Pandas DataFrame是帶有標簽軸(行和列)的二維大小可變的,可能是異構的表格數據結構。算術運算在行和列標簽上對齊。可以將其視為Series對象的dict-like容器。這是 Pandas 的主要數據結構。
Pandas DataFrame.ftypes屬性返回DataFrame中的ftypes(指示稀疏/密集和dtype)。它返回具有每個列的數據類型的Series。
用法: DataFrame.ftypes
參數:沒有
返回:係列
範例1:采用DataFrame.ftypes屬性以檢查給定Dataframe中的列是否稀疏或密集。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Weight':[45, 88, 56, 15, 71],
'Name':['Sam', 'Andrea', 'Alex', 'Robin', 'Kia'],
'Age':[14, 25, 55, 8, 21]})
# Create the index
index_ = ['Row_1', 'Row_2', 'Row_3', 'Row_4', 'Row_5']
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)輸出:
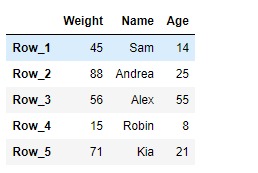
現在我們將使用DataFrame.ftypes屬性以檢查給定數據幀中列的ftype。
# check if the column are
# dense or sparse
result = df.ftypes
# Print the result
print(result)輸出:
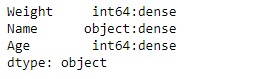
正如我們在輸出中看到的,DataFrame.ftypes屬性已成功返回包含給定數據幀中每一列的ftypes的係列。
範例2:采用DataFrame.ftypes屬性以檢查給定Dataframe中的列是否稀疏或密集。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create an array
arr = [100, 35, 125, 85, 35]
# Creating a sparse DataFrame
df = pd.SparseDataFrame(arr)
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)輸出:
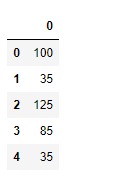
現在我們將使用DataFrame.ftypes屬性以檢查給定數據幀中列的ftype。
# check if the column are
# dense or sparse
result = df.ftypes
# Print the result
print(result)輸出:
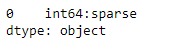
正如我們在輸出中看到的,DataFrame.ftypes屬性已成功返回給定數據幀的ftype。
相關用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.len()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.factorize()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.ne()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.between()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.where()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.add()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot_table()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.mod()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.at[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.iat[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.pivot()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.mul()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.melt()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas DataFrame.ftypes。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
