在本教程中,我们将借助示例了解 Python Set intersection() 方法。
intersection() 方法返回一个新集合,其中包含所有集合共有的元素。
示例
A = {2, 3, 5}
B = {1, 3, 5}
# compute intersection between A and B
print(A.intersection(B))
# Output: {3, 5}
用法:
用法:
A.intersection(*other_sets)
参数:
intersection() 允许任意数量的参数(集合)。
注意: *不是语法的一部分。它用于指示该方法允许任意数量的参数。
返回:
intersection() 方法返回集合 A 与所有集合的交集(作为参数传递)。
如果参数未传递给 intersection() ,则返回集合的浅拷贝( A )。
示例 1:Python 集 intersection()
A = {2, 3, 5, 4}
B = {2, 5, 100}
C = {2, 3, 8, 9, 10}
print(B.intersection(A))
print(B.intersection(C))
print(A.intersection(C))
print(C.intersection(A, B))
输出
{2, 5}
{2}
{2, 3}
{2}
工作组intersection()
两个或多个集合的交集是所有集合共有的元素集合。例如:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {2, 3, 4, 9}
C = {2, 4, 9 10}
Then,
A∩B = B∩A ={2, 3, 4}
A∩C = C∩A ={2, 4}
B∩C = C∩B ={2, 4, 9}
A∩B∩C = {2, 4}
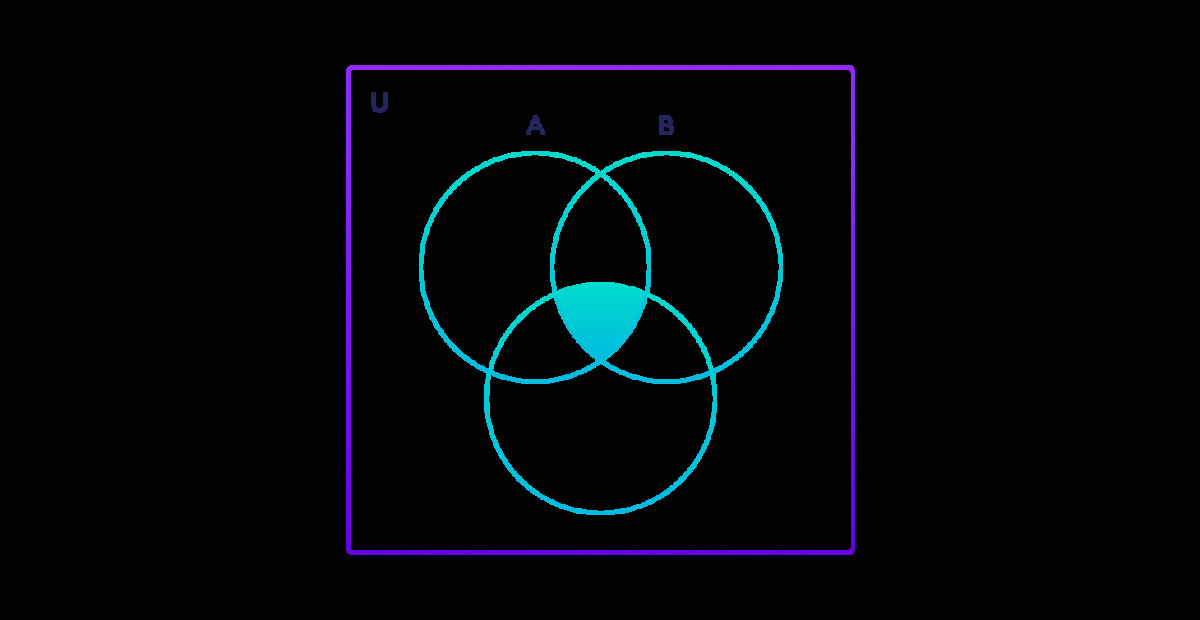
更多示例
A = {100, 7, 8}
B = {200, 4, 5}
C = {300, 2, 3}
D = {100, 200, 300}
print(A.intersection(D))
print(B.intersection(D))
print(C.intersection(D))
print(A.intersection(B, C, D))
输出
{100}
{200}
{300}
set()
示例 3:使用 & 运算符设置交集
您还可以使用& 运算符找到集合的交集。
A = {100, 7, 8}
B = {200, 4, 5}
C = {300, 2, 3, 7}
D = {100, 200, 300}
print(A & C)
print(A & D)
print(A & C & D)
print(A & B & C & D)
输出
{7}
{100}
set()
set() 相关用法
- Python Set intersection_update()用法及代码示例
- Python Set issuperset()用法及代码示例
- Python Set issubset()用法及代码示例
- Python Set isdisjoint()用法及代码示例
- Python Set difference_update()用法及代码示例
- Python Set union()用法及代码示例
- Python Set pop()用法及代码示例
- Python Set add()用法及代码示例
- Python Set clear()用法及代码示例
- Python Set symmetric_difference()用法及代码示例
- Python Set symmetric_difference_update()用法及代码示例
- Python Set discard()用法及代码示例
- Python Set copy()用法及代码示例
- Python Set difference()用法及代码示例
- Python Set remove()用法及代码示例
- Python Set update()用法及代码示例
- Python Set转String用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.cumsum()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.astype()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.nonzero()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 Python Set intersection()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
