Python是进行数据分析的一种出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的python软件包具有奇妙的生态系统。 Pandas是其中的一种,使导入和分析数据更加容易。
Pandas Timestamp.now()函数返回本地时区的当前时间。等效于datetime.now([tz])。
用法:Timestamp.now()
参数:没有
返回:时间戳记
范例1:采用Timestamp.now()函数返回本地时区的当前时间。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the Timestamp object
ts = pd.Timestamp(year = 2011, month = 11, day = 21,
hour = 10, second = 49, tz = 'US/Central')
# Print the Timestamp object
print(ts)输出:
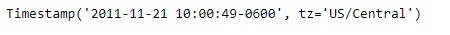
现在我们将使用Timestamp.now()函数以查找当地时区的当前时间。
# return the current time
ts.now()输出:
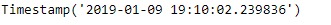
正如我们在输出中看到的,Timestamp.now()函数已返回当地时区的当前时间。它会自动检测本地时区。
范例2:采用Timestamp.now()函数返回本地时区的当前时间。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the Timestamp object
ts = pd.Timestamp(year = 2009, month = 5, day = 31,
hour = 4, second = 49, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# Print the Timestamp object
print(ts)输出:
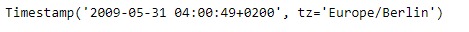
现在我们将使用Timestamp.now()函数以查找当地时区的当前时间。
# return the current time
ts.now()输出:

正如我们在输出中看到的,Timestamp.now()函数已返回当地时区的当前时间。它会自动检测本地时区。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.contains()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.std()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.sem()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.ix[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.Categorical()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.apply()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.contains用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.pad()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.take()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.all()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas series.str.get()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.add()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas Timestamp.now。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
