Python是进行数据分析的一种出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的python软件包具有奇妙的生态系统。 Pandas是其中的一种,使导入和分析数据更加容易。
dataframe.abs()是最简单的pandas DataFrame 函数之一。它返回带有绝对值的对象,并且仅适用于所有数字对象。它也不具有任何Nan值。abs()函数也可以与复数一起使用以找到其绝对值。
对于复数,绝对值定义为:

用法: DataFrame.abs() 返回:type of caller
有关在代码中使用的CSV文件的链接,请单击此处
范例1:用nba.csv文件中的“Omega Warrior”替换团队“Boston Celtics”
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Making data frame from the csv file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
# Printing the first 10 rows of the
# data frame for visualization
df[:10]
为了找到绝对值,我们还需要在 DataFrame 中使用负值。因此,出于演示目的,我们将某些值更改为负数。
# This will set the Number column
# to be all negative.
df.Number = df.Number*(-1)输出:
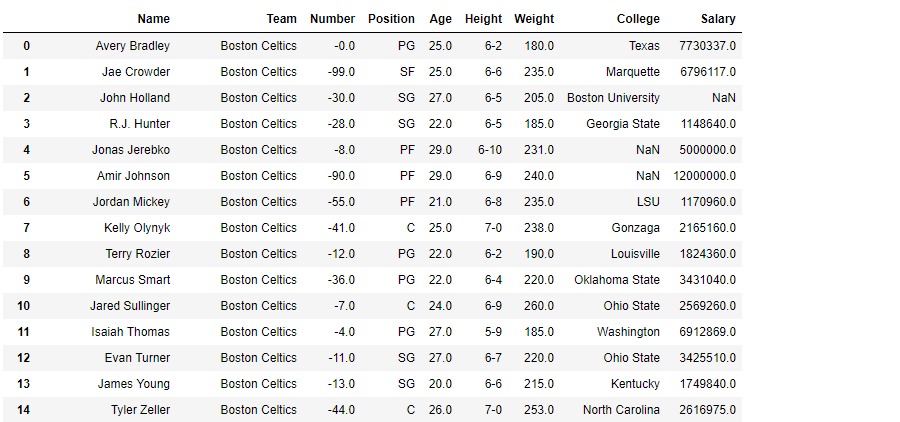
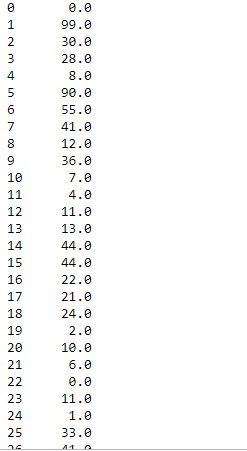
现在使用 abs() 函数仅查找Number列的绝对值。
# Applying abs() value on one column only
df.Number.abs()输出:
范例2:正在申请abs()在具有复数的序列上
# Importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating a series
ser = pd.Series([1.2 + 1j, 2 + 5j, 1 + 8j, 3.2 + 2j])
# let's print the values in ser
ser
# Using abs() function to find the
# absolute value of the complex numbers
absolute_values = s.abs()
# Print the absolute values of all complex numbers
absolute_values
相关用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.pow()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.div()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.sub()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.abs()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.sum()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.all()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Index.all()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.name用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.pad()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.now用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Dataframe.pop()用法及代码示例
- Python Pandas Series.mul()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原创作品 Python | Pandas DataFrame.abs()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
