node.each()函数用于按广度优先顺序评估每个节点的函数。在这种情况下,每个节点正好被访问一次。对于每个子节点重复调用此函数。
用法:
node.each(function);
参数:该函数接受如上所述和以下描述的单个参数:
- function:这需要在BFS顺序中的每个节点上调用一个函数。
返回值:此函数不返回任何内容。
范例1:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF-8" />
<meta name = "viewport"
path1tent = "width=device-width,
initial-scale = 1.0"/>
<script src =
"https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Constructing a tree
var tree={
name:"rootNode",
children:[
{
name:"child1"
},
{
name:"child2",
children:[
{
name:"grandchild1",
children:[
{
name:"grand_granchild1_1"
},
{
name:"grand_granchild1_2"
}
]
},
{
name:"grandchild2",
children:[
{
name:"grand_granchild2_1"
},
{
name:"grand_granchild2_2"
}
]
},
]
}
]
};
var obj = d3.hierarchy(tree);
const BFS = [];
// Function is used
obj.each(d => BFS.push(
" ".repeat(d.depth) + `${d.depth}:${d.data.name}`
));
BFS.forEach((e)=>{
console.log("level:",e);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>输出:
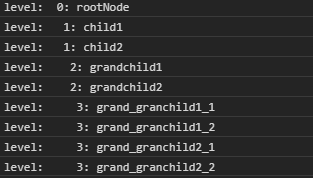
范例2:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF-8" />
<meta name = "viewport"
path1tent = "width=device-width,
initial-scale = 1.0"/>
<script src =
"https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Constructing a tree
var tree={
// Level zero
name:"rootNode",
children:[
{
// Level one
name:"child1"
},
{
// Level one
name:"child2",
children:[
{
// Level two
name:"grandchild1",
children:[{
name:"grand_granchild1_1"
},
{
name:"grand_granchild1_2"
}]
}
]
},
{
// Level one
name:"child3"
},
{
// Level one
name:"child4"
}
]
};
var obj = d3.hierarchy(tree);
const BFS = [];
// Function is used
obj.each(d => BFS.push(
" ".repeat(d.depth)
+ `${d.depth}:${d.data.name}`
));
console.log(BFS);
</script>
</body>
</html>输出:
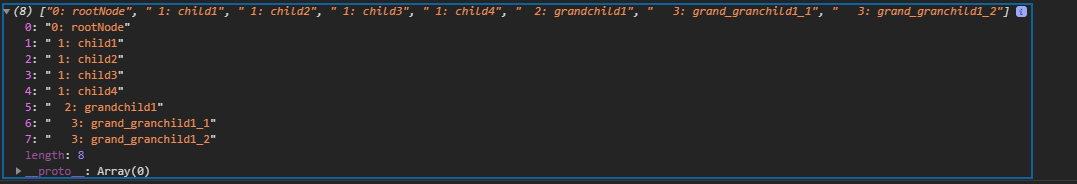
相关用法
- d3.js d3.sum()用法及代码示例
- PHP min( )用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.mean()用法及代码示例
- d3.js dsv()用法及代码示例
- PHP max( )用法及代码示例
- p5.js value()用法及代码示例
- p5.js nf()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.min()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.hsl()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Set xor()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.map.set()用法及代码示例
- p5.js nfc()用法及代码示例
- p5.js nfp()用法及代码示例
- p5.js nfs()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Set last()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Set add()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自tarun007大神的英文原创作品 D3.js node.each() Function。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
