借助sympy.stats.WignerSemicircle()方法,我们可以获得代表Wigner半圆分布的连续随机变量。
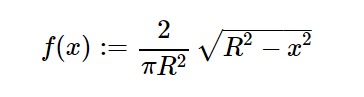
用法:sympy.stats.WignerSemicircle(name, R)
Where, R is real number.
返回:Return the continuous random variable.
范例1:
在这个例子中,我们可以通过使用sympy.stats.WignerSemicircle()通过这种方法,我们可以获得代表Wigner半圆分布的连续随机变量。
# Import sympy and WignerSemicircle
from sympy.stats import WignerSemicircle, density
from sympy import Symbol, pprint
z = Symbol("z")
r = Symbol("r", positive = True)
# Using sympy.stats.WignerSemicircle() method
X = WignerSemicircle("x", r)
gfg = density(X)(z)
pprint(gfg)输出:
_________
/ 2 2
2*\/ r - z
————-
2
pi*r
范例2:
# Import sympy and WignerSemicircle
from sympy.stats import WignerSemicircle, density
from sympy import Symbol, pprint
z = 0.87
r = 2
# Using sympy.stats.WignerSemicircle() method
X = WignerSemicircle("x", r)
gfg = density(X)(z)
pprint(gfg)输出:
0.900430452616969
—————-
pi
相关用法
- Python sympy.sin()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.nT()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.Add()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy RGS用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.ff()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.tan()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.apart()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.nC()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.nP()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.Mul()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.S()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.rf()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.eye()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.csc()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.Pow()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.gcd()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.cot()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.sec()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.cos()用法及代码示例
- Python sympy.ones()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Jitender_1998大神的英文原创作品 Sympy stats.WignerSemicircle() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
