Python是进行数据分析的一种出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的python软件包具有奇妙的生态系统。 Pandas是其中的一种,使导入和分析数据更加容易。
Pandas 系列是带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不必是唯一的,但必须是可哈希的类型。该对象同时支持基于整数和基于标签的索引,并提供了许多方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.squeeze()函数将一维轴对象压缩为标量。具有单个元素的Series或DataFrames被压缩为标量。具有单列或单行的DataFrame被压缩为Series。否则,对象不变。
用法: Series.squeeze(axis=None)
参数:
axis:要挤压的特定轴。默认情况下,所有长度为1的轴都受到挤压。
返回:挤压一个或多个轴后的投影。
范例1:采用Series.squeeze()函数将给定系列的单个元素压缩为标量。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([100, 25, 32, 118, 24, 65])
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:

让我们以仅包含那些可以被13整除的元素的方式转换系列。
# Keep only those elements which are divisible by 13
sr_temp = sr[sr % 13 == 0]
# Let's print the series
print(sr_temp)输出:
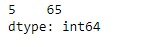
现在我们将使用Series.squeeze()函数将给定的序列对象简化为标量。
# squeeze the series to scalar
sr_temp.squeeze()输出:

从输出中可以看到,Series.squeeze()函数已成功将给定的序列简化为标量。
范例2:采用Series.squeeze()函数挤压给定的系列对象。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([19.5, 16.8, None, 22.78, None, 20.124, None, 18.1002, None])
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:

现在我们将使用Series.std()函数挤压给定的系列对象。
# squeeze the series to scalar
sr_temp.squeeze()输出:

从输出中可以看到,Series.squeeze()函数已返回相同的序列对象,因为给定的序列对象中有多个元素,因此无法将其压缩为标量值。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.contains()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.std()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.sem()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.ix[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.Categorical()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.apply()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.contains用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.now用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.pad()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.take()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.all()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas series.str.get()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas Series.squeeze()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
