本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 numpy.hamming 的用法。
用法:
numpy.hamming(M)返回漢明窗。
漢明窗是使用加權餘弦形成的錐度。
- M: int
輸出窗口中的點數。如果為零或更小,則返回一個空數組。
- out: ndarray
最大值歸一化為 1 的窗口(僅當樣本數為奇數時才會出現值 1)。
參數:
返回:
注意:
漢明窗定義為
Hamming 以 J. W. Tukey 的合夥人 R. W. Hamming 命名,並在 Blackman 和 Tukey 中有所說明。建議在時域中平滑截斷的自協方差函數。大多數對漢明窗的引用來自信號處理文獻,它被用作平滑值的許多窗函數之一。它也被稱為變跡(表示“removing the foot”,即平滑采樣信號開始和結束處的不連續性)或錐形函數。
參考:
Blackman, R.B. 和 Tukey, J.W.,(1958) 功率譜的測量,Dover Publications,紐約。
E.R. Kanasewich,“地球物理學中的時間序列分析”,阿爾伯塔大學出版社,1975 年,第 109-110 頁。
維基百科,“Window function”,https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function
W.H.出版社,B.P. Flannery、S.A. Teukolsky 和 W.T. Vetterling,“Numerical Recipes”,劍橋大學出版社,1986 年,第 425 頁。
1:
2:
3:
4:
例子:
>>> np.hamming(12) array([ 0.08 , 0.15302337, 0.34890909, 0.60546483, 0.84123594, # may vary 0.98136677, 0.98136677, 0.84123594, 0.60546483, 0.34890909, 0.15302337, 0.08 ])繪製窗口和頻率響應:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from numpy.fft import fft, fftshift >>> window = np.hamming(51) >>> plt.plot(window) [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.title("Hamming window") Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Hamming window') >>> plt.ylabel("Amplitude") Text(0, 0.5, 'Amplitude') >>> plt.xlabel("Sample") Text(0.5, 0, 'Sample') >>> plt.show()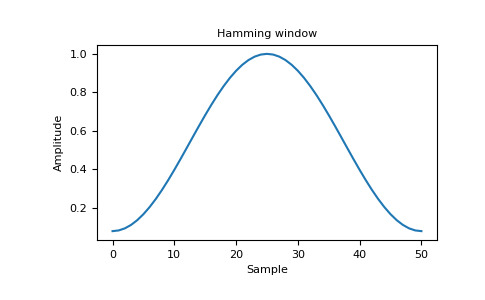
>>> plt.figure() <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes> >>> A = fft(window, 2048) / 25.5 >>> mag = np.abs(fftshift(A)) >>> freq = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, len(A)) >>> response = 20 * np.log10(mag) >>> response = np.clip(response, -100, 100) >>> plt.plot(freq, response) [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.title("Frequency response of Hamming window") Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Frequency response of Hamming window') >>> plt.ylabel("Magnitude [dB]") Text(0, 0.5, 'Magnitude [dB]') >>> plt.xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]") Text(0.5, 0, 'Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]') >>> plt.axis('tight') ... >>> plt.show()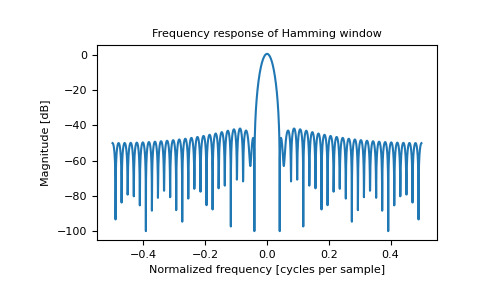
相關用法
- Python numpy hanning用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermfromroots用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermediv用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hsplit用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermline用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermpow用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermx用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermefromroots用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermmul用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.herm2poly用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermsub用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermeline用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermeint用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermeadd用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hstack用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.poly2herme用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermdiv用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermevander用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermepow用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.poly2herm用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermetrim用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermezero用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite.hermdomain用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hermite_e.hermex用法及代碼示例
- Python numpy hypot用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自numpy.org大神的英文原創作品 numpy.hamming。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
