要求norm.clip为False。
- set_under(self, color=’k’,, alpha=None):它用于设置颜色以用于超出范围的低值。它要求norm.clip为False。
例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
start_point = 'lower'
diff = 0.025
a = b = np.arange(-3.0, 3.01, diff)
A, B = np.meshgrid(a, b)
X1 = np.exp(-A**2 - B**2)
X2 = np.exp(-(A - 1)**2 - (B - 1)**2)
X = (X1 - X2) * 2
RR, RC = X.shape
# putting NaNs in one corner:
X[-RR // 6:, -RC // 6:] = np.nan
X = np.ma.array(X)
# masking the other corner:
X[:RR // 6,:RC // 6] = np.ma.masked
# masking a circle in the middle:
INNER = np.sqrt(A**2 + B**2) < 0.5
X[INNER] = np.ma.masked
# using automatic selection of
# contour levels;
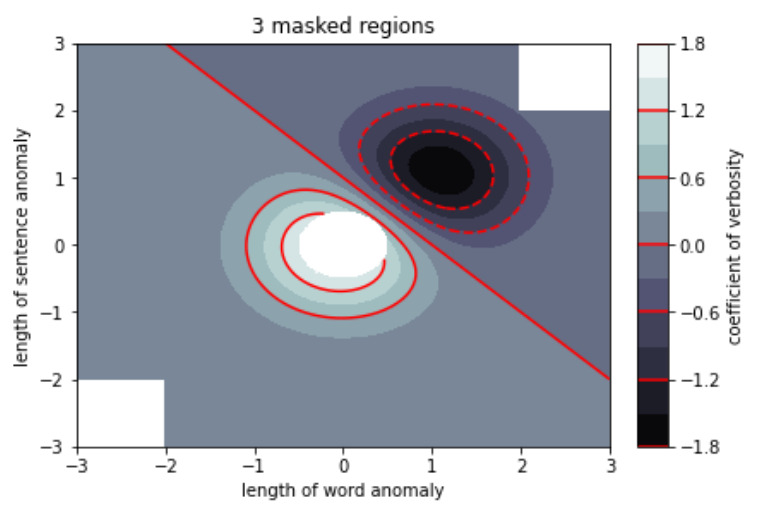
figure1, axes2 = plt.subplots(constrained_layout = True)
C = axes2.contourf(A, B, X, 10,
cmap = plt.cm.bone,
origin = start_point)
C2 = axes2.contour(C, levels = C.levels[::2],
colors ='r', origin = start_point)
axes2.set_title('3 masked regions')
axes2.set_xlabel('length of word anomaly')
axes2.set_ylabel('length of sentence anomaly')
# Make a colorbar for the ContourSet
# returned by the contourf call.
cbar = figure1.colorbar(C)
cbar.ax.set_ylabel('coefficient of verbosity')
# Add the contour line levels
# to the colorbar
cbar.add_lines(C2)
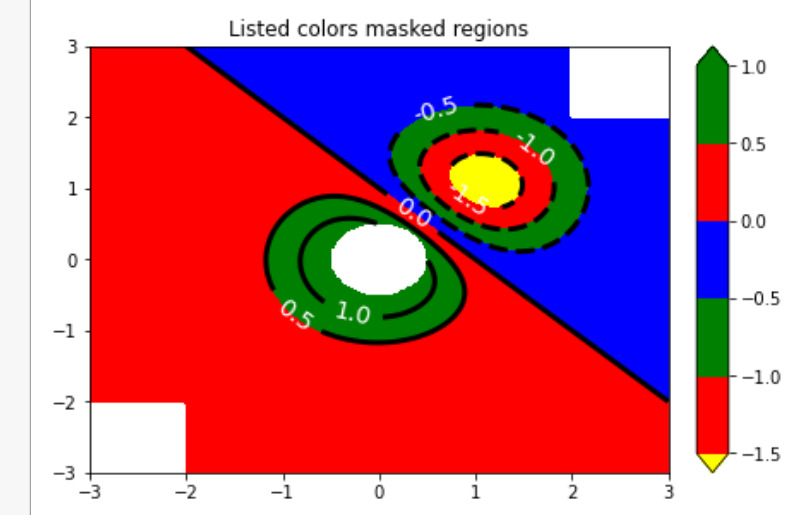
figure2, axes2 = plt.subplots(constrained_layout = True)
# making a contour plot with the
# levels specified,
levels = [-1.5, -1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1]
C3 = axes2.contourf(A, B, X, levels,
colors =('r', 'g', 'b'),
origin = start_point,
extend ='both')
# data below the lowest contour
# level yellow, data below the
# highest level green:
C3.cmap.set_under('yellow')
C3.cmap.set_over('green')
C4 = axes2.contour(A, B, X, levels,
colors =('k', ),
linewidths =(3, ),
origin = start_point)
axes2.set_title('Listed colors (3 masked regions)')
axes2.clabel(C4, fmt ='% 2.1f',
colors ='w',
fontsize = 14)
figure2.colorbar(C3)
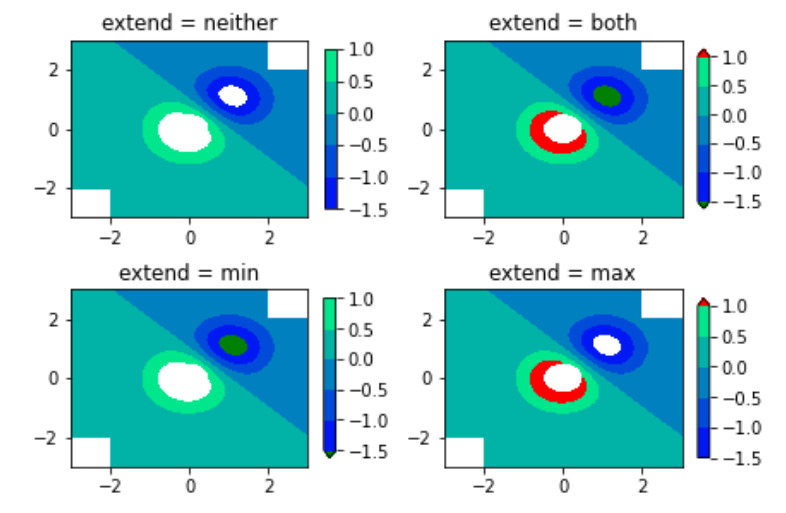
# Illustrating all 4 possible
# "extend" settings:
extends = ["neither", "both", "min", "max"]
cmap = plt.cm.get_cmap("winter")
cmap.set_under("green")
cmap.set_over("red")
figure, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2,
constrained_layout = True)
for ax, extend in zip(axes.ravel(), extends):
cs = ax.contourf(A, B, X, levels,
cmap = cmap,
extend = extend,
origin = start_point)
figure.colorbar(cs, ax = ax, shrink = 0.9)
ax.set_title("extend = % s" % extend)
ax.locator_params(nbins = 4)
plt.show()输出:
相关用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.Normalize用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.colors.Colormap class in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
