step_rose() 创建配方步骤的规范,通过扩大少数类和多数类示例的特征空间来生成合成数据样本。使用ROSE::ROSE()。
用法
step_rose(
recipe,
...,
role = NA,
trained = FALSE,
column = NULL,
over_ratio = 1,
minority_prop = 0.5,
minority_smoothness = 1,
majority_smoothness = 1,
skip = TRUE,
seed = sample.int(10^5, 1),
id = rand_id("rose")
)参数
- recipe
-
一个菜谱对象。该步骤将添加到此配方的操作序列中。
- ...
-
一个或多个选择器函数用于选择使用哪个变量对数据进行采样。有关更多详细信息,请参阅
selections()。选择应产生单因子变量。对于tidy方法,当前未使用这些。 - role
-
由于没有创建新变量,因此此步骤未使用。
- trained
-
指示预处理数量是否已估计的逻辑。
- column
-
将由
...选择器(最终)填充的变量名称的字符串。 - over_ratio
-
多数频率与少数频率之比的数值。默认值 (1) 表示对所有其他级别进行采样,使其具有与最常出现的级别相同的频率。值为 0.5 意味着少数级别的行数(最多)(大约)是多数级别的一半。
- minority_prop
-
一个数字。确定少数类的过采样。默认为 0.5。
- minority_smoothness
-
一个数字。收缩因子乘以平滑参数来估计少数类的条件核密度。默认为 1。
- majority_smoothness
-
一个数字。收缩因子乘以平滑参数来估计多数类的条件核密度。默认为 1。
- skip
-
一个合乎逻辑的。当
bake()烘焙食谱时是否应该跳过此步骤?虽然所有操作都是在prep()运行时烘焙的,但某些操作可能无法对新数据进行(例如处理结果变量)。使用skip = TRUE时应小心,因为它可能会影响后续操作的计算。 - seed
-
当 rose-ing 时将用作种子的整数。
- id
-
该步骤特有的字符串,用于标识它。
细节
用于平衡的因子变量只能有 2 个水平。
ROSE 算法的工作原理是选择属于 k 类的观测值,并在其邻域中生成新的示例,该邻域由某个矩阵 H_k 确定。这些参数的较小值具有收缩相应平滑矩阵 H_k 的条目的效果,如果担心过大的邻域可能导致与每个相关的特征空间区域之间的边界模糊,则收缩将是一个谨慎的选择类。
数据中的所有列均由 juice() 和 bake() 采样并返回。
在建模中使用时,用户应强烈考虑使用选项skip = TRUE,以便不在训练集之外进行额外采样。
整理
当您tidy()此步骤时,将返回包含列terms(选择的选择器或变量)的tibble。
参考
Lunardon, N.、Menardi, G. 和 Torelli, N. (2014)。 ROSE:二元不平衡学习包。 《R 杂志》,6:82-92。
Menardi, G. 和 Torelli, N. (2014)。使用不平衡数据训练和评估分类规则。数据挖掘和知识发现,28:92-122。
也可以看看
过采样的其他步骤:step_adasyn()、step_bsmote()、step_smotenc()、step_smote()、step_upsample()
例子
library(recipes)
library(modeldata)
data(hpc_data)
hpc_data0 <- hpc_data %>%
mutate(class = factor(class == "VF", labels = c("not VF", "VF"))) %>%
select(-protocol, -day)
orig <- count(hpc_data0, class, name = "orig")
orig
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class orig
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120
#> 2 VF 2211
up_rec <- recipe(class ~ ., data = hpc_data0) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep()
training <- up_rec %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
count(class, name = "training")
training
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class training
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2213
#> 2 VF 2209
# Since `skip` defaults to TRUE, baking the step has no effect
baked <- up_rec %>%
bake(new_data = hpc_data0) %>%
count(class, name = "baked")
baked
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> class baked
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120
#> 2 VF 2211
orig %>%
left_join(training, by = "class") %>%
left_join(baked, by = "class")
#> # A tibble: 2 × 4
#> class orig training baked
#> <fct> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 not VF 2120 2213 2120
#> 2 VF 2211 2209 2211
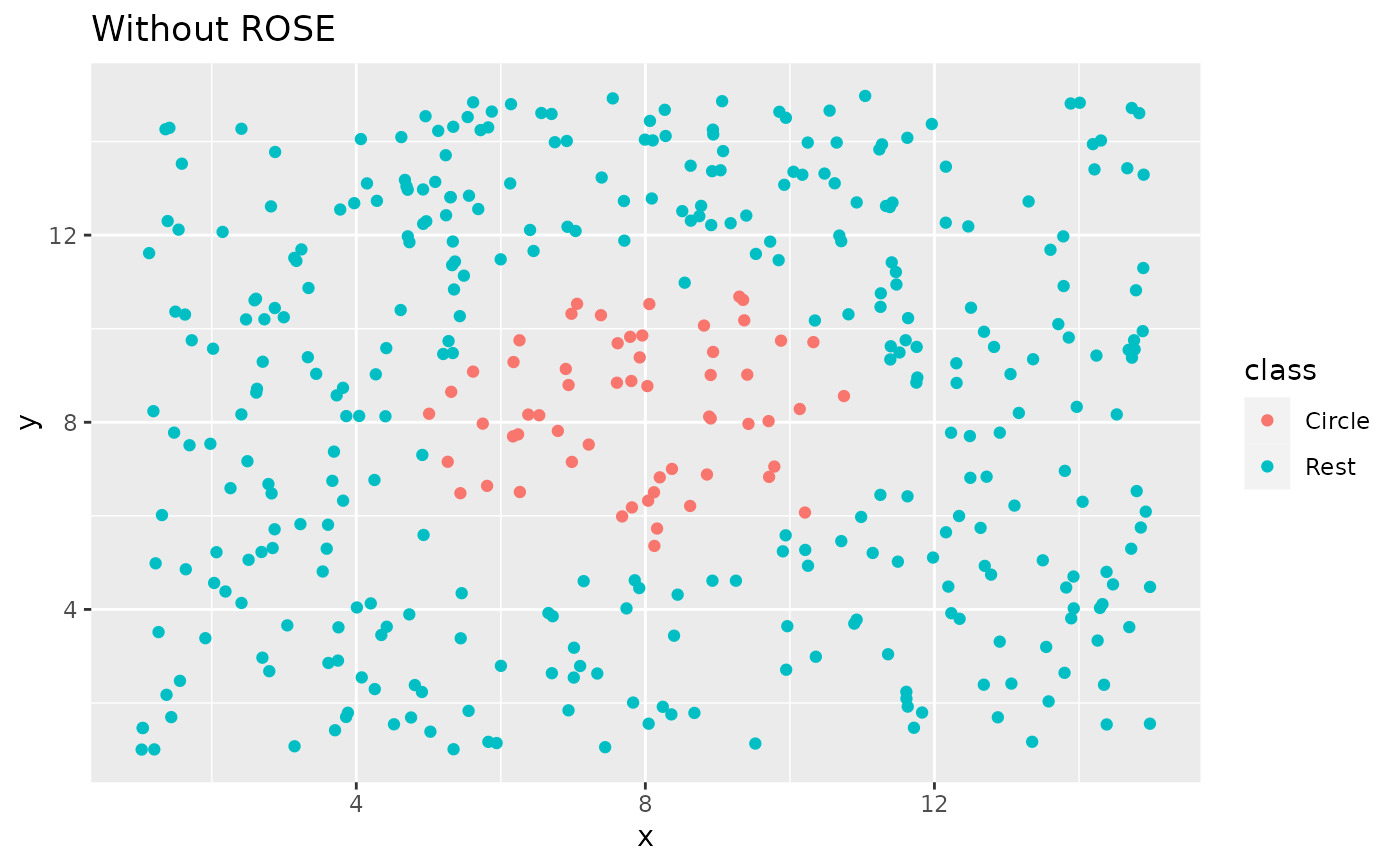
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(circle_example, aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "Without ROSE")
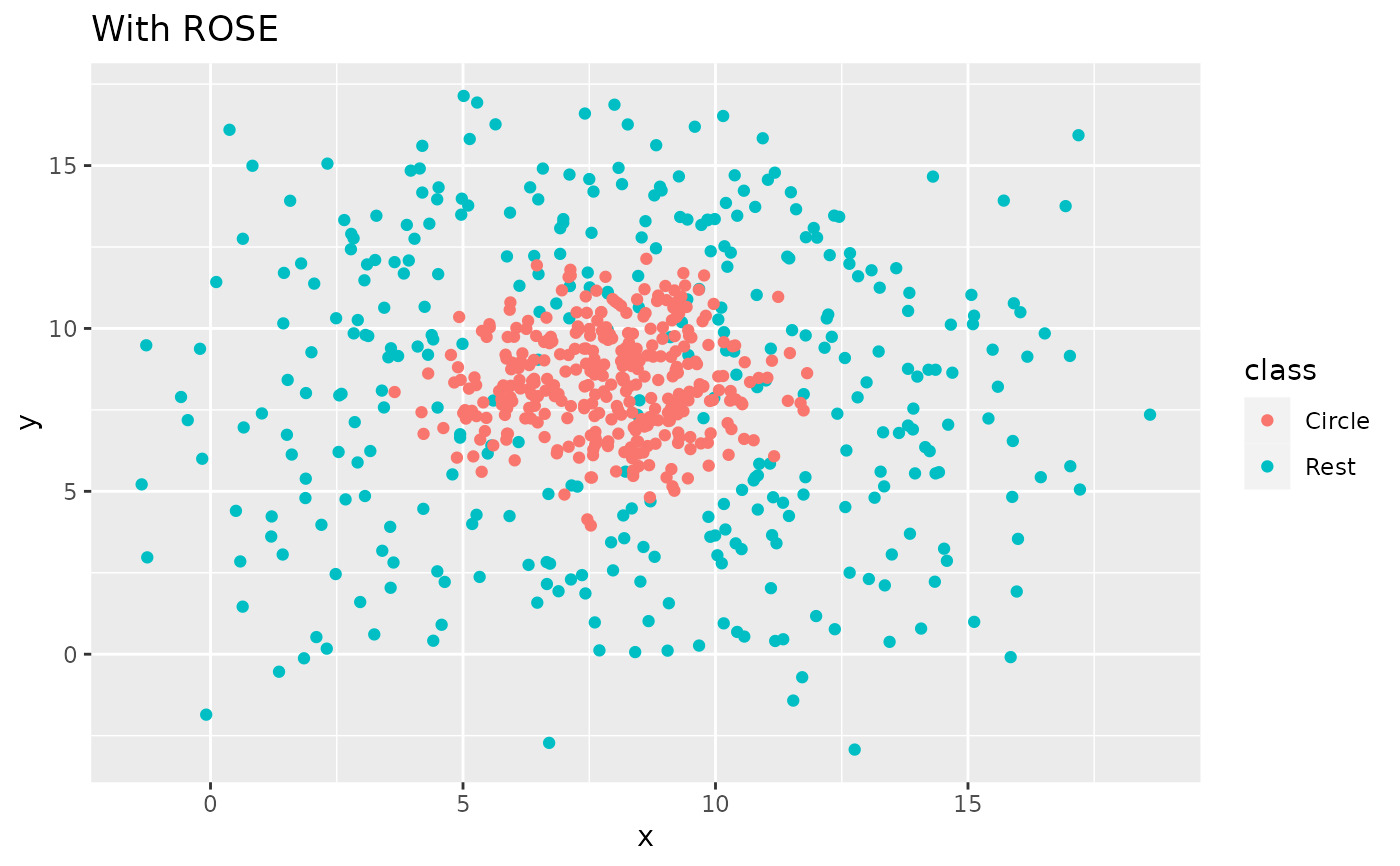
 recipe(class ~ x + y, data = circle_example) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "With ROSE")
recipe(class ~ x + y, data = circle_example) %>%
step_rose(class) %>%
prep() %>%
bake(new_data = NULL) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point() +
labs(title = "With ROSE")
相关用法
- R themis step_smote 应用SMOTE算法
- R themis step_smotenc 应用 SMOTENC 算法
- R themis step_downsample 基于因子变量对数据集进行下采样
- R themis step_tomek 删除 Tomek 的链接
- R themis step_upsample 基于因子变量对数据集进行上采样
- R themis step_bsmote 应用边界-SMOTE 算法
- R themis step_nearmiss 删除其他类附近的点
- R themis step_adasyn 应用自适应合成算法
- R themis smotenc SMOTENC算法
- R themis smote SMOTE算法
- R themis tomek 删除 Tomek 的链接
- R themis bsmote 边界-SMOTE算法
- R themis nearmiss 删除其他类附近的点
- R themis adasyn 自适应合成算法
- R update_PACKAGES 更新现有的 PACKAGES 文件
- R textrecipes tokenlist 创建令牌对象
- R print.via.format 打印实用程序
- R tibble tibble 构建 DataFrame 架
- R tidyr separate_rows 将折叠的列分成多行
- R textrecipes step_lemma 标记变量的词形还原
- R textrecipes show_tokens 显示配方的令牌输出
- R tidyr extract 使用正则表达式组将字符列提取为多列
- R prepare_Rd 准备用于渲染的解析 Rd 对象
- R tidyr chop 砍伐和砍伐
- R tidyr pivot_longer_spec 使用规范将数据从宽转为长
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自等大神的英文原创作品 Apply ROSE Algorithm。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
