Python是進行數據分析的一種出色語言,主要是因為以數據為中心的python軟件包具有奇妙的生態係統。 Pandas是其中的一種,使導入和分析數據更加容易。
Pandas dataframe.pow()函數計算數據幀和其他逐元素(二進製運算符pow)的指數冪。此函數與dataframe ** other但支持將缺失值填充到輸入數據之一中。
用法: DataFrame.pow(other, axis=’columns’, level=None, fill_value=None)
參數:
other:係列,DataFrame或常量
axis:對於係列輸入,軸與係列索引匹配
level:在一個級別上廣播,在傳遞的MultiIndex級別上匹配索引值
fill_value:在計算之前,請使用此值填充現有的缺失(NaN)值以及成功完成DataFrame對齊所需的任何新元素。如果兩個對應的DataFrame位置中的數據均丟失,則結果將丟失。
** kwargs:其他關鍵字參數將傳遞到DataFrame.shift或Series.shift中。
返回:結果:DataFrame
範例1:采用pow()函數查找數據幀中每個元素的功效。使用一係列將連續的每個元素提高到不同的冪。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the dataframe
df1 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[14, 4, 5, 4, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 20, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 6, 2, 6]})
# Print the dataframe
df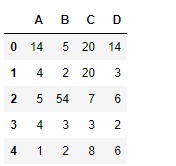
讓我們創建一個係列
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the Series
sr = pd.Series([2, 3, 4, 2], index =["A", "B", "C", "D"])
# Print the series
sr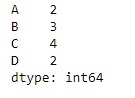
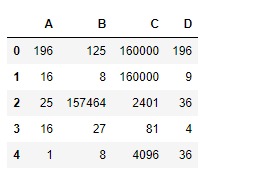
現在,讓我們使用dataframe.pow()函數將連續的每個元素提升為不同的功率。
# find the power
df.pow(sr, axis = 1)輸出:
範例2:采用pow()用於將第一數據幀的每個元素提升到另一個數據幀中的相應元素的冪的函數。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the first dataframe
df1 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[14, 4, 5, 4, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 20, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 6, 2, 6]})
# Creating the second dataframe
df2 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1, 5, 3, 4, 2],
"B":[3, 2, 4, 3, 4],
"C":[2, 2, 7, 3, 4],
"D":[4, 3, 6, 12, 7]})
# using pow() function to raise each element
# in df1 to the power of corresponding element in df2
df1.pow(df2)輸出:
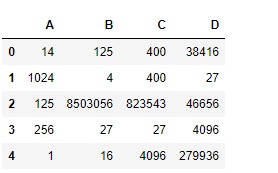
相關用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas dataframe.pow()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
