step_rose() 創建配方步驟的規範,通過擴大少數類和多數類示例的特征空間來生成合成數據樣本。使用ROSE::ROSE()。
用法
step_rose(
recipe,
...,
role = NA,
trained = FALSE,
column = NULL,
over_ratio = 1,
minority_prop = 0.5,
minority_smoothness = 1,
majority_smoothness = 1,
skip = TRUE,
seed = sample.int(10^5, 1),
id = rand_id("rose")
)參數
- recipe
-
一個菜譜對象。該步驟將添加到此配方的操作序列中。
- ...
-
一個或多個選擇器函數用於選擇使用哪個變量對數據進行采樣。有關更多詳細信息,請參閱
selections()。選擇應產生單因子變量。對於tidy方法,當前未使用這些。 - role
-
由於沒有創建新變量,因此此步驟未使用。
- trained
-
指示預處理數量是否已估計的邏輯。
- column
-
將由
...選擇器(最終)填充的變量名稱的字符串。 - over_ratio
-
多數頻率與少數頻率之比的數值。默認值 (1) 表示對所有其他級別進行采樣,使其具有與最常出現的級別相同的頻率。值為 0.5 意味著少數級別的行數(最多)(大約)是多數級別的一半。
- minority_prop
-
一個數字。確定少數類的過采樣。默認為 0.5。
- minority_smoothness
-
一個數字。收縮因子乘以平滑參數來估計少數類的條件核密度。默認為 1。
- majority_smoothness
-
一個數字。收縮因子乘以平滑參數來估計多數類的條件核密度。默認為 1。
- skip
-
一個合乎邏輯的。當
bake()烘焙食譜時是否應該跳過此步驟?雖然所有操作都是在prep()運行時烘焙的,但某些操作可能無法對新數據進行(例如處理結果變量)。使用skip = TRUE時應小心,因為它可能會影響後續操作的計算。 - seed
-
當 rose-ing 時將用作種子的整數。
- id
-
該步驟特有的字符串,用於標識它。
細節
用於平衡的因子變量隻能有 2 個水平。
ROSE 算法的工作原理是選擇屬於 k 類的觀測值,並在其鄰域中生成新的示例,該鄰域由某個矩陣 H_k 確定。這些參數的較小值具有收縮相應平滑矩陣 H_k 的條目的效果,如果擔心過大的鄰域可能導致與每個相關的特征空間區域之間的邊界模糊,則收縮將是一個謹慎的選擇類。
數據中的所有列均由 juice() 和 bake() 采樣並返回。
在建模中使用時,用戶應強烈考慮使用選項skip = TRUE,以便不在訓練集之外進行額外采樣。
整理
當您tidy()此步驟時,將返回包含列terms(選擇的選擇器或變量)的tibble。
參考
Lunardon, N.、Menardi, G. 和 Torelli, N. (2014)。 ROSE:二元不平衡學習包。 《R 雜誌》,6:82-92。
Menardi, G. 和 Torelli, N. (2014)。使用不平衡數據訓練和評估分類規則。數據挖掘和知識發現,28:92-122。
也可以看看
過采樣的其他步驟:step_adasyn()、step_bsmote()、step_smotenc()、step_smote()、step_upsample()
例子
library(recipes)
library(modeldata)
data(hpc_data)
hpc_data0 <- hpc_data %>%
mutate(class = factor(class == "VF", labels = c("not VF", "VF"))) %>%
select(-protocol, -day)
orig <- count(hpc_data0, class, name = "orig")
orig
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class orig
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120
#> 2 VF 2211
up_rec <- recipe(class ~ ., data = hpc_data0) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep()
training <- up_rec %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
count(class, name = "training")
training
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class training
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2213
#> 2 VF 2209
# Since `skip` defaults to TRUE, baking the step has no effect
baked <- up_rec %>%
bake(new_data = hpc_data0) %>%
count(class, name = "baked")
baked
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class baked
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120
#> 2 VF 2211
orig %>%
left_join(training, by = "class") %>%
left_join(baked, by = "class")
#> # A tibble: 2 × 4
#> class orig training baked
#> <fct> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120 2213 2120
#> 2 VF 2211 2209 2211
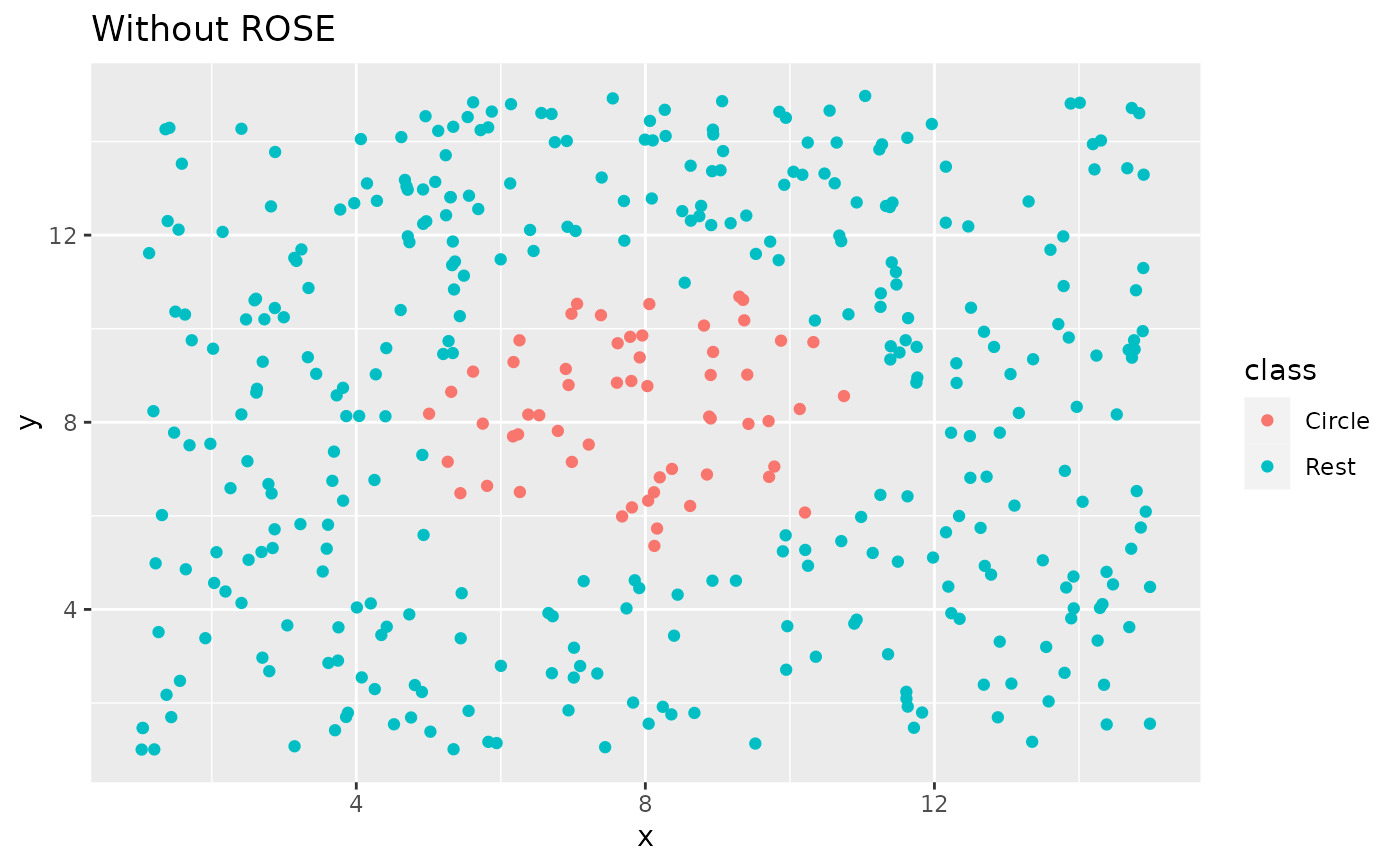
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(circle_example, aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "Without ROSE")
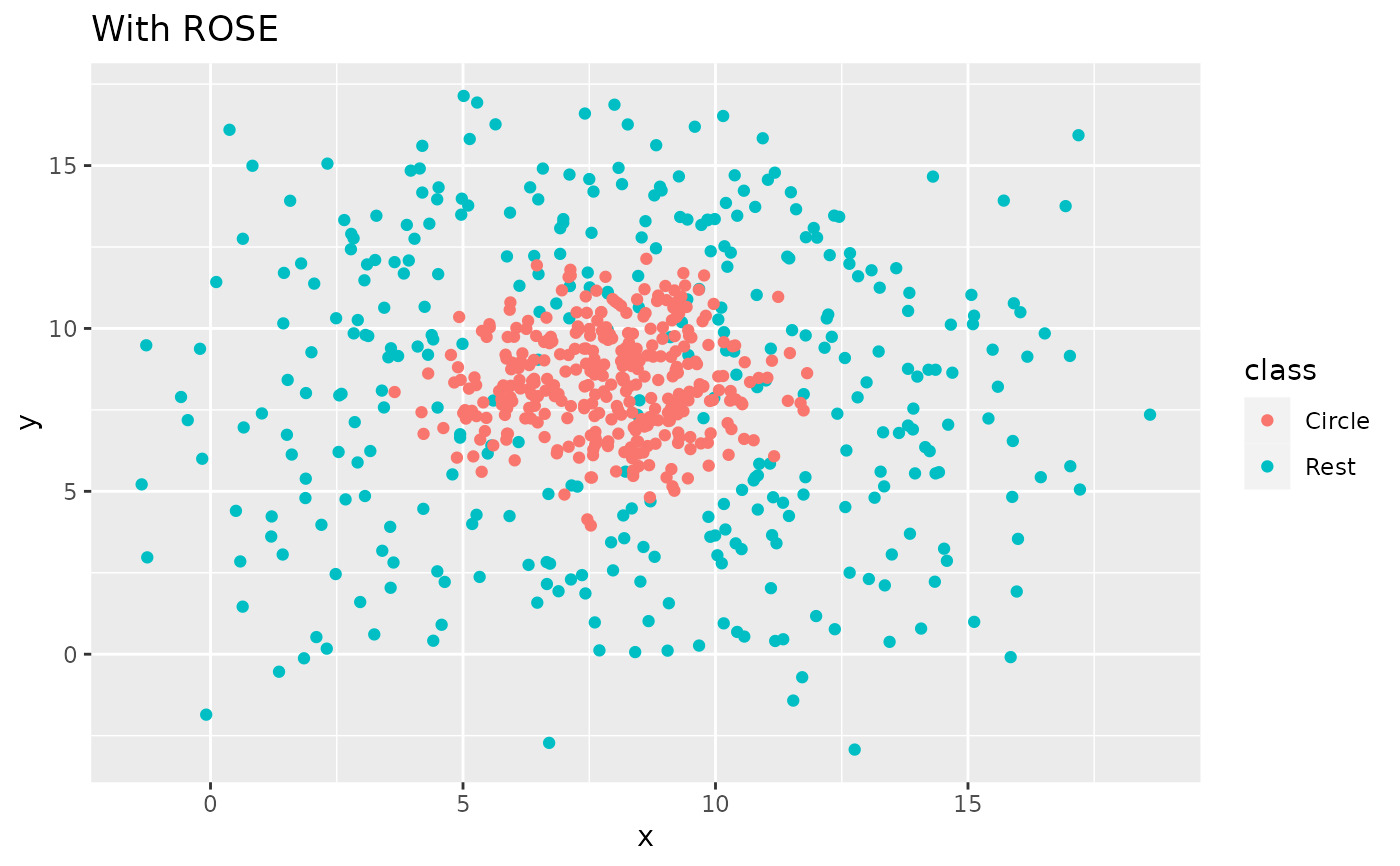
 recipe(class ~ x + y, data = circle_example) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "With ROSE")
recipe(class ~ x + y, data = circle_example) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "With ROSE")
相關用法
- R themis step_smote 應用SMOTE算法
- R themis step_smotenc 應用 SMOTENC 算法
- R themis step_downsample 基於因子變量對數據集進行下采樣
- R themis step_tomek 刪除 Tomek 的鏈接
- R themis step_upsample 基於因子變量對數據集進行上采樣
- R themis step_bsmote 應用邊界-SMOTE 算法
- R themis step_nearmiss 刪除其他類附近的點
- R themis step_adasyn 應用自適應合成算法
- R themis smotenc SMOTENC算法
- R themis smote SMOTE算法
- R themis tomek 刪除 Tomek 的鏈接
- R themis bsmote 邊界-SMOTE算法
- R themis nearmiss 刪除其他類附近的點
- R themis adasyn 自適應合成算法
- R update_PACKAGES 更新現有的 PACKAGES 文件
- R textrecipes tokenlist 創建令牌對象
- R print.via.format 打印實用程序
- R tibble tibble 構建 DataFrame 架
- R tidyr separate_rows 將折疊的列分成多行
- R textrecipes step_lemma 標記變量的詞形還原
- R textrecipes show_tokens 顯示配方的令牌輸出
- R tidyr extract 使用正則表達式組將字符列提取為多列
- R prepare_Rd 準備用於渲染的解析 Rd 對象
- R tidyr chop 砍伐和砍伐
- R tidyr pivot_longer_spec 使用規範將數據從寬轉為長
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自等大神的英文原創作品 Apply ROSE Algorithm。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
