本文簡要介紹 python 語言中 scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter 的用法。
用法:
scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter(input, sigma, order=0, output=None, mode='reflect', cval=0.0, truncate=4.0, *, radius=None, axes=None)#多維高斯濾波器。
- input: array_like
輸入數組。
- sigma: 標量或標量序列
高斯核的標準差。每個軸的高斯濾波器的標準偏差作為一個序列或單個數字給出,在這種情況下,它對所有軸都是相等的。
- order: int 或整數序列,可選
過濾器沿每個軸的順序以整數序列或單個數字的形式給出。 0 階對應於具有高斯核的卷積。正階對應於具有高斯導數的卷積。
- output: 數組或數據類型,可選
放置輸出的數組,或返回數組的 dtype。默認情況下,將創建一個與輸入具有相同 dtype 的數組。
- mode: str 或序列,可選
mode 參數確定當過濾器與邊框重疊時如何擴展輸入數組。通過傳遞長度等於輸入數組維數的模式序列,可以沿每個軸指定不同的模式。默認值為‘reflect’。有效值及其行為如下:
- ‘reflect’ (d c b a | a b c d | d c b a)
通過反射最後一個像素的邊來擴展輸入。此模式有時也稱為half-sample 對稱模式。
- ‘constant’ (k k k k | a b c d |呸呸呸呸)
通過使用 cval 參數定義的相同常量值填充邊之外的所有值來擴展輸入。
- ‘nearest’ (啊啊啊啊| a b c d |嘀嘀嘀嘀)
通過複製最後一個像素來擴展輸入。
- ‘mirror’ (d c b | a b c d | c b a)
通過反射最後一個像素的中心來擴展輸入。此模式有時也稱為whole-sample 對稱模式。
- ‘wrap’ (a b c d | a b c d | A B C D)
通過環繞到相對邊來擴展輸入。
為了與插值函數保持一致,還可以使用以下模式名稱:
- ‘grid-constant’
這是‘constant’ 的同義詞。
- ‘grid-mirror’
這是‘reflect’ 的同義詞。
- ‘grid-wrap’
這是‘wrap’ 的同義詞。
- cval: 標量,可選
如果模式為‘constant’,則填充過去輸入邊的值。默認值為 0.0。
- truncate: 浮點數,可選
在這麽多標準偏差處截斷過濾器。默認值為 4.0。
- radius: 無或 int 或整數序列,可選
高斯核的半徑。每個軸的半徑以序列或單個數字的形式給出,在這種情況下,所有軸的半徑都相等。如果指定,則內核沿每個軸的大小將為
2*radius + 1, 和截短被忽略。默認為“無”。- axes: int 或 None 的元組,可選
如果無,則沿所有軸過濾輸入。否則,將沿指定軸過濾輸入。當指定軸時,用於 sigma、階、模式和/或半徑的任何元組都必須與軸的長度匹配。這些元組中的第 i 個條目對應於軸中的第 i 個條目。
- gaussian_filter: ndarray
返回與形狀相同的數組輸入.
參數 ::
返回 ::
注意:
多維濾波器被實現為一維卷積濾波器序列。中間數組存儲在與輸出相同的數據類型中。因此,對於精度有限的輸出類型,結果可能不精確,因為存儲的中間結果可能精度不足。
高斯核的大小
2*radius + 1沿著每個軸。如果半徑為 None,默認值radius = round(truncate * sigma)將會被使用。例子:
>>> from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter >>> import numpy as np >>> a = np.arange(50, step=2).reshape((5,5)) >>> a array([[ 0, 2, 4, 6, 8], [10, 12, 14, 16, 18], [20, 22, 24, 26, 28], [30, 32, 34, 36, 38], [40, 42, 44, 46, 48]]) >>> gaussian_filter(a, sigma=1) array([[ 4, 6, 8, 9, 11], [10, 12, 14, 15, 17], [20, 22, 24, 25, 27], [29, 31, 33, 34, 36], [35, 37, 39, 40, 42]])>>> from scipy import datasets >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> plt.gray() # show the filtered result in grayscale >>> ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121) # left side >>> ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122) # right side >>> ascent = datasets.ascent() >>> result = gaussian_filter(ascent, sigma=5) >>> ax1.imshow(ascent) >>> ax2.imshow(result) >>> plt.show()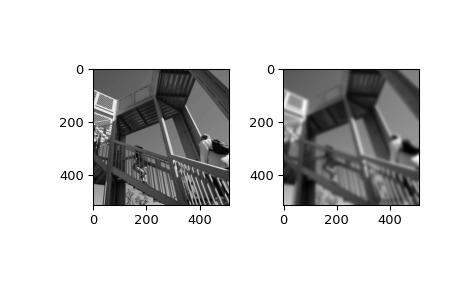
相關用法
- Python SciPy ndimage.gaussian_filter1d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.gaussian_laplace用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.gaussian_gradient_magnitude用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.generic_laplace用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.generate_binary_structure用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.grey_erosion用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.generic_filter1d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.generic_gradient_magnitude用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.generic_filter用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.grey_closing用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.grey_opening用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.geometric_transform用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.grey_dilation用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.correlate用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.morphological_gradient用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.variance用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.correlate1d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.binary_dilation用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.distance_transform_bf用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.find_objects用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.label用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.maximum_filter1d用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.iterate_structure用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.map_coordinates()用法及代碼示例
- Python SciPy ndimage.binary_opening用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自scipy.org大神的英文原創作品 scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
