Pandas 系列是带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不必是唯一的,但必须是可哈希的类型。该对象同时支持基于整数和基于标签的索引,并提供了许多方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.factorize()函数将对象编码为枚举类型或分类变量。当所有重要的事情是识别不同的值时,此方法对于获取数组的数字表示很有用。
用法: Series.factorize(sort=False, na_sentinel=-1)
参数:
sort:排序唯一性和随机标签以保持关系。
na_sentinel:标记“not found”的值。
返回:
labels:ndarray
uniques:ndarray,索引或分类
范例1:采用Series.factorize()函数编码给定系列对象的基础数据。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', None, 'Rio'])
# Create the Index
sr.index = ['City 1', 'City 2', 'City 3', 'City 4', 'City 5']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:

现在我们将使用Series.factorize()函数编码给定系列对象的基础数据。
# encode the values
result = sr.factorize()
# Print the result
print(result)输出:

正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.factorize()函数已成功编码给定系列对象的基础数据。注意,缺少的值已分配为代码-1。
范例2:采用Series.factorize()函数编码给定系列对象的基础数据。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([80, 25, 3, 80, 24, 25])
# Create the Index
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)输出:
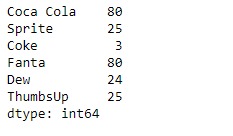
现在我们将使用Series.factorize()函数编码给定系列对象的基础数据。
# encode the values
result = sr.factorize()
# Print the result
print(result)输出:
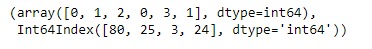
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.factorize()函数已成功编码给定系列对象的基础数据。
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.contains()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.std()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.sem()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.ix[ ]用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.Categorical()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas.apply()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.contains用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.now用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.pad()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.take()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.all()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas series.str.get()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas Series.factorize()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
