
在本文中,我將討論什麽是Elasticsearch以及如何在Python中使用Elasticsearch(簡稱ES)。
什麽是ElasticSearch?
ElasticSearch(ES)是基於Apache Lucene構建的分布式高可用開源搜索引擎。ES使用JAVA開發,可用於很多平台。ES以JSON格式存儲非結構化數據,可以作為NoSQL數據庫。ES不但具有NoSQL數據庫特性,還提供了搜索及很多其他相關功能。
ElasticSearch用例
可以將ES用於多種用途,下麵提供了其中的幾個例子:
- 您正在運行的網站提供許多動態內容。無論是電子商務網站還是博客,通過部署ES,不僅可以為Web應用程序提供強大的搜索能力,還可以在應用程序中提供本機自動補全功能。
- 您可以收集不同種類的日誌數據,然後借助ES查找趨勢和統計數據。
設置和運行
安裝ElasticSearch的最簡單方法是下載它並運行可執行文件。必須確保使用的是Java 7或更高版本。
下載後,解壓縮並運行其二進製文件。
elasticsearch-6.2.4 bin/elasticsearch滾動窗口中將有很多文本,如果您看到類似下麵的內容,則表明啟動成功。
[2018-05-27T17:36:11,744][INFO ][o.e.h.n.Netty4HttpServerTransport] [c6hEGv4] publish_address {127.0.0.1:9200}, bound_addresses {[::1]:9200}, {127.0.0.1:9200}為了進一步驗證一切正常,請訪問該URL:http://localhost:9200,可以在瀏覽器中打開或通過cURL,ES會返回以下內容。
{
"name" : "c6hEGv4",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "HkRyTYXvSkGvkvHX2Q1-oQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.2.4",
"build_hash" : "ccec39f",
"build_date" : "2018-04-12T20:37:28.497551Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.2.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}ES提供了REST API,我們嘗試使用它來執行不同的任務。
基本範例
要做的第一件事就是創建一個索引(Index)。一切都存儲在索引中。 RDBMS(關係數據庫管理係統)跟這裏所說的索引(Index)相對應的是一個數據庫。因此,請勿將這裏的Index與您在RDBMS中學習的典型索引概念相混淆。這裏用用PostMan運行REST API。
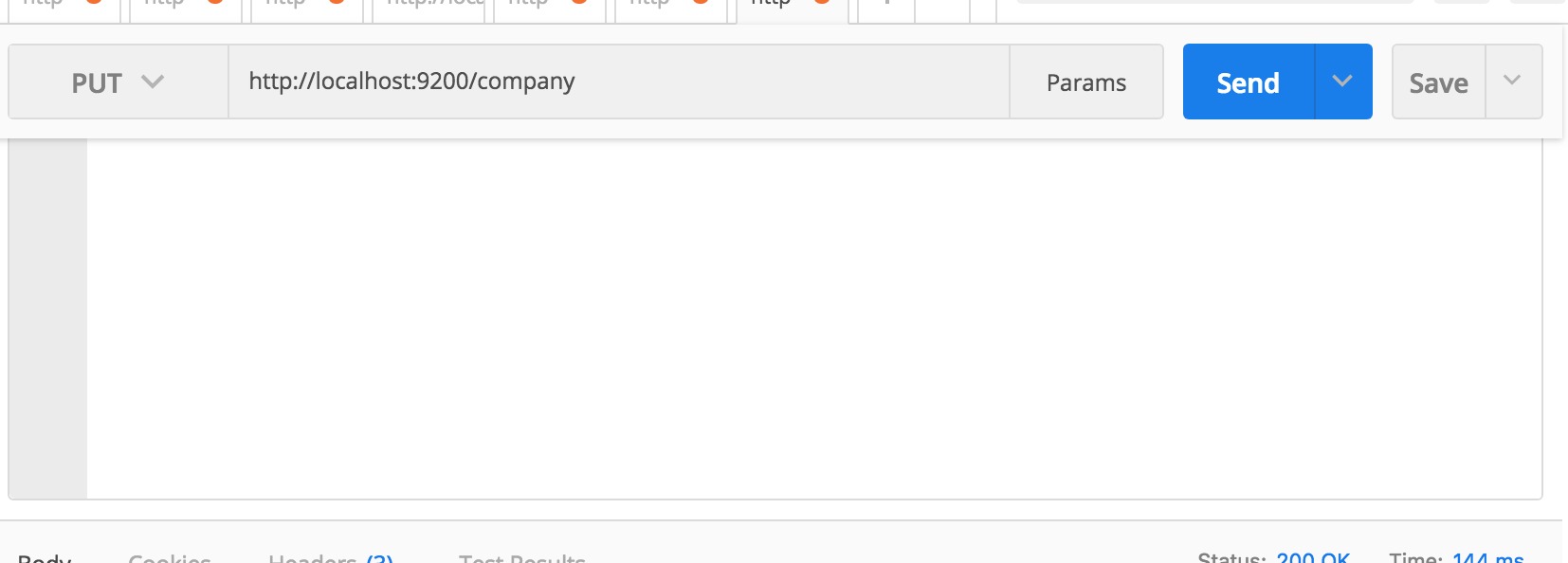
如果運行成功,您將看到如下類似的響應。
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "company"
}即,我們創建了一個數據庫,名稱為company。換句話說,我們創建了一個Index叫company。如果從瀏覽器訪問http://localhost:9200/company,您將看到類似以下內容:
{
"company": {
"aliases": {
},
"mappings": {
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"creation_date": "1527638692850",
"number_of_shards": "5",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "RnT-gXISSxKchyowgjZOkQ",
"version": {
"created": "6020499"
},
"provided_name": "company"
}
}
}
}暫時忽略其中的mappings,這個我們稍後再討論。creation_date是創建時間戳。number_of_shards告訴將保留此Index數據的分區數。如果您正在運行包含多個Elastic節點的集群,則整個數據將在節點之間拆分。簡而言之,如果有5個分片,則整個數據可在5個分片上使用,並且ElasticSearch集群可以從它的任何節點處理請求。
number_of_replicas是指數據的鏡像。如果您熟悉數據庫主從(master-slave)的概念,那麽這對您來說並不新鮮。可以從這裏了解有關基本ES概念的更多信息。
使用cURL創建索引可以一行代碼搞定:
➜ elasticsearch-6.2.4 curl -X PUT localhost:9200/company
{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"company"}%您還可以一次執行索引創建和記錄插入任務,要做的就是以JSON格式傳遞數據記錄。對應的PostMan用法如下:
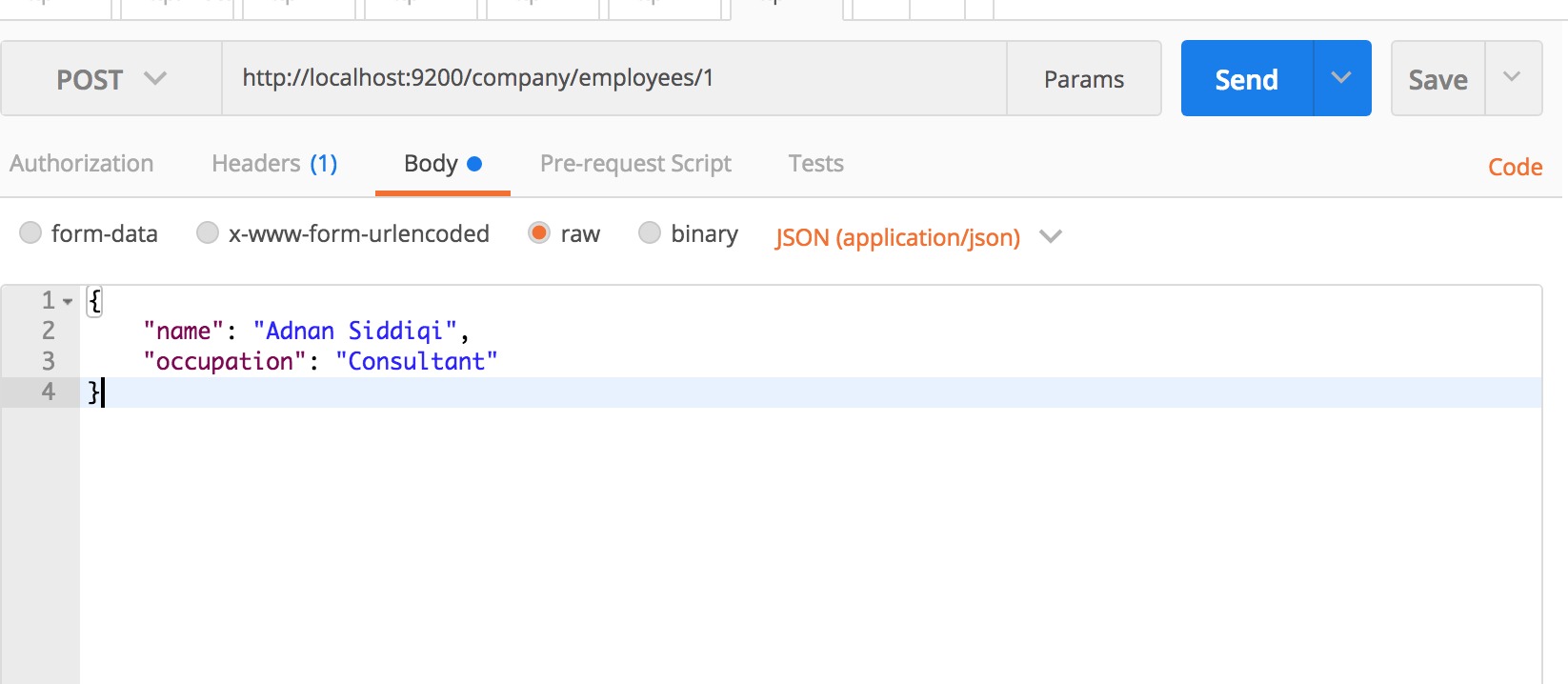
確保設置Content-Type為application/json
它將創建一個名為company的索引(如果不存在),然後創建一個新的Type(類型)叫employees。ES中的Type(類型)實際上對應在RDBMS中的Table。
上麵的請求將輸出以下JSON結構:
{
"_index": "company",
"_type": "employees",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}然後,您以JSON格式傳入數據,該數據最終將作為新記錄或文檔插入。如果您從瀏覽器訪問http://localhost:9200/company/employees/1,將看到以下內容。
{"_index":"company","_type":"employees","_id":"1","_version":1,"found":true,"_source":{
"name": "Adnan Siddiqi",
"occupation": "Consultant"
}}可以看到實際記錄以及元數據。如果您願意,可以將請求更改為http://localhost:9200/company/employees/1/_source則隻會輸出記錄的JSON結構。
cURL版本為:
➜ elasticsearch-6.2.4 curl -X POST \
> http://localhost:9200/company/employees/1 \
> -H 'content-type: application/json' \
> -d '{
quote> "name": "Adnan Siddiqi",
quote> "occupation": "Consultant"
quote> }'
{"_index":"company","_type":"employees","_id":"1","_version":1,"result":"created","_shards":{"total":2,"successful":1,"failed":0},"_seq_no":0,"_primary_term":1}%如果您想更新該記錄怎麽辦?也很簡單。您要做的就是更改JSON記錄。如下所示:

它將生成以下輸出:
{
"_index": "company",
"_type": "employees",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1
}注意_result現在設置為updated(替代created)。
當然,您也可以刪除某些記錄。

如果要刪除所有數據,可以用命令:curl -XDELETE localhost:9200/_all【謹慎操作!】。
接下來嘗試一些基本的檢索。如果你運行:http://localhost:9200/company/employees/_search?q=adnan,它將搜索employees類型下的所有字段並返回相關記錄。
{
"took": 7,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 0.2876821,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "company",
"_type": "employees",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.2876821,
"_source": {
"name": "Adnan Siddiqi",
"occupation": "Software Consultant"
}
}
]
}
}max_score字段表明記錄的相關性,即記錄的最高分數。
您還可以通過傳遞字段名稱來將搜索條件限製為某個字段。例如,http://localhost:9200/company/employees/_search?q=name:Adnan,將僅搜索name文檔的字段。它實際上等效於SQL:SELECT * from table where name='Adnan'
ES還可以做很多事情,可以另行參考文檔。這裏我們切換到介紹如何使用Python訪問ES。
在Python中訪問ElasticSearch
老實說,ES的REST API足夠好,您可以使用requests庫來執行所有任務。不過,您也可以使用Python庫處理ElasticSearch從而專注於您的主要任務,而不必擔心如何創建請求。
通過pip安裝ES,然後可以在Python程序中訪問它。
pip install elasticsearch
為確保已正確安裝,請從命令行運行以下基本代碼段:
➜ elasticsearch-6.2.4 python
Python 3.6.4 |Anaconda custom (64-bit)| (default, Jan 16 2018, 12:04:33)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Clang 4.0.1 (tags/RELEASE_401/final)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
>>> es = Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200}])
>>> es
<Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200}])>網頁抓取和Elasticsearch
讓我們討論一下使用Elasticsearch的一些實際用例。目的是訪問在線食譜並將其存儲在Elasticsearch中用於搜索和分析目的。我們將首先從Allrecipes抓取數據並將其存儲在ES中。要注意的是,我們需要創建一個嚴格的Schema或Mapping,以確保以正確的格式和類型對數據進行索引。具體步驟如下:
抓取數據
import json from time import sleepimport requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoupdef parse(u): title = '-' submit_by = '-' description = '-' calories = 0 ingredients = [] rec = {}try: r = requests.get(u, headers=headers)if r.status_code == 200: html = r.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # title title_section = soup.select('.recipe-summary__h1') # submitter submitter_section = soup.select('.submitter__name') # description description_section = soup.select('.submitter__description') # ingredients ingredients_section = soup.select('.recipe-ingred_txt')# calories calories_section = soup.select('.calorie-count') if calories_section: calories = calories_section[0].text.replace('cals', '').strip()if ingredients_section: for ingredient in ingredients_section: ingredient_text = ingredient.text.strip() if 'Add all ingredients to list' not in ingredient_text and ingredient_text != '': ingredients.append({'step': ingredient.text.strip()})if description_section: description = description_section[0].text.strip().replace('"', '')if submitter_section: submit_by = submitter_section[0].text.strip()if title_section: title = title_section[0].textrec = {'title': title, 'submitter': submit_by, 'description': description, 'calories': calories, 'ingredients': ingredients} except Exception as ex: print('Exception while parsing') print(str(ex)) finally: return json.dumps(rec)if __name__ == '__main__': headers = { 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_11_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.181 Safari/537.36', 'Pragma': 'no-cache' } url = 'https://www.allrecipes.com/recipes/96/salad/' r = requests.get(url, headers=headers) if r.status_code == 200: html = r.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') links = soup.select('.fixed-recipe-card__h3 a') for link in links: sleep(2) result = parse(link['href']) print(result) print('=================================')
以上是提取數據的基本程序。由於需要JSON格式的數據,因此我進行了相應的轉換。
創建索引
有了所需的數據之後,接下來考慮如何存儲。我們要做的第一件事就是創建Index(索引)。將索引命名為recipes,Type為salads。要做的另一件事是給文檔結構創建一個 mapping(映射)。
在創建索引之前,我們必須連接ElasticSearch服務器。
import logging def connect_elasticsearch(): _es = None _es = Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200}]) if _es.ping(): print('Yay Connect') else: print('Awww it could not connect!') return _esif __name__ == '__main__': logging.basicConfig(level=logging.ERROR)
其中_es.ping()對服務器發送ping請求,如果連接上的話返回True。
def create_index(es_object, index_name='recipes'):
created = False
# index settings
settings = {
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"members": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"submitter": {
"type": "text"
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"calories": {
"type": "integer"
},
}
}
}
}
try:
if not es_object.indices.exists(index_name):
# Ignore 400 means to ignore "Index Already Exist" error.
es_object.indices.create(index=index_name, ignore=400, body=settings)
print('Created Index')
created = True
except Exception as ex:
print(str(ex))
finally:
return created對上麵的代碼做個簡要說明:
首先,我們傳遞了一個config變量,其中包含整個文檔結構的映射。Mapping是Elastic的Schema術語。就像我們在數據庫Table表中設置某些字段數據類型一樣,我們在這裏做類似的事情。除了calories是Integer之外,所有其他字段均為text類型。
然後,我要確保索引根本不存在,然後再創建它。參數ignore=400在檢查之後不再需要它,但是如果您不檢查是否存在,則可以抑製該錯誤並覆蓋現有索引。不過這有風險,就像覆蓋數據庫一樣。
如果索引創建成功,則可以通過訪問http://localhost:9200/recipes/_mappings 進行驗證,它將打印如下內容:
{
"recipes": {
"mappings": {
"salads": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"calories": {
"type": "integer"
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"submitter": {
"type": "text"
},
"title": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
}通過傳入dynamic:strict,我們強迫Elasticsearch對所有傳入文檔進行嚴格檢查。這裏,salads實際上是文檔類型。
存入索引
下一步是存儲實際數據或文檔。
def store_record(elastic_object, index_name, record):
try:
outcome = elastic_object.index(index=index_name, doc_type='salads', body=record)
except Exception as ex:
print('Error in indexing data')
print(str(ex))運行它,您將看到以下輸出:
Error in indexing data
TransportError(400, 'strict_dynamic_mapping_exception', 'mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [ingredients] within [salads] is not allowed')你能猜出為什麽會這樣嗎?由於在我們的映射中沒有設置ingredients,ES不允許我們存儲包含ingredients字段的文檔。現在,我們認識到了Mapping的好處,它可以避免破壞數據。現在,讓我們對映射進行一些更改,如下所示:
"mappings": {
"salads": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"submitter": {
"type": "text"
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"calories": {
"type": "integer"
},
"ingredients": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"step": {"type": "text"}
}
},
}
}
}我們在Mapping中增加了ingrdients,其類型為nested。然後設置了其內部字段的數據類型,也就是text
nested數據類型讓您設置嵌套JSON對象的類型。再次運行它,將會看到以下輸出:
{
'_index': 'recipes',
'_type': 'salads',
'_id': 'OvL7s2MBaBpTDjqIPY4m',
'_version': 1,
'result': 'created',
'_shards': {
'total': 1,
'successful': 1,
'failed': 0
},
'_seq_no': 0,
'_primary_term': 1
}由於您沒有通過_id設置文檔ID,ES為存儲的文檔分配了動態ID。我在Chrome瀏覽器中使用ES數據查看器查看數據,它的工具名為ElasticSearch工具箱。
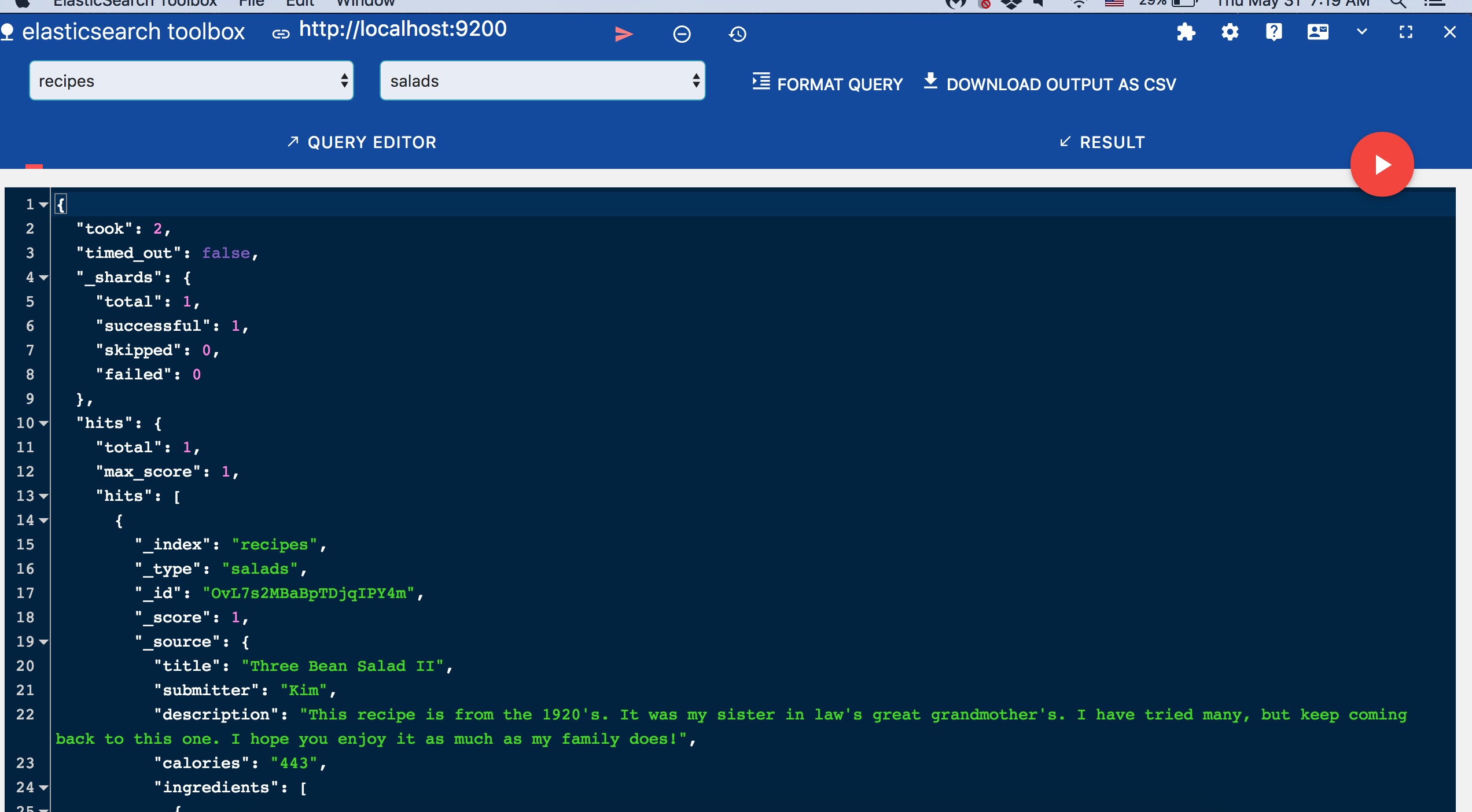
在繼續之前,我們先存儲一個字符串給calories字段,看看情況如何。(記住我們已經將calories設置為integer類型)。結果會出現以下錯誤:
TransportError(400, 'mapper_parsing_exception', 'failed to parse [calories]')
現在我們進一步了解到為文檔設置Mapping的好處。當然,如果您不這樣做也可以,因為Elasticsearch將在運行時自動進行基本的默認映射。
查詢記錄
建好索引之後,可以根據需要進行查詢。我要創建一個名為search()的函數,它將顯示查詢結果。
def search(es_object, index_name, search):
res = es_object.search(index=index_name, body=search)這讓我們嘗試一些查詢。
if __name__ == '__main__':
es = connect_elasticsearch()
if es is not None:
search_object = {'query': {'match': {'calories': '102'}}}
search(es, 'recipes', json.dumps(search_object))上麵的查詢將返回其中calories等於102的所有記錄。在我們的例子中,輸出為:
{'_shards': {'failed': 0, 'skipped': 0, 'successful': 1, 'total': 1},
'hits': {'hits': [{'_id': 'YkTAuGMBzBKRviZYEDdu',
'_index': 'recipes',
'_score': 1.0,
'_source': {'calories': '102',
'description': "I've been making variations of "
'this salad for years. I '
'recently learned how to '
'massage the kale and it makes '
'a huge difference. I had a '
'friend ask for my recipe and I '
"realized I don't have one. "
'This is my first attempt at '
'writing a recipe, so please '
'let me know how it works out! '
'I like to change up the '
'ingredients: sometimes a pear '
'instead of an apple, '
'cranberries instead of '
'currants, Parmesan instead of '
'feta, etc. Great as a side '
'dish or by itself the next day '
'for lunch!',
'ingredients': [{'step': '1 bunch kale, large '
'stems discarded, '
'leaves finely '
'chopped'},
{'step': '1/2 teaspoon salt'},
{'step': '1 tablespoon apple '
'cider vinegar'},
{'step': '1 apple, diced'},
{'step': '1/3 cup feta cheese'},
{'step': '1/4 cup currants'},
{'step': '1/4 cup toasted pine '
'nuts'}],
'submitter': 'Leslie',
'title': 'Kale and Feta Salad'},
'_type': 'salads'}],
'max_score': 1.0,
'total': 1},
'timed_out': False,
'took': 2}如果您想在其中獲取calories大於20的記錄怎麽辦?
search_object = {'_source': ['title'], 'query': {'range': {'calories': {'gte': 20}}}}
您還可以指定要返回的列或字段。上麵的查詢將返回所有calories大於20的記錄。
結論
Elasticsearch是一個功能強大的工具,能夠為各種應用提供豐富準確的查詢功能。我們剛剛介紹了要點,可以進一步閱讀文檔來熟悉這個工具。特別是模糊搜索功能非常出色。如果有機會,我將在以後的文章中介紹Query DSL。
注:本文代碼可以在Github找到。
本文最初發表於這裏。
