Matplotlib是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的二维图。 Matplotlib是一个基于NumPy数组的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.patches.Circle
这个matplotlib.patches.Circle类用于在给定的中心创建圆形补丁xy = (x, y)具有给定的半径。它使用贝塞尔曲线样条曲线,并且更接近scale-free圆。
用法: class matplotlib.patches.Circle(xy, radius=5, **kwargs)
parameters:
- xy:它是圆的中心。
- 半径:它设置要绘制的圆的半径。其默认值为5个单位,并且是可选的。
下表提供了可选的有效kwargs;
| PROPERTY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| agg_filter | 一个过滤器函数,它接受一个(m,n,3)浮点数组,一个dpi值返回一个(m,n,3)数组 |
| alpha | 浮点数或无 |
| animated | bool |
| 抗锯齿或抗锯齿 | unknown |
| capstyle | {‘butt’,“回合”,‘projecting’} |
| clip_box | Bbox |
| clip_on | bool |
| clip_path | [(Path,Transform)|补丁|无] |
| color | rgba元组的颜色或顺序 |
| contains | callable |
| edgecolor或ec或edgecolors | 颜色或无或‘auto’ |
| facecolor或fc或facecolors | 颜色或无 |
| figure | figure |
| fill | bool |
| gid | str |
| hatch | {‘/’、‘\’、‘|’、‘-’、‘+’、‘x’, ‘o’、‘O’、‘.’、‘*’} |
| in_layout | bool |
| joinstyle | {‘miter’,“回合”,‘bevel’} |
| 线型或ls | {“-”,“-”,“-。”,“:”,“,(偏移量,on-off-seq),...} |
| 线宽或线宽或lw | 浮点数或无 |
| path_effects | AbstractPathEffect |
| picker | 无或布尔或浮点数或可赎回 |
| path_effects | AbstractPathEffect |
| picker | float或callable [[Artist,Event],Tuple [bool,dict]] |
| rasterized | 布尔还是无 |
| sketch_params | (比例:浮点数,长度:浮点数,随机性:浮点数) |
| snap | 布尔还是无 |
| transform | matplotlib.transforms.Transform |
| url | str |
| visible | bool |
| zorder | float |
范例1:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Circle
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib import animation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
patches = []
# create circles with random sizes
# and locations
N = 12 # number of circles
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
radii = 0.1 * np.random.rand(N)
for x1, y1, r in zip(x, y, radii):
circle = Circle((x1, y1), r)
patches.append(circle)
# add these circles to a collection
p = PatchCollection(patches, cmap = cm.prism, alpha = 0.4)
ax.add_collection(p)
def animate(i):
# random index to color map
colors = 100 * np.random.rand(len(patches))
# set new color colors
p.set_array(np.array(colors))
return p,
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate,
frames = 50, interval = 50)
plt.show()输出:
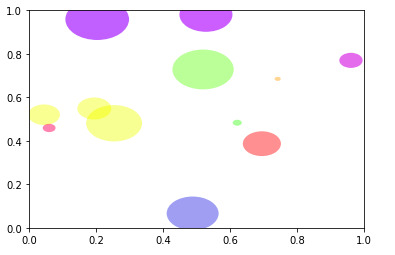
范例2:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.patches import Circle, Wedge, Polygon, Ellipse
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as matpatches
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize =(8, 8))
patches = []
circle = Circle((2, 2), 2)
patches.append(circle)
polygon = matpatches.PathPatch(patches[0].get_path())
patches.append(polygon)
colors = 2 * np.random.rand(len(patches))
p = PatchCollection(patches,
cmap = matplotlib.cm.jet,
alpha = 0.4)
p.set_array(np.array(colors))
ax.add_collection(p)
plt.axis([-10, 10, -10, 10])
plt.show()
contain2 = patches[0].get_path().contains_points([[0.5, 0.5],
[1.0, 1.0]])
contain3 = patches[0].contains_point([0.5, 0.5])
contain4 = patches[0].contains_point([1.0, 1.0])输出:
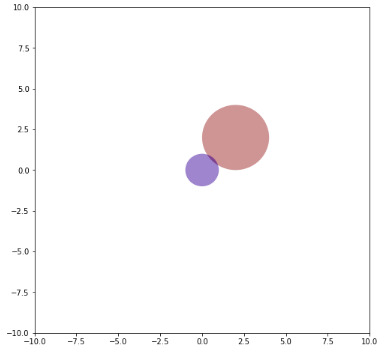
相关用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代码示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.Normalize用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.patches.Circle class in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
