Matplotlib是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的二维图。 Matplotlib是一个基于NumPy数组的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm
matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm类属于matplotlib.colors模块。 matplotlib.colors模块用于将颜色或数字参数转换为RGBA或RGB。此模块用于将数字映射到颜色或以一维颜色数组(也称为colormap)进行颜色规格转换。
matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm类用于基于离散间隔创建颜色图。 BoundaryNorm将值映射到整数,这与Normalize或LogNorm映射到0到1的间隔不同。分段线性插值可用于映射到o-间隔,但是,使用整数更简单,并且减少了数量在整数和浮点数之间来回转换。
参数:
- boundaries:这是一个像对象的数组,它单调增加边界序列
- ncolor:它接受一个整数值,该值表示将要使用的颜色图中的多种颜色。
- clip:它接受布尔值,并且是一个可选参数。如果剪辑是
True,则超出范围且它们位于bounds [0]之下的值将映射为0,而如果它们位于boundary [-1]之上,则将它们映射为ncolors-1。如果剪辑设置为False,则超出范围的值且它们低于boundaries[0]被映射为-1,而如果它们在bounds [-1]之上,则它们被映射为ncolor。这Colormap.__call__()将它们转换为有效索引。
注意:箱的边由边界定义,并且落在箱中的数据被映射到相同的颜色索引。如果ncolors不等于bin的数量,则使用线性插值为其选择颜色。
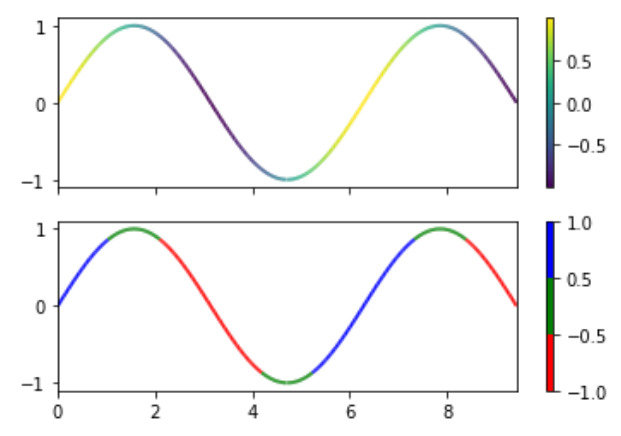
范例1:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap, BoundaryNorm
a = np.linspace(0, 3 * np.pi, 500)
b = np.sin(a)
# this is the first derivative
dbda = np.cos(0.5 * (a[:-1] + a[1:]))
# Createing line segments so
# to color them individually
points = np.array([a, b]).T.reshape(-1, 1, 2)
set_of_segments = np.concatenate([points[:-1],
points[1:]],
axis = 1)
figure, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1,
sharex = True,
sharey = True)
# Mapping the data points with
# continous norm
continous_norm = plt.Normalize(dbda.min(),
dbda.max())
line_collection = LineCollection(set_of_segments,
cmap ='viridis',
norm = continous_norm)
# Set the values used for
# colormapping
line_collection.set_array(dbda)
line_collection.set_linewidth(2)
line = axes[0].add_collection(line_collection)
figure.colorbar(line, ax = axes[0])
# Use a boundary norm instead
cmap = ListedColormap(['r', 'g', 'b'])
boundary_norm = BoundaryNorm([-1, -0.5, 0.5, 1],
cmap.N)
line_collection = LineCollection(set_of_segments,
cmap = cmap,
norm = boundary_norm)
line_collection.set_array(dbda)
line_collection.set_linewidth(2)
line = axes[1].add_collection(line_collection)
figure.colorbar(line, ax = axes[1])
axes[0].set_xlim(a.min(), a.max())
axes[0].set_ylim(-1.1, 1.1)
plt.show()输出:
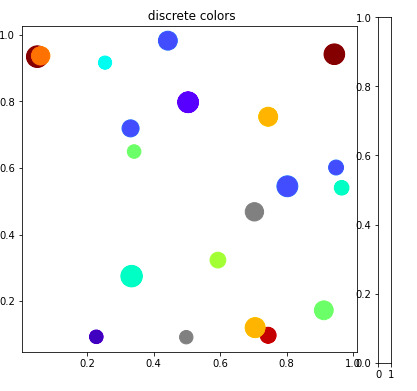
范例2:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
# setup the plot
figure, axes = plt.subplots(1, 1,
figsize=(6, 6))
# defining random data
x = np.random.rand(20)
y = np.random.rand(20)
tag = np.random.randint(0, 20, 20)
tag[10:12] = 0
# defining the colormap
cmap = plt.cm.jet
# extracting all colors
cmaplist = [cmap(i) for i in range(cmap.N)]
# making first color entry grey
cmaplist[0] = (.5, .5, .5, 1.0)
# new map
cmap = mpl.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list(
'Custom cmap', cmaplist, cmap.N)
# defining the bins and norms
bounds = np.linspace(0, 20, 21)
norm = mpl.colors.BoundaryNorm(bounds,
cmap.N)
# the scatter
scat = axes.scatter(x, y, c=tag,
s=np.random.randint(100,
500,
20),
cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
# axes for the colorbar
ax2 = figure.add_axes([0.95, 0.1,
0.03, 0.8])
axes.set_title(' discrete colors')输出:
相关用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.Normalize用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm class in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
