使用線性回歸模型來校準數值預測
用法
cal_estimate_linear(
.data,
truth = NULL,
estimate = dplyr::matches("^.pred$"),
smooth = TRUE,
parameters = NULL,
...,
.by = NULL
)
# S3 method for data.frame
cal_estimate_linear(
.data,
truth = NULL,
estimate = dplyr::matches("^.pred$"),
smooth = TRUE,
parameters = NULL,
...,
.by = NULL
)
# S3 method for tune_results
cal_estimate_linear(
.data,
truth = NULL,
estimate = dplyr::matches("^.pred$"),
smooth = TRUE,
parameters = NULL,
...
)
# S3 method for grouped_df
cal_estimate_linear(
.data,
truth = NULL,
estimate = NULL,
smooth = TRUE,
parameters = NULL,
...
)參數
- .data
-
是未分組的
data.frame對象或tune_results對象,其中包含預測列。 - truth
-
觀察到的結果數據的列標識符(數字)。這應該是一個不帶引號的列名。
- estimate
-
預測值的列標識符
- smooth
-
適用於線性模型。當
TRUE時,它在使用樣條項的廣義加法模型之間切換;當FALSE時,它在簡單線性回歸之間切換。 - parameters
-
(可選)可選的調整參數值小標題,可用於在處理之前過濾預測值。僅適用於
tune_results對象。 - ...
-
傳遞給用於計算新預測的模型或例程的附加參數。
- .by
-
分組變量的列標識符。這應該是一個不帶引號的列名稱,用於選擇用於分組的定性變量。默認為
NULL。當.by = NULL時,不會進行分組。
細節
該函數使用其他包中的現有建模函數來創建校準:
-
當
smooth設置為FALSE時,使用stats::glm() -
當
smooth設置為TRUE時,使用mgcv::gam()
這些方法估計未修改的預測值中的關係,然後在調用 cal_apply() 時消除該趨勢。
例子
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
head(boosting_predictions_test)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 2
#> outcome .pred
#> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 -4.65 4.12
#> 2 1.12 1.83
#> 3 14.7 13.1
#> 4 36.3 19.1
#> 5 14.1 14.9
#> 6 -4.22 8.10
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
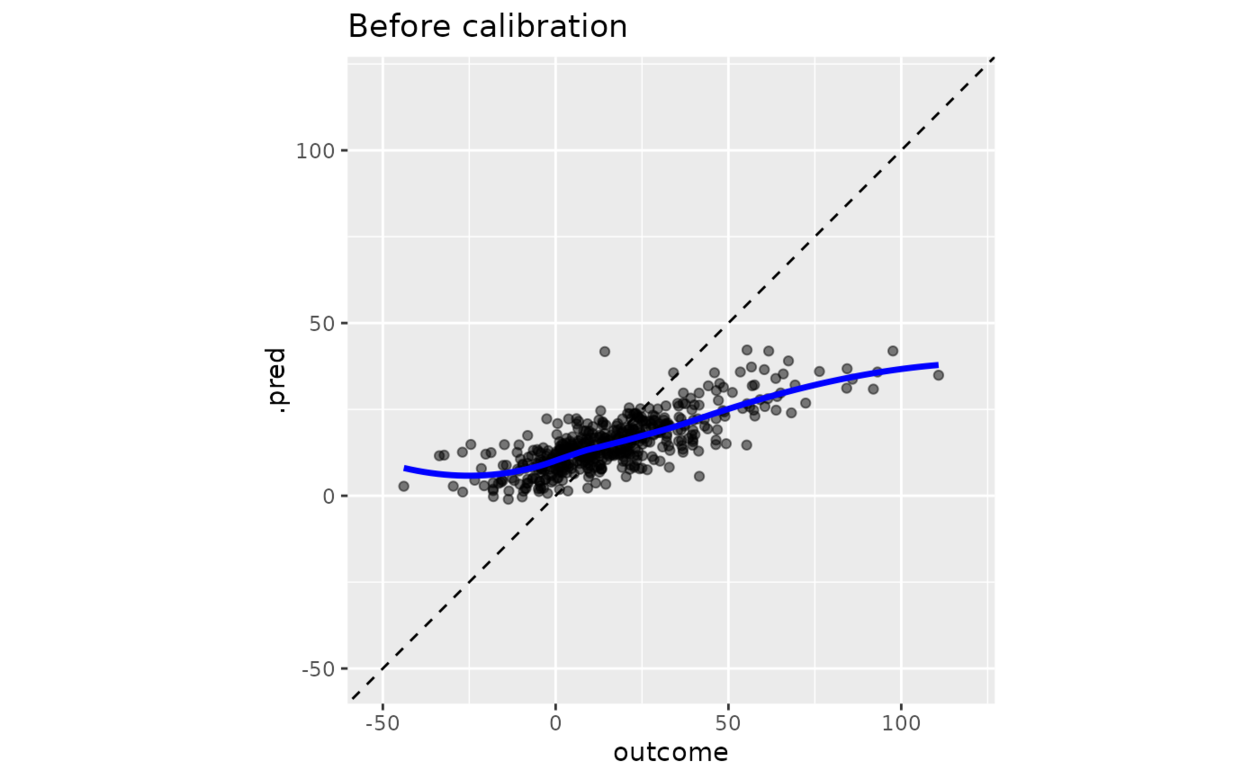
# Before calibration
y_rng <- extendrange(boosting_predictions_test$outcome)
boosting_predictions_test %>%
ggplot(aes(outcome, .pred)) +
geom_abline(lty = 2) +
geom_point(alpha = 1 / 2) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE, col = "blue", linewidth = 1.2, alpha = 3 / 4) +
coord_equal(xlim = y_rng, ylim = y_rng) +
ggtitle("Before calibration")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
 # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Smoothed trend removal
smoothed_cal <-
boosting_predictions_oob %>%
# It will automatically identify the predicted value columns when the
# standard tidymodels naming conventions are used.
cal_estimate_linear(outcome)
smoothed_cal
#>
#> ── Regression Calibration
#> Method: Generalized additive model
#> Source class: Data Frame
#> Data points: 2,000
#> Truth variable: `outcome`
#> Estimate variable: `.pred`
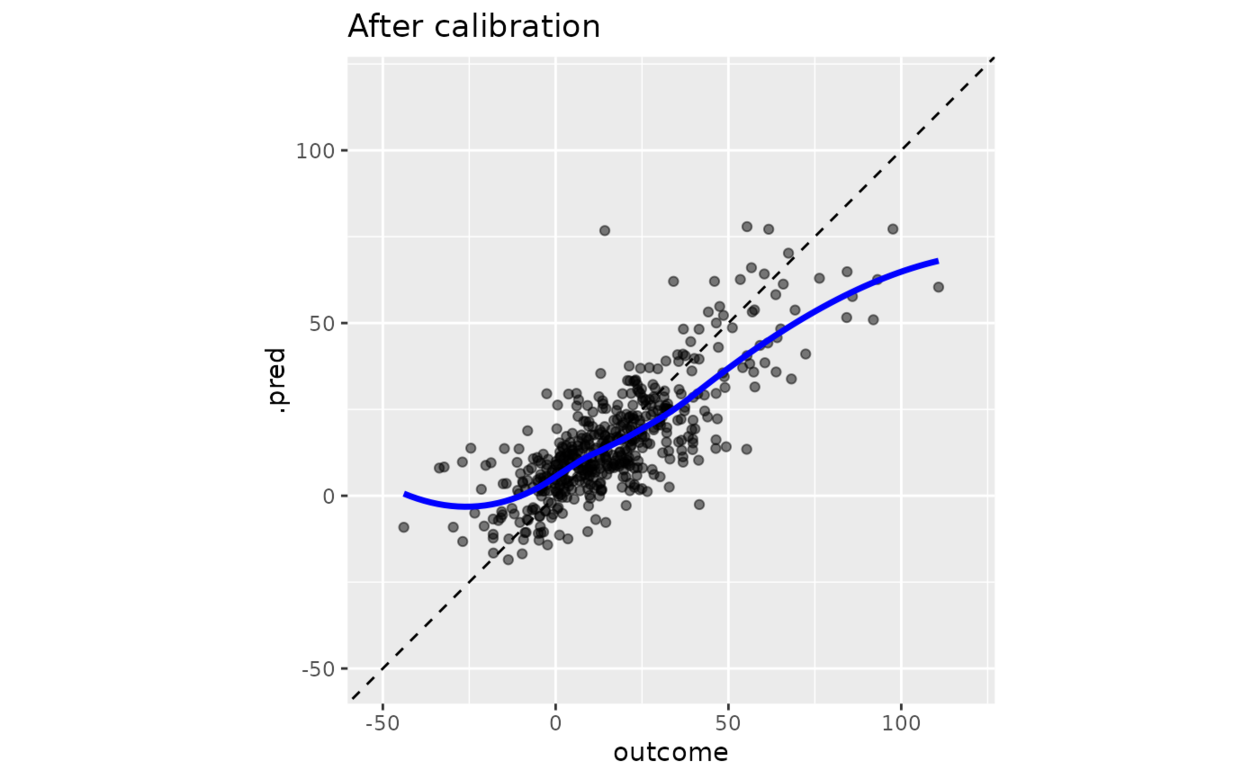
boosting_predictions_test %>%
cal_apply(smoothed_cal) %>%
ggplot(aes(outcome, .pred)) +
geom_abline(lty = 2) +
geom_point(alpha = 1 / 2) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE, col = "blue", linewidth = 1.2, alpha = 3 / 4) +
coord_equal(xlim = y_rng, ylim = y_rng) +
ggtitle("After calibration")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Smoothed trend removal
smoothed_cal <-
boosting_predictions_oob %>%
# It will automatically identify the predicted value columns when the
# standard tidymodels naming conventions are used.
cal_estimate_linear(outcome)
smoothed_cal
#>
#> ── Regression Calibration
#> Method: Generalized additive model
#> Source class: Data Frame
#> Data points: 2,000
#> Truth variable: `outcome`
#> Estimate variable: `.pred`
boosting_predictions_test %>%
cal_apply(smoothed_cal) %>%
ggplot(aes(outcome, .pred)) +
geom_abline(lty = 2) +
geom_point(alpha = 1 / 2) +
geom_smooth(se = FALSE, col = "blue", linewidth = 1.2, alpha = 3 / 4) +
coord_equal(xlim = y_rng, ylim = y_rng) +
ggtitle("After calibration")
#> `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
相關用法
- R probably cal_estimate_logistic 使用邏輯回歸模型來校準概率
- R probably cal_estimate_multinomial 使用多項校準模型來計算新的概率
- R probably cal_estimate_beta 使用 Beta 校準模型來計算新概率
- R probably cal_estimate_isotonic 使用等滲回歸模型來校準模型預測。
- R probably cal_estimate_isotonic_boot 使用引導等滲回歸模型來校準概率
- R probably cal_plot_logistic 通過邏輯回歸繪製概率校準圖
- R probably cal_plot_breaks 通過分箱繪製概率校準圖
- R probably cal_validate_logistic 使用和不使用邏輯校準來測量性能
- R probably cal_validate_isotonic_boot 使用和不使用袋裝等滲回歸校準來測量性能
- R probably cal_plot_regression 回歸校準圖
- R probably cal_validate_multinomial 使用和不使用多項式校準來測量性能
- R probably cal_apply 對一組現有預測應用校準
- R probably cal_validate_linear 使用和不使用線性回歸校準來測量性能
- R probably cal_plot_windowed 通過移動窗口繪製概率校準圖
- R probably cal_validate_isotonic 使用和不使用等滲回歸校準來測量性能
- R probably cal_validate_beta 使用和不使用 Beta 校準來測量性能
- R probably class_pred 創建類別預測對象
- R probably append_class_pred 添加 class_pred 列
- R probably threshold_perf 生成跨概率閾值的性能指標
- R probably as_class_pred 強製轉換為 class_pred 對象
- R probably levels.class_pred 提取class_pred級別
- R probably locate-equivocal 找到模棱兩可的值
- R probably int_conformal_quantile 通過保形推理和分位數回歸預測區間
- R probably make_class_pred 根據類概率創建 class_pred 向量
- R probably reportable_rate 計算報告率
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Max Kuhn等大神的英文原創作品 Uses a linear regression model to calibrate numeric predictions。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
